The genomes of recombinant inbred lines - PubMed (original) (raw)
The genomes of recombinant inbred lines
Karl W Broman. Genetics. 2005 Feb.
Erratum in
- Genetics. 2006 Aug;173(4):2419
Abstract
Recombinant inbred lines (RILs) can serve as powerful tools for genetic mapping. Recently, members of the Complex Trait Consortium proposed the development of a large panel of eight-way RILs in the mouse, derived from eight genetically diverse parental strains. Such a panel would be a valuable community resource. The use of such eight-way RILs will require a detailed understanding of the relationship between alleles at linked loci on an RI chromosome. We extend the work of Haldane and Waddington on two-way RILs and describe the map expansion, clustering of breakpoints, and other features of the genomes of multiple-strain RILs as a function of the level of crossover interference in meiosis.
Figures
Figure 1.—
The production of recombinant inbred lines by selfing (A) and by sibling mating (B).
Figure 2.—
The production of an eight-way recombinant inbred line by selfing (A) and by sibling mating (B).
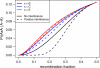
Figure 3.—
Three-point coincidence in meiosis (A), RILs by selfing (B), the X chromosome for RILs by sibling mating (C), and autosomes for RILs by sibling mating (D). Solid curves are for the case of no interference; dashed curves correspond to strong positive crossover interference (according to the gamma model with ν = 11.3, as estimated for the mouse genome). (B–D) Black, blue, and red curves correspond to two-way, four-way, and eight-way RILs, respectively. Note that coincidence on the RIL chromosome is displayed as a function of the recombination fraction at meiosis.
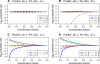
Figure 4.—
Assessment of symmetry in the three-point probabilities on the autosomes of eight-way RILs by sibling mating. The conditional probabilities Pr(AxA|A_–_A) are displayed as a function of the recombination fraction between adjacent loci, with the solid curves corresponding to no interference and the dashed curves corresponding to strong positive interference.
Figure 5.—
Assessment of the Markov property in the three-point probabilities on autosomes of eight-way RILs by sibling mating. Log2{Pr(xyA|xy_–)/Pr(–_yA|–_y_–)} is displayed for each distinct case of x, y, with the solid and dashed curves corresponding to no interference and strong positive crossover interference, respectively.
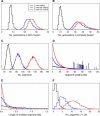
Figure 6.—
Results of 10,000 simulations of two-way RILs by selfing (black), two-way RILs by sibling mating (blue), and eight-way RILs by sibling mating (red), with a mouse-like genome of length 1665 cM and exhibiting strong crossover interference. (A) Distribution of the number of generations of breeding to achieve 99% fixation. (B) Distribution of the number of generations of breeding to achieve complete, genome-wide fixation. (C) Distribution of the total number of segments, genome-wide. (D) Distribution of the lengths of segments. (E) Distribution of the length of the smallest segment, genome-wide. (F) Distribution of the number of segments <1 cM in length.
Similar articles
- The genetic structure of recombinant inbred mice: high-resolution consensus maps for complex trait analysis.
Williams RW, Gu J, Qi S, Lu L. Williams RW, et al. Genome Biol. 2001;2(11):RESEARCH0046. doi: 10.1186/gb-2001-2-11-research0046. Epub 2001 Oct 22. Genome Biol. 2001. PMID: 11737945 Free PMC article. - Two- and three-locus tests for linkage analysis using recombinant inbred lines.
Martin OC, Hospital F. Martin OC, et al. Genetics. 2006 May;173(1):451-9. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.047175. Epub 2006 Feb 19. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16489236 Free PMC article. - Design and construction of recombinant inbred lines.
Pollard DA. Pollard DA. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;871:31-9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-785-9_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22565831 - Use of recombinant inbred strains for studying genetic determinants of responses to alcohol.
Crabbe JC, Belknap JK, Buck KJ, Metten P. Crabbe JC, et al. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1994;2:67-71. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1994. PMID: 8974318 Review. - Analysing complex genetic traits with chromosome substitution strains.
Nadeau JH, Singer JB, Matin A, Lander ES. Nadeau JH, et al. Nat Genet. 2000 Mar;24(3):221-5. doi: 10.1038/73427. Nat Genet. 2000. PMID: 10700173 Review.
Cited by
- Recombination fraction in pre-recombinant inbred lines (PRERIL) - revisiting a century old problem in genetics.
Xu S, Osorio Y Fortéa J. Xu S, et al. BMC Genomics. 2024 Sep 2;25(1):822. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10699-z. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39223519 Free PMC article. - From pharmacogenetics to pharmaco-omics: Milestones and future directions.
Auwerx C, Sadler MC, Reymond A, Kutalik Z. Auwerx C, et al. HGG Adv. 2022 Mar 16;3(2):100100. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2022.100100. eCollection 2022 Apr 14. HGG Adv. 2022. PMID: 35373152 Free PMC article. Review. - Quantitative epigenetics through epigenomic perturbation of isogenic lines.
Johannes F, Colomé-Tatché M. Johannes F, et al. Genetics. 2011 May;188(1):215-27. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.127118. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21385727 Free PMC article. - Signatures of Dobzhansky-Muller Incompatibilities in the Genomes of Recombinant Inbred Lines.
Colomé-Tatché M, Johannes F. Colomé-Tatché M, et al. Genetics. 2016 Feb;202(2):825-41. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.179473. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 26680662 Free PMC article.
References
- Complex Trait Consortium, 2004. The Collaborative Cross, a community resource for the genetic analysis of complex traits. Nat. Genet. 36: 1133–1137. - PubMed
- Hospital, F., C. Dillmann and A. E. Melchinger, 1996. A general algorithm to compute multilocus genotype frequencies under various mating systems. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 12: 455–462. - PubMed
- Ihaka, R., and R. Gentleman, 1996. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comp. Graph. Stat. 5: 299–314.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources