Geography predicts neutral genetic diversity of human populations - PubMed (original) (raw)
Geography predicts neutral genetic diversity of human populations
Franck Prugnolle et al. Curr Biol. 2005.
No abstract available
Figures
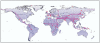
Figure 1
Shortest routes (in purple) through landmasses and specified land bridges between the 51 populations analysed (red dots) and a hypothetical East African origin. Geographic distances have been computed as paths connecting vertices (in blue) on land with a newly developed algorithm based on graph theory (see supplementary material).
Figure 2
Relationship between mean genetic diversity of 51 human populations computed over 377 autosomal microsatellite markers and their geographic distances in km from East Africa. The percentage of variance explained by geographic distance is R 2 = 85% (p < 10−4). The different colours correspond to the different ethnic groups defined by Rosenberg and colleagues [6]. If those ethnic groups are entered as an additional variable in the model, they do not allow explaining a significantly higher proportion of the variance (p = 0.35). There is also no significant difference between the individual regressions computed for each ethnic group separately (slopes p = 0.12 ; intercepts p = 0.27).
Similar articles
- Landscape location affects genetic variation of Canada lynx (Lynx canadensis).
Schwartz MK, Mills LS, Ortega Y, Ruggiero LF, Allendorf FW. Schwartz MK, et al. Mol Ecol. 2003 Jul;12(7):1807-16. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294x.2003.01878.x. Mol Ecol. 2003. PMID: 12803633 - GM haplotype diversity of 82 populations over the world suggests a centrifugal model of human migrations.
Dugoujon JM, Hazout S, Loirat F, Mourrieras B, Crouau-Roy B, Sanchez-Mazas A. Dugoujon JM, et al. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2004 Oct;125(2):175-92. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.10405. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2004. PMID: 15365983 - Understanding human DNA sequence variation.
Kidd KK, Pakstis AJ, Speed WC, Kidd JR. Kidd KK, et al. J Hered. 2004 Sep-Oct;95(5):406-20. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esh060. J Hered. 2004. PMID: 15388768 Review. - Going the distance: human population genetics in a clinal world.
Handley LJ, Manica A, Goudet J, Balloux F. Handley LJ, et al. Trends Genet. 2007 Sep;23(9):432-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2007.07.002. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Trends Genet. 2007. PMID: 17655965 Review. - Approximate Bayesian computation reveals the factors that influence genetic diversity and population structure of foxsnakes.
Row JR, Brooks RJ, MacKinnon CA, Lawson A, Crother BI, White M, Lougheed SC. Row JR, et al. J Evol Biol. 2011 Nov;24(11):2364-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2011.02362.x. Epub 2011 Aug 16. J Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21848978
Cited by
- Integrating the signatures of demic expansion and archaic introgression in studies of human population genomics.
Sugden LA, Ramachandran S. Sugden LA, et al. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016 Dec;41:140-149. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016. PMID: 27743539 Free PMC article. Review. - Identifying the environmental factors that determine the genetic structure of populations.
Foll M, Gaggiotti O. Foll M, et al. Genetics. 2006 Oct;174(2):875-91. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.059451. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16951078 Free PMC article. - The blunted vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) response to high-altitude hypoxia and genetic variants in the promoter region of the VEGFA gene in Sherpa highlanders.
Droma Y, Hanaoka M, Kinjo T, Kobayashi N, Yasuo M, Kitaguchi Y, Ota M. Droma Y, et al. PeerJ. 2022 Aug 17;10:e13893. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13893. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35996666 Free PMC article. - Amerindian Helicobacter pylori strains go extinct, as european strains expand their host range.
Domínguez-Bello MG, Pérez ME, Bortolini MC, Salzano FM, Pericchi LR, Zambrano-Guzmán O, Linz B. Domínguez-Bello MG, et al. PLoS One. 2008 Oct 2;3(10):e3307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003307. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18830403 Free PMC article. - Language: Its Origin and Ongoing Evolution.
Markov I, Kharitonova K, Grigorenko EL. Markov I, et al. J Intell. 2023 Mar 28;11(4):61. doi: 10.3390/jintelligence11040061. J Intell. 2023. PMID: 37103246 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Stringer C, Andrews P. Genetic and fossil evidence for the origin of modern humans. Science. 1988;239:1263–1268. - PubMed
- Tishkoff S, Kidd K. Implications of biogeography of human populations for ‘race’ and medicine. Nature Genet. 2004;36:S21–S27. - PubMed
- Harpending H, Rogers A. Genetic perspectives on human origins and differentiation. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2000;1:361–385. - PubMed
- Excoffier L. Human demographic history: refining the recent African origin model. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002;12:675–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources