Regulation of gephyrin and GABAA receptor binding within the amygdala after fear acquisition and extinction - PubMed (original) (raw)
Regulation of gephyrin and GABAA receptor binding within the amygdala after fear acquisition and extinction
Jasmeer P Chhatwal et al. J Neurosci. 2005.
Abstract
Both the acquisition and extinction of conditioned fear appear to require the basolateral amygdala (BLA). Because these two forms of learning have opposing effects on the expression of conditioned fear, we hypothesized that they may modulate GABAergic tone differentially within the BLA. Previously, we reported that gene expression for the GABA(A) receptor clustering protein gephyrin was significantly downregulated in the BLA after fear acquisition (Ressler et al., 2002). Here we demonstrate an analogous decrease in BLA gephyrin protein levels, together with a decrease in the surface expression of GABA(A) receptors in the BLA after fear acquisition, as evidenced by decreased binding of H3-flunitrazepam. In marked contrast, gephyrin mRNA and protein levels in the BLA significantly increased after extinction training, as did H3-flunitrazepam binding. These results implicate the protein gephyrin in both fear acquisition and extinction and suggest that the modulation of gephyrin and GABA(A) receptor expression in the BLA may play a role in the experience-dependent plasticity underlying both of these types of learning. Furthermore, these results demonstrate that physiologically relevant, dynamic alterations of GABAergic synapses occur during the consolidation phase of BLA-dependent learning and may interact with previously described alterations in glutamatergic transmission to initiate and stabilize memory formation in vivo.
Figures
Figure 1.
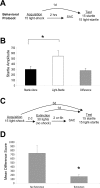
Behavioral paradigms. A, Schematic of fear-conditioning protocol. B, Control animals tested for FPS 24 hr after training demonstrate robust FPS (defined as a significant increase in the light-startle condition compared with startle alone). C, Schematic of extinction protocol. D, Control animals tested 24 hr after extinction training show a significant reduction in FPS. *p < 0.05. Error bars indicate ±SEM. See Results for statistics.
Figure 3.
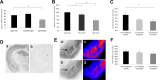
Gephyrin mRNA is increased after extinction training. A, Gephyrin mRNA (2 hr) is increased in the BLA of extinction-trained animals compared with animals who were fear conditioned but not extinction trained (no extinction group) and animals who were neither fear-conditioned nor extinction trained (home cage group; n = 6 per group). B, Increasing the strength of extinction training leads to greater increases in gephyrin mRNA 2 hr after extinction (n = 6 per group). C, Gephyrin protein is increased 6 hr after extinction compared with controls (extinction 2 hr, n = 6; extinction 6 hr, n = 11; no extinction, n = 6). D, Qualitative comparison of the in situ hybridization study quantified in B. Arrows highlight the location of the BLA complex. *p < 0.05. Error bars indicate ±SEM. See Results for statistics.
Figure 2.
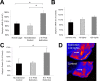
Gephyrin and GABAA binding are decreased after fear acquisition. A, Gephyrin mRNA in the BLA is significantly decreased 2 hr after fear conditioning in trained animals (light-shock) compared with animals presented with lights alone or unpaired lights and shocks during training (n = 5 per group). B, Gephyrin protein in the BLA is significantly decreased 2 hr after fear acquisition in trained (light-shock) animals compared with animals who received only lights or shocks during training (n = 6 per group) C, F, Binding of H3-Flu is significantly decreased 6 hr after fear conditioning in trained animals compared with naive controls (nonconditioned controls). A similar reduction in H3-Flu binding was not observed in the ventral striatum (F; n = 6 per group). Da, Db, Low-power image of 15 n
m
H3-Flu binding in a fear-conditioned animal in the absence (Da) and presence (Db) of 30 μ
m
clonazepam. Ea, Eb, Example autoradiographs of home cage control (Ea) or fear-conditioned (Eb) animals. Ec, Ed, Pseudo-color images of Ea and Eb, respectively, demonstrating qualitative decreases in GABAA binding within the BLA after fear conditioning. Arrows highlight the location of the BLA complex. *p < 0.05. Error bars indicate ±SEM. See Results for statistics.
Figure 4.
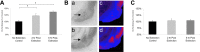
GABAA binding is increased after extinction training. A, B, Binding of H3-Flu in the BLA is significantly increased 2 and 6 hr after extinction in trained animals (2 and 6 hr, n = 4 per group) compared with animals who were fear conditioned but not extinction trained (no extinction group, n = 6). A similar reduction in H3-Flu binding was not observed in the ventral striatum (C). Ba, Bb, Example autoradiographs from no extinction (Ba) and extinction-trained (Bb) animals. Bc, Bd, Pseudocolor images of Ba and Bb, respectively, demonstrating qualitative increases in GABAA binding within the BLA after extinction. Arrows highlight the location of the BLA complex. *p < 0.05. Error bars indicate ±SEM. See Results for statistics.
Similar articles
- Training-induced changes in the expression of GABAA-associated genes in the amygdala after the acquisition and extinction of Pavlovian fear.
Heldt SA, Ressler KJ. Heldt SA, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2007 Dec;26(12):3631-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05970.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18088283 Free PMC article. - Differences in the density of GABA-A receptor alpha-2 subunits and gephyrin in brain structures of rats selected for low and high anxiety in basal and fear-stimulated conditions, in a model of contextual fear conditioning.
Lehner M, Wisłowska-Stanek A, Skórzewska A, Maciejak P, Szyndler J, Turzyńska D, Sobolewska A, Płaźnik A. Lehner M, et al. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010 Nov;94(4):499-508. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.09.001. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010. PMID: 20833253 - The role of the basolateral amygdala and infralimbic cortex in (re)learning extinction.
Lingawi NW, Laurent V, Westbrook RF, Holmes NM. Lingawi NW, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):303-312. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4957-x. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 29959461 Review. - [GABA-Receptors in Modulation of Fear Memory Extinction].
Dubrovina NI. Dubrovina NI. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2016 Mar-Apr;66(2):131-47. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2016. PMID: 27538279 Review. Russian.
Cited by
- The promise of extinction research for the prevention and treatment of anxiety disorders.
Anderson KC, Insel TR. Anderson KC, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2006 Aug 15;60(4):319-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.06.022. Biol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16919521 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available. - Training-induced changes in the expression of GABAA-associated genes in the amygdala after the acquisition and extinction of Pavlovian fear.
Heldt SA, Ressler KJ. Heldt SA, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2007 Dec;26(12):3631-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05970.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18088283 Free PMC article. - GABAergic Synapses at the Axon Initial Segment of Basolateral Amygdala Projection Neurons Modulate Fear Extinction.
Saha R, Knapp S, Chakraborty D, Horovitz O, Albrecht A, Kriebel M, Kaphzan H, Ehrlich I, Volkmer H, Richter-Levin G. Saha R, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017 Jan;42(2):473-484. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.205. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27634356 Free PMC article. - Center for Behavioral Neuroscience: a prototype multi-institutional collaborative research center.
Powell KR, Albers HE. Powell KR, et al. J Biomed Discov Collab. 2006 Jul 17;1:9. doi: 10.1186/1747-5333-1-9. J Biomed Discov Collab. 2006. PMID: 16846500 Free PMC article. - A biologically realistic network model of acquisition and extinction of conditioned fear associations in lateral amygdala neurons.
Li G, Nair SS, Quirk GJ. Li G, et al. J Neurophysiol. 2009 Mar;101(3):1629-46. doi: 10.1152/jn.90765.2008. Epub 2008 Nov 26. J Neurophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19036872 Free PMC article.
References
- Betz H (1998) Gephyrin, a major player in GABAergic postsynaptic membrane assembly? Nat Neurosci 1: 541-543. - PubMed
- Bissiere S, Humeau Y, Luthi A (2003) Dopamine gates LTP induction in lateral amygdala by suppressing feedforward inhibition. Nat Neurosci 6: 587-592. - PubMed
- Bremner JD, Innis RB, Southwick SM, Staib L, Zoghbi S, Charney DS (2000) Decreased benzodiazepine receptor binding in prefrontal cortex in combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry 157: 1120-1126. - PubMed
- Caldji C, Diorio J, Meaney MJ (2003) Variations in maternal care alter GABAA receptor subunit expression in brain regions associated with fear. Neuropsychopharmacology 28: 1950-1959. - PubMed
- Davis M (2000) The role of the amygdala in conditioned and unconditioned fear and anxiety. In: The amygdala, Vol 2 (Aggleton JP, ed), pp 213-287. Oxford: Oxford UP.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH047840/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH47840/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F30 MH070218/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH69884/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH070218/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH069884/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH047840/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008169/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources