Pax6, Tbr2, and Tbr1 are expressed sequentially by radial glia, intermediate progenitor cells, and postmitotic neurons in developing neocortex - PubMed (original) (raw)
Pax6, Tbr2, and Tbr1 are expressed sequentially by radial glia, intermediate progenitor cells, and postmitotic neurons in developing neocortex
Chris Englund et al. J Neurosci. 2005.
Abstract
The developing neocortex contains two types of progenitor cells for glutamatergic, pyramidal-projection neurons. The first type, radial glia, produce neurons and glia, divide at the ventricular surface, and express Pax6, a homeodomain transcription factor. The second type, intermediate progenitor cells, are derived from radial glia, produce only neurons, and divide away from the ventricular surface. Here we show that the transition from radial glia to intermediate progenitor cell is associated with upregulation of Tbr2, a T-domain transcription factor, and downregulation of Pax6. Accordingly, Tbr2 expression in progenitor compartments (the subventricular zone and ventricular zone) rises and falls with cortical plate neurogenesis. The subsequent transition from intermediate progenitor cell to postmitotic neuron is marked by downregulation of Tbr2 and upregulation of Tbr1, another T-domain transcription factor. These findings delineate the transcription factor sequence Pax6 --> Tbr2 --> Tbr1 in the differentiation of radial glia --> intermediate progenitor cell --> postmitotic projection neuron. This transcription factor sequence is modified in preplate neurons, in which Tbr2 is transiently coexpressed with Tbr1, and in the direct differentiation pathway from radial glia --> postmitotic projection neuron, in which Tbr2 is expressed briefly or not at all.
Figures
Figure 1.
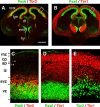
Expression of Pax6, Tbr2, and Tbr1 protein in E14.5 cortex (coronal sections). A, C, Pax6 (green) and Tbr2 (red). Boxed area in A is shown at higher magnification in C. B, D, Pax6 (green) and Tbr1 (red). Boxed area in B is shown at higher magnification in D. E, Tbr2 (green) and Tbr1 (red). All three TFs were expressed in the neocortex (nctx) and eminentia thalami (emt). Pax6 was also expressed in the ventricular zone of the dorsal thalamus (dt), hypothalamus (hy), and lateral part of the lateral ganglionic eminence (lge). Within the neocortex, Pax6 was expressed in the ventricular zone (vz) only; Tbr2 was expressed in the ventricular zone, subventricular zone (svz), and intermediate zone (iz); and Tbr1 was expressed in the intermediate zone (iz), subplate (sp), cortical plate (cp), and marginal zone (mz). Rarely, Tbr2+ cells and Pax6+ cells occupied superficial zones (arrowheads in C). Scale bar (in A): A, B, 500 μm; _C_-E,50 μm.
Figure 2.
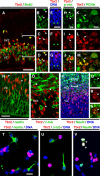
Tbr2 is expressed by NS-div IPCs. _A_-S, Confocal images of coronal sections through E14.5 cortex. A-D, Tbr2 (red) and BrdU (green). The bracketed area in A is shown in separate color channels in _B_-D. Tbr2 was expressed by most S-phase cells in the SVZ and some in the VZ (arrowheads in _B_-D). E-G, Tbr2 (red) and DNA (blue). Tbr2 was expressed by NS-div cells (red arrowhead in E-G) but not by S-div cells (green arrowheads). H-J, Tbr2 (red) was expressed by phosphovimentin+ (p-vim) M-phase cells (green) in the SVZ (arrowheads). K-M, Tbr2 (red) and PCNA (green). Most Tbr2+ cells contained PCNA, including mitotic figures (arrowheads). N, Tbr2 (red) and nestin (green). Most Tbr2+ cells (arrowheads) appeared to lack nestin. O, Tbr2 (red) and βIII-tubulin (β-tub; green). Most Tbr2+ cells (arrowheads) lacked βIII-tubulin. P-S, Tbr2 (red), NeuN (green), and DNA (blue). The bracketed area in P is enlarged and shown in separate color channels in Q-S. Most Tbr2+ cells did not express NeuN, but those that did included some mitotic figures (arrowheads in Q-S). _T_-V, E14.5 cortical cells cultured for 1 d in vitro, labeled to detect Tbr2 (red), DNA (blue), and, in green, nestin (T), βIII-tubulin (U), or NeuN (V). Few Tbr2+ cells expressed nestin (5.1%) or βIII-tubulin (12.7%), but more expressed NeuN (20.8%; arrowheads). Scale bars: (in A) A-D, P, 50 μm; (in E) E-G, 20 μm; (in H) H-J, Q-S, 10 μm; (in K) K-M, O, 10 μm; (in N) N, 20 μm; (in T) T-V, 20 μm.
Figure 3.
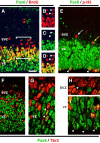
Pax6 is substantially downregulated in most Tbr2+ IPCs. A-I, Confocal images of coronal sections through E14.5 cortex. A-D, Pax6 (green) and BrdU (red). The bracketed area in A is shown in separate color channels in B-D. Pax6 was not expressed by most S-phase cells in the SVZ (arrowheads in B-D) but was expressed by most S-phase cells in the VZ. E, Pax6 (green) and phosphohistone-H3 (red). Pax6 was strongly expressed in S-div mitotic figures (arrowheads) but only weakly (yellow arrow) or not at all (white arrow) in NS-div cells. F-I, Pax6 (green) and Tbr2 (red) double immunofluorescence. Most VZ and SVZ cells expressed Pax6 or Tbr2 but not both. Double-labeled cells appeared yellow (arrowheads in G). H-I, Higher magnification of mitotic figures in the SVZ (H) and VZ (I). NS-div mitoses were predominantly Tbr2+ (arrowhead in H), and S-div mitoses were Pax6+ (arrowheads in I). Scale bar (in A): A-E,30 μm; F,40 μm; G-I,12 μm.
Similar articles
- Development of the deep cerebellar nuclei: transcription factors and cell migration from the rhombic lip.
Fink AJ, Englund C, Daza RA, Pham D, Lau C, Nivison M, Kowalczyk T, Hevner RF. Fink AJ, et al. J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 15;26(11):3066-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5203-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16540585 Free PMC article. - Progressive loss of PAX6, TBR2, NEUROD and TBR1 mRNA gradients correlates with translocation of EMX2 to the cortical plate during human cortical development.
Bayatti N, Sarma S, Shaw C, Eyre JA, Vouyiouklis DA, Lindsay S, Clowry GJ. Bayatti N, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Oct;28(8):1449-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06475.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18973570 Free PMC article. - Pax6 regulates Tbr1 and Tbr2 expressions in olfactory bulb mitral cells.
Imamura F, Greer CA. Imamura F, et al. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 May;54:58-70. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.01.002. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23353076 Free PMC article. - Control of Neuronal Development by T-Box Genes in the Brain.
Mihalas AB, Hevner RF. Mihalas AB, et al. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017;122:279-312. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28057268 Review. - Intermediate progenitors and Tbr2 in cortical development.
Hevner RF. Hevner RF. J Anat. 2019 Sep;235(3):616-625. doi: 10.1111/joa.12939. Epub 2019 Jan 24. J Anat. 2019. PMID: 30677129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Antiviral immunity within neural stem cells distinguishes Enterovirus-D68 strain differences in forebrain organoids.
Vazquez C, Negatu SG, Bannerman CD, Sriram S, Ming GL, Jurado KA. Vazquez C, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Nov 5;21(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03275-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 39501367 Free PMC article. - Forebrain Eml1 depletion reveals early centrosomal dysfunction causing subcortical heterotopia.
Zaidi D, Chinnappa K, Yigit BN, Viola V, Cifuentes-Diaz C, Jabali A, Uzquiano A, Lemesre E, Perez F, Ladewig J, Ferent J, Ozlu N, Francis F. Zaidi D, et al. J Cell Biol. 2024 Dec 2;223(12):e202310157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202310157. Epub 2024 Sep 24. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39316454 - Spatial transcriptome reveals the region-specific genes and pathways regulated by Satb2 in neocortical development.
Yang J, Li Y, Tang Y, Yang L, Guo C, Peng C. Yang J, et al. BMC Genomics. 2024 Aug 2;25(1):757. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10672-w. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39095712 Free PMC article. - Purinosomes and Purine Metabolism in Mammalian Neural Development: A Review.
Yamada S, Mizukoshi T, Sato A, Sakakibara SI. Yamada S, et al. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2024 Jun 28;57(3):89-100. doi: 10.1267/ahc.24-00027. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2024. PMID: 38988694 Free PMC article. Review. - Indirect neurogenesis in space and time.
Thor S. Thor S. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2024 Aug;25(8):519-534. doi: 10.1038/s41583-024-00833-x. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38951687 Review.
References
- Boulder Committee (1970) Embryonic vertebrate central nervous system: revised terminology. Anat Rec 166: 257-261. - PubMed
- Bulfone A, Smiga SM, Shimamura K, Peterson A, Puelles L, Rubenstein JLR (1995) T-brain-1: a homolog of Brachyury whose expression defines molecularly distinct domains within the cerebral cortex. Neuron 15: 63-78. - PubMed
- Bulfone A, Martinez S, Marigo V, Campanella M, Basile A, Quaderi N, Gat-tuso C, Rubenstein JLR, Ballabio A (1999) Expression pattern of the Tbr2 (Eomesodermin) gene during mouse and chick brain development. Mech Dev 84: 133-138. - PubMed
- Estivill-Torrus G, Pearson H, van Heyningen V, Price DJ, Rashbass P (2002) Pax6 is required to regulate the cell cycle and the rate of progression from symmetrical to asymmetrical division in mammalian cortical progenitors. Development 129: 455-466. - PubMed
- Götz M, Stoykova A, Gruss P (1998) Pax6 controls radial glia differentiation in the cerebral cortex. Neuron 21: 1031-1044. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases