characterization of bacterial community diversity in cystic fibrosis lung infections by use of 16s ribosomal DNA terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism profiling - PubMed (original) (raw)
characterization of bacterial community diversity in cystic fibrosis lung infections by use of 16s ribosomal DNA terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism profiling
G B Rogers et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Nov.
Abstract
Progressive loss of lung function resulting from the inflammatory response to bacterial colonization is the leading cause of mortality in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. A greater understanding of these bacterial infections is needed to improve lung disease management. As culture-based diagnoses are associated with fundamental drawbacks, we used terminal restriction fragment (T-RF) length polymorphism profiling and 16S rRNA clone data to characterize, without prior cultivation, the bacterial community in 71 sputa from 34 adult CF patients. Nineteen species from 15 genera were identified in 53 16S rRNA clones from three patients. Of these, 15 species have not previously been reported in CF lung infections and many were species requiring strict anaerobic conditions for growth. The species richness and evenness were determined from the T-RF length and volume for the 71 profiles. Species richness was on average 13.3 +/- 7.9 per sample and 13.4 +/- 6.7 per patient. On average, the T-RF bands of the lowest and highest volumes represented 0.6 and 59.2% of the total volume in each profile, respectively. The second through fifth most dominant T-RF bands represented 15.3, 7.5, 4.7, and 2.8% of the total profile volume, respectively. On average, the remaining T-RF bands represented 10.2% of the total profile volume. The T-RF band corresponding to Pseudomonas aeruginosa had the highest volume in 61.1% of the samples. However, 18 other T-RF band lengths were dominant in at least one sample. In conclusion, this reveals the enormous complexity of bacteria within the CF lung. Although their significance is yet to be determined, these findings alter our perception of CF lung infections.
Figures
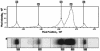
FIG. 1.
Gel image and band extraction. The figure shows both the trace from a region of an electrophoretic lane that forms the basis of the band assignment and signal intensity measurement process (upper panel) and the corresponding image from which this trace is derived as it appears on the automated sequencer output (lower panel).
FIG. 2.
Graph of mean percentage of total band volume represented by rank-ordered T-RF bands.
Similar articles
- Bacterial diversity in cases of lung infection in cystic fibrosis patients: 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) length heterogeneity PCR and 16S rDNA terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism profiling.
Rogers GB, Hart CA, Mason JR, Hughes M, Walshaw MJ, Bruce KD. Rogers GB, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Aug;41(8):3548-58. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.8.3548-3558.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12904354 Free PMC article. - Use of 16S rRNA gene profiling by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis to compare bacterial communities in sputum and mouthwash samples from patients with cystic fibrosis.
Rogers GB, Carroll MP, Serisier DJ, Hockey PM, Jones G, Kehagia V, Connett GJ, Bruce KD. Rogers GB, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Jul;44(7):2601-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02282-05. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16825392 Free PMC article. - Bacterial activity in cystic fibrosis lung infections.
Rogers GB, Carroll MP, Serisier DJ, Hockey PM, Kehagia V, Jones GR, Bruce KD. Rogers GB, et al. Respir Res. 2005 Jun 1;6(1):49. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-6-49. Respir Res. 2005. PMID: 15929792 Free PMC article. - Fungal and Bacterial Diversity of Airway Microbiota in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis: Concordance Between Conventional Methods and Ultra-Deep Sequencing, and Their Practical use in the Clinical Laboratory.
Botterel F, Angebault C, Cabaret O, Stressmann FA, Costa JM, Wallet F, Wallaert B, Bruce K, Delhaes L. Botterel F, et al. Mycopathologia. 2018 Feb;183(1):171-183. doi: 10.1007/s11046-017-0185-x. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Mycopathologia. 2018. PMID: 28766039 - Studying bacterial infections through culture-independent approaches.
Rogers GB, Carroll MP, Bruce KD. Rogers GB, et al. J Med Microbiol. 2009 Nov;58(Pt 11):1401-1418. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.013334-0. Epub 2009 Jun 25. J Med Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19556372 Review.
Cited by
- Inflammation-associated nitrate facilitates ectopic colonization of oral bacterium Veillonella parvula in the intestine.
Rojas-Tapias DF, Brown EM, Temple ER, Onyekaba MA, Mohamed AMT, Duncan K, Schirmer M, Walker RL, Mayassi T, Pierce KA, Ávila-Pacheco J, Clish CB, Vlamakis H, Xavier RJ. Rojas-Tapias DF, et al. Nat Microbiol. 2022 Oct;7(10):1673-1685. doi: 10.1038/s41564-022-01224-7. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Nat Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36138166 Free PMC article. - Pyocyanina contributory factor in haem acquisition and virulence enhancement of Porphyromonas gingivalis in the lung [corrected].
Benedyk M, Byrne DP, Glowczyk I, Potempa J, Olczak M, Olczak T, Smalley JW. Benedyk M, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Feb 23;10(2):e0118319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118319. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25706529 Free PMC article. - From hairballs to hypotheses-biological insights from microbial networks.
Röttjers L, Faust K. Röttjers L, et al. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2018 Nov 1;42(6):761-780. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuy030. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30085090 Free PMC article. Review. - Complexity, temporal stability, and clinical correlates of airway bacterial community composition in primary ciliary dyskinesia.
Rogers GB, Carroll MP, Zain NM, Bruce KD, Lock K, Walker W, Jones G, Daniels TW, Lucas JS. Rogers GB, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Dec;51(12):4029-35. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02164-13. Epub 2013 Sep 25. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24068019 Free PMC article. - Comparing the microbiota of the cystic fibrosis lung and human gut.
Rogers GB, Carroll MP, Hoffman LR, Walker AW, Fine DA, Bruce KD. Rogers GB, et al. Gut Microbes. 2010 Mar;1(2):85-93. doi: 10.4161/gmic.1.2.11350. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Gut Microbes. 2010. PMID: 21326915 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
- Baron, E. J., P. J. Summanen, J. Downes, M. C. Roberts, H. Wexler, and S. M. Finegold. 1989. Bilophila wadsorthia, gen. nov. and sp. nov., a unique Gram-negative anaerobic rod recovered from appendicitis specimens and human faeces. J. Gen. Microbiol. 135:3405-3411. - PubMed
- Bercovier, H., O. Kafri, and S. Sela. 1986. Mycobacteria possess a surprisingly small number of ribosomal RNA genes in relation to the size of their genome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 136:1136-1141. - PubMed
- Bonsell, S. Isolated knee joint infection with Neisseria meningitidis. Orthopedics 25:537-539. - PubMed
- Brook, I. 1989. Bacteriology of chronic maxillary sinusitis in adults. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 98:426-428. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials