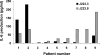Helicobacter pylori modulates the T helper cell 1/T helper cell 2 balance through phase-variable interaction between lipopolysaccharide and DC-SIGN - PubMed (original) (raw)
Helicobacter pylori modulates the T helper cell 1/T helper cell 2 balance through phase-variable interaction between lipopolysaccharide and DC-SIGN
Mathijs P Bergman et al. J Exp Med. 2004.
Abstract
The human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori spontaneously switches lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Lewis (Le) antigens on and off (phase-variable expression), but the biological significance of this is unclear. Here, we report that Le+ H. pylori variants are able to bind to the C-type lectin DC-SIGN and present on gastric dendritic cells (DCs), and demonstrate that this interaction blocks T helper cell (Th)1 development. In contrast, Le- variants escape binding to DCs and induce a strong Th1 cell response. In addition, in gastric biopsies challenged ex vivo with Le+ variants that bind DC-SIGN, interleukin 6 production is decreased, indicative of increased immune suppression. Our data indicate a role for LPS phase variation and Le antigen expression by H. pylori in suppressing immune responses through DC-SIGN.
Figures
Figure 1.
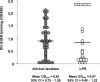
Clinically isolated H. pylori and purified LPS bind to DC-SIGN. H. pylori strains (•) isolated from patients from different continents (reference 5) and purified LPS (○) were coated on ELISA plates, and binding of recombinant DC-SIGN-Fc was assessed with peroxidase-labeled goat anti–human Fc.
Figure 2.
Le blood group and related antigens and some of their substructures bind to DC-SIGN. (A) Le antigens expressed by H. pylori and discussed in this paper. (B and C) Carbohydrates, representing blood group antigens or their substructures, conjugated to polyacrylamide (B) or ceramide (C), were coated and binding of recombinant DC-SIGN-Fc was measured after incubation with peroxidase-labeled goat anti–human Fc. The mean (+ SD) of three independent experiments is shown.
Figure 3.
Binding of H. pylori is dependent on Le antigen expression. (A–C) H. pylori α3-fucosyltransferase mutants (A), strains (B), and phase variants (C) were coated, and binding of recombinant DC-SIGN-Fc was measured after incubation with peroxidase-labeled goat anti–human Fc. H. pylori were coated and incubated with mAbs specific for Le antigens indicated, and their serotype was determined after incubation with peroxidase-labeled anti–mouse Igs. The mean (+ SD) of three independent experiments is shown.
Figure 4.
LPS phase variation in H. pylori occurs in vivo. (A) After a short time of culturing directly from the biopsy, followed by one single passage in fluid phase and distribution over solid media, Lex/y+ phase variants of J223 were detected by colony blotting with mAbs specific for the indicated Le antigens. C-tract sequencing was performed to determine the on and off status of genes futA (HP0379) and futB (HP0651). The J223.3 futB mutant was generated by natural transformation with construct containing a chloramphenicol resistance marker cassette inserted in gene HP0651, and serotyped as indicated for J223. (B) Consequences of the C-tract length for functional expression of futA and futB.
Figure 5.
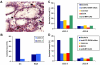
DC-SIGN is expressed on gastric DCs and is the major receptor for Le+ H. pylori. (A) A tissue section of stomach was fixed and stained with anti–DC-SIGN antibodies. A magnification of 20. Arrows indicate DC-SIGN+ DC-like cells in the lamina propria. (B–D) Monocyte-derived DCs and RAW 264 macrophages (B), monocyte-derived DCs (C), or K-562 cells transfected with DC-SIGN (D) were incubated with FITC-labeled H. pylori J223.3 or J223.8, and binding was analyzed using flow cytometry. In C and D, cells were preincubated with anti–DC-SIGN antibodies, mannan, EDTA, or anti-MR antibodies. One representative out of four experiments is shown.
Figure 6.
Binding of H. pylori induces DC-SIGN–dependent increase of IL-10. (A) DCs were incubated with H. pylori J223.3 or J223.8 at an MOI of 20 in the presence or absence of anti–DC-SIGN antibodies for 1 h, washed, and cultured for 20 h. Supernatant was harvested and the amount of IL-10 was analyzed by ELISA. (B) Upon coculture of DCs with H. pylori J223.3 or J223.8, cells were incubated with CD40L-transfected J558 fibroblasts in the absence or presence of IFN-γ for 24 h. Supernatant was harvested and the amount of IL-12p70 was analyzed by ELISA. One representative experiment out of four is shown.
Figure 7.
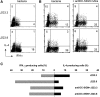
Binding of H. pylori to DC-SIGN blocks skewing of naive T cells to Th1 cells. After preincubation with anti–DC-SIGN antibodies, DCs were incubated with H. pylori J223.3 or J223.8 at an MOI of 10 for 48 h, washed, and then cocultured with highly purified CD45RA+ CD4+ T cells. Quiescent T cells were restimulated with PMA and ionomycin, and IL-4 and IFN-γ was analyzed on a single cell basis by intracellular flow cytometry. Data from two representative donors (A and B/C) are shown from nine independent experiments.
Figure 8.
Ex vivo challenge with DC-SIGN–binding H. pylori induces lower expression of IL-6 in stomach biopsies. Gastric biopsies were cocultured with 10 × 106 H. pylori J223.3 or J223.8 for 48 h and supernatants were harvested for analysis of cytokines, as indicated in Materials and Methods, by ELISA.
Similar articles
- Relevance of fucosylation and Lewis antigen expression in the bacterial gastroduodenal pathogen Helicobacter pylori.
Moran AP. Moran AP. Carbohydr Res. 2008 Aug 11;343(12):1952-65. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2007.12.012. Epub 2007 Dec 25. Carbohydr Res. 2008. PMID: 18279843 Review. - Fucose-specific DC-SIGN signalling directs T helper cell type-2 responses via IKKε- and CYLD-dependent Bcl3 activation.
Gringhuis SI, Kaptein TM, Wevers BA, Mesman AW, Geijtenbeek TB. Gringhuis SI, et al. Nat Commun. 2014 May 28;5:3898. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4898. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24867235 - DC-SIGN mediates adhesion and rolling of dendritic cells on primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells through LewisY antigen expressed on ICAM-2.
García-Vallejo JJ, van Liempt E, da Costa Martins P, Beckers C, van het Hof B, Gringhuis SI, Zwaginga JJ, van Dijk W, Geijtenbeek TB, van Kooyk Y, van Die I. García-Vallejo JJ, et al. Mol Immunol. 2008 Apr;45(8):2359-69. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.11.001. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18155766 - Neisseria meningitidis expressing lgtB lipopolysaccharide targets DC-SIGN and modulates dendritic cell function.
Steeghs L, van Vliet SJ, Uronen-Hansson H, van Mourik A, Engering A, Sanchez-Hernandez M, Klein N, Callard R, van Putten JP, van der Ley P, van Kooyk Y, van de Winkel JG. Steeghs L, et al. Cell Microbiol. 2006 Feb;8(2):316-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00623.x. Cell Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16441441 - C-type lectins on dendritic cells: key modulators for the induction of immune responses.
van Kooyk Y. van Kooyk Y. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Dec;36(Pt 6):1478-81. doi: 10.1042/BST0361478. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 19021579 Review.
Cited by
- Pattern recognition receptors in companion and farm animals - the key to unlocking the door to animal disease?
Werling D, Coffey TJ. Werling D, et al. Vet J. 2007 Sep;174(2):240-51. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2006.10.010. Epub 2006 Nov 29. Vet J. 2007. PMID: 17137812 Free PMC article. Review. - Is there a link between the lipopolysaccharide of Helicobacter pylori gastric MALT lymphoma associated strains and lymphoma pathogenesis?
Lehours P, Zheng Z, Skoglund A, Mégraud F, Engstrand L. Lehours P, et al. PLoS One. 2009 Oct 6;4(10):e7297. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007297. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19806222 Free PMC article. - The role of glycans in immune evasion: the human fetoembryonic defence system hypothesis revisited.
Clark GF. Clark GF. Mol Hum Reprod. 2014 Mar;20(3):185-99. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gat064. Epub 2013 Sep 15. Mol Hum Reprod. 2014. PMID: 24043694 Free PMC article. Review. - DC-SIGN and L-SIGN: the SIGNs for infection.
Khoo US, Chan KY, Chan VS, Lin CL. Khoo US, et al. J Mol Med (Berl). 2008 Aug;86(8):861-74. doi: 10.1007/s00109-008-0350-2. Epub 2008 May 6. J Mol Med (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18458800 Free PMC article. Review. - N-linked glycosylation facilitates sialic acid-independent attachment and entry of influenza A viruses into cells expressing DC-SIGN or L-SIGN.
Londrigan SL, Turville SG, Tate MD, Deng YM, Brooks AG, Reading PC. Londrigan SL, et al. J Virol. 2011 Mar;85(6):2990-3000. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01705-10. Epub 2010 Dec 29. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21191006 Free PMC article.
References
- Ernst, P.B., and B.D. Gold. 2000. The disease spectrum of Helicobacter pylori: the immunopathogenesis of gastroduodenal ulcer and gastric cancer. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 54:615–640. - PubMed
- Uemura, N., S. Okamoto, S. Yamamoto, N. Matsumura, S. Yamaguchi, M. Yamakido, K. Taniyama, N. Sasaki, and R.J. Schlemper. 2001. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 345:784–789. - PubMed
- Aspinall, G.O., and M.A. Monteiro. 1996. Lipopolysaccharides of Helicobacter pylori strains P466 and MO19: structures of the O antigen and core oligosaccharide regions. Biochemistry. 35:2498–2504. - PubMed
- Aspinall, G.O., M.A. Monteiro, H. Pang, E.J. Walsh, and A.P. Moran. 1996. Lipopolysaccharide of the Helicobacter pylori type strain NCTC 11637 (ATCC 43504): structure of the O antigen chain and core oligosaccharide regions. Biochemistry. 35:2489–2497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources