Human metapneumovirus RNA in encephalitis patient - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
doi: 10.3201/eid1103.040676.
Thomas Glatzel, Tilman Geikowski, Bärbel Scheibner, Bertfried Matz, Lutz Bindl, Mark Born, Sergei Viazov, Anja Wilkesmann, Gisela Knöpfle, Michael Roggendorf, Arne Simon
Affiliations
- PMID: 15757568
- PMCID: PMC3298257
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1103.040676
Case Reports
Human metapneumovirus RNA in encephalitis patient
Oliver Schildgen et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Mar.
Abstract
We describe a fatal case of encephalitis that might be correlated with primary human metapneumovirus (HMPV) encephalitis. Postmortem HMPV RNA was detected in brain and lung tissue samples from the patient. Furthermore, HMPV RNA was found in culture fluids from cells coincubated with lung tissue.
Figures
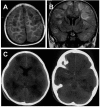
Figure 1
Axial T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan (A) and coronal fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) (B) show multifocal, mainly cortical and subcortical lesions of high signal intensity, which are most probably caused by multifocal encephalitis. C) Nonenhanced axial computed tomographic (CT) scan performed 2 days after the MRI shows multiple, hypodense lesions and signs of general edema. Additionally, it shows a hyperdense arachnoid collection that was not yet visible on the MRI 2 days before (panels A and B).
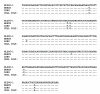
Figure 2
Alignment of 302 nucleotide human metapneumovirus (HMPV) sequences amplified from brain and lung tissues of the patient and from the supernatant of infected Vero cell culture. Sequence of the HMPV strain NLD00-1 was used as a prototype sequence. Conditions of the reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction were described elsewhere (5).
Similar articles
- A fatal case of encephalopathy possibly associated with human metapneumovirus infection.
Hata M, Ito M, Kiyosawa S, Kimpara Y, Tanaka S, Yamashita T, Hasegawa A, Kobayashi S, Koyama N, Minagawa H. Hata M, et al. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2007 Sep;60(5):328-9. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17881883 No abstract available. - Human metapneumovirus associated with central nervous system infection in children.
Arnold JC, Singh KK, Milder E, Spector SA, Sawyer MH, Gavali S, Glaser C. Arnold JC, et al. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009 Dec;28(12):1057-60. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181acd221. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009. PMID: 19755929 - Variant isolates of human metapneumovirus subgroup B genotype 1 in Campinas, Brazil.
da Silva LH, Spilki FR, Riccetto AG, de Almeida RS, Baracat EC, Arns CW. da Silva LH, et al. J Clin Virol. 2008 May;42(1):78-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2007.11.010. Epub 2008 Jan 7. J Clin Virol. 2008. PMID: 18178521 - Clinical impact and diagnosis of human metapneumovirus infection.
van den Hoogen BG, Osterhaus DM, Fouchier RA. van den Hoogen BG, et al. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004 Jan;23(1 Suppl):S25-32. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000108190.09824.e8. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004. PMID: 14730267 Review. - Human metapneumovirus: a not so new virus.
Mejías A, Chávez-Bueno S, Ramilo O. Mejías A, et al. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004 Jan;23(1):1-7; quiz 8-10. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000105103.60288.0e. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004. PMID: 14743038 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Human metapneumovirus: review of an important respiratory pathogen.
Panda S, Mohakud NK, Pena L, Kumar S. Panda S, et al. Int J Infect Dis. 2014 Aug;25:45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.03.1394. Epub 2014 May 17. Int J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24841931 Free PMC article. Review. - Modulation of Host Immunity by the Human Metapneumovirus.
Céspedes PF, Palavecino CE, Kalergis AM, Bueno SM. Céspedes PF, et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016 Oct;29(4):795-818. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00081-15. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27413096 Free PMC article. Review. - Square the Circle: Diversity of Viral Pathogens Causing Neuro-Infectious Diseases.
Nurmukanova V, Matsvay A, Gordukova M, Shipulin G. Nurmukanova V, et al. Viruses. 2024 May 15;16(5):787. doi: 10.3390/v16050787. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38793668 Free PMC article. Review. - Multi-year study of human metapneumovirus infection at a large US Midwestern Medical Referral Center.
Gray GC, Capuano AW, Setterquist SF, Erdman DD, Nobbs ND, Abed Y, Doern GV, Starks SE, Boivin G. Gray GC, et al. J Clin Virol. 2006 Dec;37(4):269-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2006.08.016. Epub 2006 Sep 27. J Clin Virol. 2006. PMID: 17008122 Free PMC article. - Human metapneumovirus in children, Singapore.
Loo LH, Tan BH, Ng LM, Tee NW, Lin RT, Sugrue RJ. Loo LH, et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007 Sep;13(9):1396-8. doi: 10.3201/eid1309.070220. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 18252120 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources