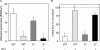CXCR2- and E-selectin-induced neutrophil arrest during inflammation in vivo - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
CXCR2- and E-selectin-induced neutrophil arrest during inflammation in vivo
Michael L Smith et al. J Exp Med. 2004.
Abstract
The signaling events leading to the activation of integrins and firm arrest of rolling neutrophils in inflamed venules have yet to be elucidated. In vitro assays suggest that both E-selectin and chemokines can trigger arrest of rolling neutrophils, but E-selectin(-/-) mice have normal levels of adherent neutrophils in inflamed venules. To test whether chemokine-induced neutrophil arrest in vivo can be unmasked by blocking E-selectin, we investigated neutrophil adhesion in inflamed cremaster muscle venules in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha-treated CXCR2(-/-) or wild-type (WT) mice injected with E-selectin blocking monoclonal antibody (mAb) 9A9. To block chemokine receptor signaling, we investigated E-selectin(-/-) or WT mice treated with pertussis toxin (PTx) intravenously. Neutrophil adhesion was unchanged in CXCR2(-/-), E-selectin(-/-), PTx-treated WT, or mAb 9A9-treated WT mice. However, TNF-alpha-induced neutrophil adhesion was almost completely abrogated in E-selectin(-/-) mice treated with PTx and significantly reduced in CXCR2(-/-) mice treated with the E-selectin blocking mAb. In thioglycollate-induced peritonitis, PTx treatment blocked neutrophil recruitment into the peritoneum of E-selectin(-/-) mice, but had only a partial effect in WT animals. These data show that E-selectin- and chemokine-mediated arrest mechanisms are overlapping in this model and identify CXCR2 as an important neutrophil arrest chemokine in vivo.
Figures
Figure 1.
Adherent leukocytes per 200-μm length of vessel (increase above background; A) and percent reduction in leukocyte rolling flux (B) due to injection of 600 ng KC into the carotid artery cannula. Data was acquired 1 min before and after injection into WT (7 venules in 3 mice; white bars), WT plus 4 μg PTx 3 h before cremaster exteriorization (10 venules in 4 mice; light gray bars), E-selectin−/− (6 venules in 2 mice; dark gray bars), and E-selectin−/− plus PTx (5 venules in 2 mice; black bars). *, P < 0.05 versus WT control (A) or rolling flux before KC injection (B).
Figure 2.
Numbers of adherent cells per mm2 in murine cremaster muscle venules. Cremaster muscle exteriorized 3 h after intrascrotal injection of 500 ng TNF-α in WT (11 venules in 3 mice), WT plus 4 μg PTx 5 min before TNF-α injection (12 venules in 3 mice), E-selectin−/− (13 venules in 3 mice), E-selectin−/− plus PTx (17 venules in 3 mice), and WT plus PTx plus 60 μg α–E-selectin mAb 9A9 5 min before TNF-α injection (10 venules in 2 mice) using mice on a C57Bl/6 background (A), and WT (11 venules in 2 mice), CXCR2−/− (13 venules in 3 mice), and CXCR2−/− plus mAb 9A9 (11 venules in 2 mice) using mice on a BALB/c background (B). *, P < 0.05 versus all other groups.
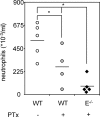
Figure 3.
Peritoneal neutrophil influx 4 h after 1 ml injection of 4% thioglycollate into WT (five mice; open circles), WT plus 4 μg PTx 3 h before thioglycollate injection (four mice; light gray circles), E-selectin−/− (four mice; dark gray bars), and E-selectin−/− plus PTx (five mice; closed diamonds). Data expressed as numbers of neutrophils (×103) per ml peritoneal lavage fluid counted using Kimura-stained samples. *, P < 0.05.
Similar articles
- Spleen tyrosine kinase Syk is necessary for E-selectin-induced alpha(L)beta(2) integrin-mediated rolling on intercellular adhesion molecule-1.
Zarbock A, Lowell CA, Ley K. Zarbock A, et al. Immunity. 2007 Jun;26(6):773-83. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.04.011. Epub 2007 May 31. Immunity. 2007. PMID: 17543554 Free PMC article. - Differential effect of E-selectin antibodies on neutrophil rolling and recruitment to inflammatory sites.
Ramos CL, Kunkel EJ, Lawrence MB, Jung U, Vestweber D, Bosse R, McIntyre KW, Gillooly KM, Norton CR, Wolitzky BA, Ley K. Ramos CL, et al. Blood. 1997 Apr 15;89(8):3009-18. Blood. 1997. PMID: 9108422 - Moesin regulates neutrophil rolling velocity in vivo.
Matsumoto M, Hirata T. Matsumoto M, et al. Cell Immunol. 2016 Jun-Jul;304-305:59-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Cell Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27131737 - Neutrophil adhesion and activation under flow.
Zarbock A, Ley K. Zarbock A, et al. Microcirculation. 2009 Jan;16(1):31-42. doi: 10.1080/10739680802350104. Microcirculation. 2009. PMID: 19037827 Free PMC article. Review. - Mechanisms and consequences of neutrophil interaction with the endothelium.
Zarbock A, Ley K. Zarbock A, et al. Am J Pathol. 2008 Jan;172(1):1-7. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070502. Epub 2007 Dec 13. Am J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18079440 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Therapeutic inhibition of CXCR1/2: where do we stand?
Sitaru S, Budke A, Bertini R, Sperandio M. Sitaru S, et al. Intern Emerg Med. 2023 Sep;18(6):1647-1664. doi: 10.1007/s11739-023-03309-5. Epub 2023 May 30. Intern Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37249756 Free PMC article. Review. - ELMO1 Deficiency Reduces Neutrophil Chemotaxis in Murine Peritonitis.
Yu S, Geng X, Liu H, Zhang Y, Cao X, Li B, Yan J. Yu S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 30;24(9):8103. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098103. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175809 Free PMC article. - The immunological function of CXCR2 in the liver during sepsis.
Liu N, Bauer M, Press AT. Liu N, et al. J Inflamm (Lond). 2022 Nov 30;19(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12950-022-00321-y. J Inflamm (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36451225 Free PMC article. Review. - Staphylococcus aureus Causes the Arrest of Neutrophils in the Bloodstream in a Septicemia Model.
Pleskova SN, Bobyk SZ, Kriukov RN, Gorshkova EN, Bezrukov NA. Pleskova SN, et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 24;10(9):1696. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10091696. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36144298 Free PMC article. - Soluble uric acid inhibits β2 integrin-mediated neutrophil recruitment in innate immunity.
Ma Q, Immler R, Pruenster M, Sellmayr M, Li C, von Brunn A, von Brunn B, Ehmann R, Wölfel R, Napoli M, Li Q, Romagnani P, Böttcher RT, Sperandio M, Anders HJ, Steiger S. Ma Q, et al. Blood. 2022 Jun 9;139(23):3402-3417. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021011234. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35303071 Free PMC article.
References
- Springer, T.A. 1995. Traffic signals on endothelium for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 57:827–872. - PubMed
- Kunkel, E.J., J.L. Dunne, and K. Ley. 2000. Leukocyte arrest during cytokine-dependent inflammation in vivo. J. Immunol. 164:3301–3308. - PubMed
- Constantin, G., M. Majeed, C. Giagulli, L. Piccio, J.Y. Kim, E.C. Butcher, and C. Laudanna. 2000. Chemokines trigger immediate β2 integrin affinity and mobility changes: differential regulation and roles in lymphocyte arrest under flow. Immunity. 13:759–769. - PubMed
- Rainger, G.E., A.C. Fisher, and G.B. Nash. 1997. Endothelial-borne platelet-activating factor and interleukin-8 rapidly immobilize rolling neutrophils. Am. J. Physiol. 272:H114–H122. - PubMed
- Simon, S.I., Y. Hu, D. Vestweber, and C.W. Smith. 2000. Neutrophil tethering on E-selectin activates β2 integrin binding to ICAM-1 through a mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J. Immunol. 164:4348–4358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM007267/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL54136/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008715/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM 08715-01A1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM07267-23/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases