Silencing near tRNA genes requires nucleolar localization - PubMed (original) (raw)
Silencing near tRNA genes requires nucleolar localization
Li Wang et al. J Biol Chem. 2005.
Abstract
Transcription by RNA polymerase II is antagonized by the presence of a nearby tRNA gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. To test hypotheses concerning the mechanism of this tRNA gene-mediated (tgm) silencing, the effects of specific gene deletions were determined. The results show that the mechanism of silencing near tRNA genes is fundamentally different from other forms of transcriptional silencing in yeast. Rather, tgm silencing is dependent on the ability to cluster the dispersed tRNA genes in or near the nucleolus, constituting a form of three-dimensional gene control.
Figures
Fig. 1. Deletion of genes affecting rRNA gene transcription relieves tgm silencing
A, a reporter construct was maintained in various deletion strains on a low copy CEN plasmid (4). The presence of the tRNA gene (SUP4) silences transcription of HIS3 from the GAL1 promoter/UASG unless tgm silencing is weakened. B, yeast strains carrying the indicated gene deletions were tested for silencing by plating serial dilutions on media containing or lacking histidine (SGR-ura or SGR-ura-his). Growth on SGR-ura-his indicates silencing is compromised. Four strains having defective pol I transcription (Δ_rpa12_, Δ_rpa49_, Δ_rrn10_, Δ_uaf30_) showed weakened silencing. Two of the tested genes affecting pol I transcription do not affect silencing in this assay (Δ_rpa34_ and Δ_rpa14_) A sir2 deletion is shown as a representative control for gene deletions that do not affect tgm silencing.
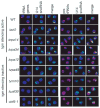
Fig. 2. Loss of nucleolar tRNA gene localization in strains that lose tgm silencing
Strains tested in Fig. 1 were probed for the position of the ten tRNALeu (CAA) genes and their pre-tRNALeu transcripts. Fixed cells were probed with fluorescent oligonucleotides complementary to the pre-tRNA intron or to the non-RNA strand of the tRNA genes. When the 10 dispersed tRNALeu genes lose the ability to localize to the nucleolus, they become distributed in the nucleoplasm and no fluorescent signal is detected above background (10). tRNA genes and pre-tRNAs are shown in red, with the nucleolar U14 snoRNA marker in green and the nucleoplasm in blue (4′,6-diamidino-2-phe-nylindole staining).
References
- Grewal SIS, Moazed D. Science. 2003;301:798–802. -PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases