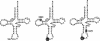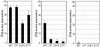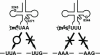Codon-specific translational defect caused by a wobble modification deficiency in mutant tRNA from a human mitochondrial disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Codon-specific translational defect caused by a wobble modification deficiency in mutant tRNA from a human mitochondrial disease
Yohei Kirino et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004.
Abstract
Point mutations in the mitochondrial (mt) tRNA(Leu(UUR)) gene are responsible for mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS), a subgroup of mitochondrial encephalomyopathic diseases. We previously showed that mt tRNA(Leu(UUR)) with an A3243G or T3271C mutation derived from patients with MELAS are deficient in a normal taurine-containing modification (taum5U; 5-taurinomethyluridine) at the anticodon wobble position. To examine decoding disorder of the mutant tRNA due to the wobble modification deficiency independent of the pathogenic point mutation itself, we used a molecular surgery technique to construct an mt tRNA(Leu(UUR)) molecule lacking the taurine modification but without the pathogenic mutation. This "operated" mt tRNA(Leu(UUR)) without the taurine modification showed severely reduced UUG translation but no decrease in UUA translation. We thus concluded that the UUG codon-specific translational defect of the mutant mt tRNAs(Leu(UUR)) is the primary cause of MELAS at the molecular level. This result could explain the complex I deficiency observed clinically in MELAS.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Cloverleaf structures of human mt tRNAsLeu(UUR) from WT cells (Left) and from MELAS cybrid cells with the A3243G mutation (Center) or T3271C mutation (Right). “U” on a round black background indicates unmodified wobble uridine. White letters on a square black background represent the respective point mutations. Symbols for the modifications are 5-taurinomethyluridine (τm5U), 1-methyladenosine (m1A), 1-methylguanosine (m1G), 2-methylguanosine (m2G), pseudouridine (Ψ), ribothymidine (T), dihydrouridine (D), and 5-methylcytidine (m5C) (17).
Fig. 2.
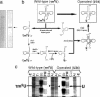
Construction of mt tRNALeu(UUR) with an unmodified uridine at position 34 using the molecular surgery technique. (a) Purification of mt tRNALeu(UUR) from human placenta. (Left) Denaturing gel electrophoresis of the total RNA fraction extracted from human placenta. (Right) Purified human mt tRNALeu(UUR) (indicated by an arrow). (b) Schematic depiction of the molecular surgery procedure used to construct mt tRNALeu(UUR) with an unmodified wobble uridine. The details of each step are described in Materials and Methods. BAP and PNK represent bacterial alkaline phosphatase and polynucleotide kinase, respectively. (c) RNA sequence ladders for the 5′ end-labeled WT and operated tRNALeu(UUR) were obtained by the Donis-Keller method (27). –E, without enzyme; Al, treatment with alkali; T1, RNase T1 (specific for G); U2, RNase U2 (for A > G); PM, RNase Phy M (for A and U); and CL3, RNase CL3 (for C). Arrows indicate the bands that were cleaved by RNase PhyM digestion. There is no band for τm5U34 in the WT tRNA because the modification prevents PhyM digestion, but there is a cleaved band for U34 in the operated tRNA. Arrowheads show the wobble positions in the alkaline ladders. The band corresponding to τm5U34 is shifted up due to its bulky substituent, whereas U34 shows a normal band in the ladder.
Fig. 3.
Translational activity of the operated tRNALeu(UUR) without the wobble modification and of the MELAS mutant tRNAsLeu(UUR). In vitro mitochondrial translation of test mRNAs containing the UUA (Left), UUG (Center), or UUC (Right) (negative control) codons was performed with WT tRNALeu(UUR)(WT), operated tRNALeu(UUR) with an unmodified wobble uridine (OP), and two MELAS mutant tRNAsLeu(UUR) that bear the A3243G (3243) or U3271C (3271) mutations and an unmodified wobble uridine. The radioactivity of the [3H]leucyl-tRNA input to the reaction mixture was defined arbitrarily as 100. The averages of three independent experiments with SD values are shown.
Fig. 4.
Ability of the operated tRNALeu(UUR) without the wobble modification to bind to UUR codons. Shown is binding of the WT tRNALeu(UUR) (filled circles) and the operated tRNALeu(UUR) that lacks the wobble modification (filled squares) to ribosomal A-sites containing UUA (Left) or UUG (Right). Three independent experiments were performed, and the average values are plotted with SD values.
Fig. 5.
Possible mechanism of molecular pathogenesis caused by the wobble modification deficiency of the mutant tRNAs in MELAS (Left) and MERRF (Right) patients. Pathogenic point mutation (A3243G or U3271C) in mutant tRNALeu(UUR) from MELAS patients causes a τm5U-modification deficiency, which results in a UUG codon–specific translational defect. The MERRF 8344 mutation in tRNALys causes a τm5s2U-modification deficiency that results in a translational defect for both cognate codons (AAA and AAG) (21).
Similar articles
- Acquisition of the wobble modification in mitochondrial tRNALeu(CUN) bearing the G12300A mutation suppresses the MELAS molecular defect.
Kirino Y, Yasukawa T, Marjavaara SK, Jacobs HT, Holt IJ, Watanabe K, Suzuki T. Kirino Y, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2006 Mar 15;15(6):897-904. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl007. Epub 2006 Jan 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2006. PMID: 16446307 - Human mitochondrial diseases associated with tRNA wobble modification deficiency.
Kirino Y, Suzuki T. Kirino Y, et al. RNA Biol. 2005 Apr;2(2):41-4. doi: 10.4161/rna.2.2.1610. Epub 2005 Apr 14. RNA Biol. 2005. PMID: 17132941 Review. - Specific correlation between the wobble modification deficiency in mutant tRNAs and the clinical features of a human mitochondrial disease.
Kirino Y, Goto Y, Campos Y, Arenas J, Suzuki T. Kirino Y, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 17;102(20):7127-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500563102. Epub 2005 May 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15870203 Free PMC article. - Taurine deficiency and MELAS are closely related syndromes.
Schaffer SW, Jong CJ, Warner D, Ito T, Azuma J. Schaffer SW, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;776:153-65. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-6093-0_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23392880 Review.
Cited by
- MTO1 mediates tissue specificity of OXPHOS defects via tRNA modification and translation optimization, which can be bypassed by dietary intervention.
Tischner C, Hofer A, Wulff V, Stepek J, Dumitru I, Becker L, Haack T, Kremer L, Datta AN, Sperl W, Floss T, Wurst W, Chrzanowska-Lightowlers Z, De Angelis MH, Klopstock T, Prokisch H, Wenz T. Tischner C, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Apr 15;24(8):2247-66. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu743. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 25552653 Free PMC article. - RNA modification landscape of the human mitochondrial tRNALys regulates protein synthesis.
Richter U, Evans ME, Clark WC, Marttinen P, Shoubridge EA, Suomalainen A, Wredenberg A, Wedell A, Pan T, Battersby BJ. Richter U, et al. Nat Commun. 2018 Sep 27;9(1):3966. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06471-z. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30262910 Free PMC article. - A natural non-Watson-Crick base pair in human mitochondrial tRNAThr causes structural and functional susceptibility to local mutations.
Wang Y, Zeng QY, Zheng WQ, Ji QQ, Zhou XL, Wang ED. Wang Y, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 May 18;46(9):4662-4676. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky243. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29648639 Free PMC article. - Errors in translational decoding: tRNA wobbling or misincorporation?
Ou X, Cao J, Cheng A, Peppelenbosch MP, Pan Q. Ou X, et al. PLoS Genet. 2019 Mar 28;15(3):e1008017. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008017. eCollection 2019 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 30921315 Free PMC article. Review. - Analysis of mitochondrial function in human induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with mitochondrial diabetes due to the A3243G mutation.
Matsubara M, Kanda H, Imamura H, Inoue M, Noguchi M, Hosoda K, Kakizuka A, Nakao K. Matsubara M, et al. Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 17;8(1):949. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19264-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29343702 Free PMC article.
References
- Schon, E. A., Bonilla, E. & DiMauro, S. (1997) J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 29, 131–149. - PubMed
- Kobayashi, Y., Momoi, M. Y., Tominaga, K., Momoi, T., Nihei, K., Yanagisawa, M., Kagawa, Y. & Ohta, S. (1990) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 173, 816–822. - PubMed
- Goto, Y., Nonaka, I. & Horai, S. (1990) Nature 348, 651–653. - PubMed
- Goto, Y., Nonaka, I. & Horai, S. (1991) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1097, 238–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources