DNA content and nucleoid distribution in Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus - PubMed (original) (raw)
DNA content and nucleoid distribution in Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus
Alan I Majerník et al. J Bacteriol. 2005 Mar.
Abstract
Flow cytometry and epifluorescence microscopy results for the euryarchaeon Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus were consistent with filaments containing multiple cells. Filaments of one to four cells contained two to eight nucleoids. Single chromosome-containing cells were not observed. Filaments containing multiple genome copies displayed synchronous DNA replication initiation. Chromosome segregation occurred during replication or rapidly after replication termination.
Figures
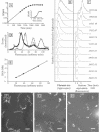
FIG. 1.
(A) Growth curve of M. thermautotrophicus in batch fermentor culture. The log(OD600) values of bioreactor samples were plotted against time. The insert shows a linear plot of the same data. (B and C) Flow cytometry filament size (light scatter) and DNA content (fluorescence after staining with a combination of ethidium bromide and mithramycin A) distributions in the same culture at different time points. The time (in minutes) after inoculation of the culture and the OD600 (average of four independent samples) are indicated to the right. (D) Superimposed DNA fluorescence peak positions from M. thermautotrophicus (thick line) and E. coli MG1655 seqA::Tn_10_ treated with rifampin (thin line). The numbers next to the M. thermautotrophicus peaks indicate the deduced numbers of genome equivalents. (E) Peak positions plotted versus chromosome sizes of E. coli (open circles) and M. thermautotrophicus (closed circles) indicate a comparable linear relationship between fluorescence and DNA content for both organisms. (F to H) Epifluorescence micrographs of DAPI-stained M. thermautotrophicus filaments demonstrating that filamentation decreases in a fermentor batch culture over time. Bars, 5 μm. (F) Exponentially growing cells from the 1,390-min time point. (G) Cells from the 1,945-min time point. (H) Stationary-phase cells from the 2,665-min time point.
Similar articles
- DNA binding by the Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus Cdc6 protein is inhibited by the minichromosome maintenance helicase.
Kasiviswanathan R, Shin JH, Kelman Z. Kasiviswanathan R, et al. J Bacteriol. 2006 Jun;188(12):4577-80. doi: 10.1128/JB.00168-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16740965 Free PMC article. - Archaeal cell cycle progress.
Lundgren M, Bernander R. Lundgren M, et al. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005 Dec;8(6):662-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2005.10.008. Epub 2005 Oct 24. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16249118 Review. - Nucleoid structure and partition in Methanococcus jannaschii: an archaeon with multiple copies of the chromosome.
Malandrin L, Huber H, Bernander R. Malandrin L, et al. Genetics. 1999 Aug;152(4):1315-23. doi: 10.1093/genetics/152.4.1315. Genetics. 1999. PMID: 10430562 Free PMC article. - Chromosome replication, nucleoid segregation and cell division in archaea.
Bernander R. Bernander R. Trends Microbiol. 2000 Jun;8(6):278-83. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(00)01760-1. Trends Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10838586 Review.
Cited by
- Analysis of a Methanogen and an Actinobacterium Dominating the Thermophilic Microbial Community of an Electromethanogenic Biocathode.
Kobayashi H, Toyoda R, Miyamoto H, Nakasugi Y, Momoi Y, Nakamura K, Fu Q, Maeda H, Goda T, Sato K. Kobayashi H, et al. Archaea. 2021 Mar 1;2021:8865133. doi: 10.1155/2021/8865133. eCollection 2021. Archaea. 2021. PMID: 33746613 Free PMC article. - The cell cycle of archaea.
Lindås AC, Bernander R. Lindås AC, et al. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Sep;11(9):627-38. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3077. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23893102 Review. - The Targeted Deletion of Genes Responsible for Expression of the Mth60 Fimbriae Leads to Loss of Cell-Cell Connections in Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus ΔH.
Fink C, Martinez-Cano G, Shuster J, Panzera A, Rennhack KE, Rohbohm N, Angenent LT, Molitor B. Fink C, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Jul 26;89(7):e0057523. doi: 10.1128/aem.00575-23. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37310347 Free PMC article. - Recovery of ionizing-radiation damage after high doses of gamma ray in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus gammatolerans.
Tapias A, Leplat C, Confalonieri F. Tapias A, et al. Extremophiles. 2009 Mar;13(2):333-43. doi: 10.1007/s00792-008-0221-3. Epub 2009 Jan 11. Extremophiles. 2009. PMID: 19137239 - Driving Apart and Segregating Genomes in Archaea.
Barillà D. Barillà D. Trends Microbiol. 2016 Dec;24(12):957-967. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Trends Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27450111 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bernander, R. 2003. The archaeal cell cycle: current issues. Mol. Microbiol. 48:599-604. - PubMed
- Bernander, R., J. E. D. Palm, and S. G. Svärd. 2001. Genome ploidy in different stages of the Giardia lamblia life cycle. Cell Microbiol. 3:55-62. - PubMed
- Bernander, R., T. Stokke, and E. Boye. 1998. Flow cytometry of bacterial cells: comparison between different flow cytometers and different DNA stains. Cytometry 31:29-36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources