Going in GTP cycles in the nucleolus - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comment
Going in GTP cycles in the nucleolus
Tom Misteli. J Cell Biol. 2005.
Abstract
Proteins are directed to cellular compartments by specific localization signals. A GTP-driven cycle has now been identified as a mechanism for protein targeting to the nucleolus. The involvement of a GTP switch suggests that nucleolar localization can be regulated and may be responsive to extracellular stimuli via signaling pathways. The uncovered mechanism also implies that localization is determined by increased retention rather than directed targeting.
Figures
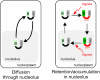
Figure 1.
Nucleolar localization by GTP-dependent retention. (Left) In the absence of GTP binding, nucleostemin diffuses rapidly through the nucleolus. (Right) Upon binding of GTP, the inhibitory action of the inhibitory domain (I) is relieved. As nucleostemin diffuses through the nucleolus, the basic domain (B) is able to undergo lasting interactions with nucleolar components. Nucleostemin accumulates in the nucleolus due to its prolonged retention. Exchange of GTP reverses the stable binding, and nucleostemin dissociates from the nucleolus. Signaling pathways may affect the availability of the protein for nucleolar import and/or its retention.
Comment on
- A multistep, GTP-driven mechanism controlling the dynamic cycling of nucleostemin.
Tsai RY, McKay RD. Tsai RY, et al. J Cell Biol. 2005 Jan 17;168(2):179-84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200409053. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15657390 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- A multistep, GTP-driven mechanism controlling the dynamic cycling of nucleostemin.
Tsai RY, McKay RD. Tsai RY, et al. J Cell Biol. 2005 Jan 17;168(2):179-84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200409053. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15657390 Free PMC article. - A novel lysine-rich domain and GTP binding motifs regulate the nucleolar retention of human guanine nucleotide binding protein, GNL3L.
Rao MR, Kumari G, Balasundaram D, Sankaranarayanan R, Mahalingam S. Rao MR, et al. J Mol Biol. 2006 Dec 8;364(4):637-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.007. Epub 2006 Sep 8. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 17034816 - Nucleolar targeting runs on GTP cycles.
Swaminathan S. Swaminathan S. Nat Cell Biol. 2005 Mar;7(3):217. doi: 10.1038/ncb0305-217. Nat Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15738973 No abstract available. - [Nucleocytoplasmic transport of proteins].
Imamoto N. Imamoto N. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2000 Oct;45(14):2369-77. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2000. PMID: 11051838 Review. Japanese. No abstract available. - Nucleolar targeting: the hub of the matter.
Emmott E, Hiscox JA. Emmott E, et al. EMBO Rep. 2009 Mar;10(3):231-8. doi: 10.1038/embor.2009.14. Epub 2009 Feb 20. EMBO Rep. 2009. PMID: 19229283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The nucleolus.
Pederson T. Pederson T. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Mar 1;3(3):a000638. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000638. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21106648 Free PMC article. Review. - Multiple controls regulate nucleostemin partitioning between nucleolus and nucleoplasm.
Meng L, Yasumoto H, Tsai RY. Meng L, et al. J Cell Sci. 2006 Dec 15;119(Pt 24):5124-36. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03292. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 17158916 Free PMC article. - Nucleolar stress with and without p53.
James A, Wang Y, Raje H, Rosby R, DiMario P. James A, et al. Nucleus. 2014 Sep-Oct;5(5):402-26. doi: 10.4161/nucl.32235. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 25482194 Free PMC article. Review. - Identification and functional analysis of NOL7 nuclear and nucleolar localization signals.
Zhou G, Doçi CL, Lingen MW. Zhou G, et al. BMC Cell Biol. 2010 Sep 27;11:74. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-11-74. BMC Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20875127 Free PMC article. - A nonribosomal landscape in the nucleolus revealed by the stem cell protein nucleostemin.
Politz JC, Polena I, Trask I, Bazett-Jones DP, Pederson T. Politz JC, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jul;16(7):3401-10. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-02-0106. Epub 2005 Apr 27. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15857956 Free PMC article.
References
- Andersen, J.S., C.E. Lyon, A.H. Fox, A.K. Leung, Y.W. Lam, H. Steen, M. Mann, and A.I. Lamond. 2002. Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus. Curr. Biol. 12:1–11. - PubMed
- Azzam, R., S.L. Chen, W. Shou, A.S. Mah, G. Alexandru, K. Nasmyth, R.S. Annan, S.A. Carr, and R.J. Deshaies. 2004. Phosphorylation by cyclin B-Cdk underlies release of mitotic exit activator Cdc14 from the nucleolus. Science. 305:516–519. - PubMed
- Dundr, M., and T. Misteli. 2002. Nucleolomics: an inventory of the nucleolus. Mol. Cell. 9:5–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous