Comparative analysis of bacterial diversity in freshwater sediment of a shallow eutrophic lake by molecular and improved cultivation-based techniques - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Comparative analysis of bacterial diversity in freshwater sediment of a shallow eutrophic lake by molecular and improved cultivation-based techniques
Hideyuki Tamaki et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Apr.
Abstract
Comparative analysis of bacterial diversity in freshwater sediment collected from a shallow eutrophic lake was performed by using 16S rRNA gene clone library and improved cultivation-based techniques. Our study demonstrated that the use of gellan gum as a gelling reagent instead of agar was more effective at increasing culturability, cultivating a diverse array of novel microbes, and reducing the gaps of the results between molecular and cultivation-based analyses.
Figures
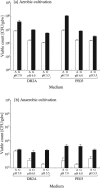
FIG. 1.
Effects of medium composition, pH conditions, and gelling reagents on viable counts after 11 weeks of incubation under aerobic (a) and anaerobic (b) conditions. White and black bars represent CFU counts from agar-based (A) and gellan gum-based (G) media, respectively. The vertical bars indicate 1 SD from the mean.
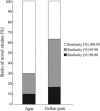
FIG. 2.
Effects of gelling reagents (agar [a] and gellan gum [b]) on the phylogenetic distribution of microbes cultivated from freshwater sediment with PE03 medium (pH 7.0) over various bacterial lineages on the basis of 16S rRNA gene analysis.
FIG. 3.
Effects of gelling reagents in PE03 medium (pH 7.0) on the cultivation of novel microbes from freshwater sediment under aerobic conditions. The similarity percentages shown are the 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities between the cultivated microbes and their closest relatives in the GenBank database.
Similar articles
- Effect of gelling agent on colony formation in solid cultivation of microbial community in lake sediment.
Tamaki H, Hanada S, Sekiguchi Y, Tanaka Y, Kamagata Y. Tamaki H, et al. Environ Microbiol. 2009 Jul;11(7):1827-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01907.x. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19302540 - Vertical distribution of bacteria in a lake sediment from Antarctica by culture-independent and culture-dependent approaches.
Shivaji S, Kumari K, Kishore KH, Pindi PK, Rao PS, Radha Srinivas TN, Asthana R, Ravindra R. Shivaji S, et al. Res Microbiol. 2011 Feb-Mar;162(2):191-203. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2010.09.020. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Res Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21126578 - Bacterial and archaeal assemblages in sediments of a large shallow freshwater lake, Lake Taihu, as revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis.
Liu FH, Lin GH, Gao G, Qin BQ, Zhang JS, Zhao GP, Zhou ZH, Shen JH. Liu FH, et al. J Appl Microbiol. 2009 Mar;106(3):1022-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.04069.x. Epub 2009 Jan 21. J Appl Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19191955 - Identification and characterization of ecologically significant prokaryotes in the sediment of freshwater lakes: molecular and cultivation studies.
Spring S, Schulze R, Overmann J, Schleifer K. Spring S, et al. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2000 Dec;24(5):573-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2000.tb00559.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2000. PMID: 11077151 Review. - A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria.
Newton RJ, Jones SE, Eiler A, McMahon KD, Bertilsson S. Newton RJ, et al. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011 Mar;75(1):14-49. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00028-10. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21372319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Trace amounts of furan-2-carboxylic acids determine the quality of solid agar plates for bacterial culture.
Hara S, Isoda R, Tahvanainen T, Hashidoko Y. Hara S, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41142. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041142. Epub 2012 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848437 Free PMC article. - A Simple and Effective Method for Solid Medium Cultivation of Strictly Hydrogen- and Sulfur-oxidizing Chemolithoautotrophs Predominant in Deep-sea Hydrothermal Fields.
Muto H, Miyazaki J, Sawayama S, Takai K, Nakagawa S. Muto H, et al. Microbes Environ. 2023;38(6):ME23072. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME23072. Microbes Environ. 2023. PMID: 38104970 Free PMC article. - Characterization of biofilm formation on a humic material.
Rodrigues AL, Brito AG, Janknecht P, Silva J, Machado AV, Nogueira R. Rodrigues AL, et al. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008 Nov;35(11):1269-76. doi: 10.1007/s10295-008-0424-8. Epub 2008 Aug 20. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18712549 - Stratified Bacterial and Archaeal Community in Mangrove and Intertidal Wetland Mudflats Revealed by High Throughput 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing.
Zhou Z, Meng H, Liu Y, Gu JD, Li M. Zhou Z, et al. Front Microbiol. 2017 Nov 2;8:2148. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02148. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29163432 Free PMC article. - Sediment Bacterial Community Structure Under the Influence of Different Domestic Sewage Types.
Zhang L, Xu M, Li X, Lu W, Li J. Zhang L, et al. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Sep 28;30(9):1355-1366. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2004.04023. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32627763 Free PMC article.
References
- Altmann, D., P. Stief, R. Amann, D. De Beer, and A. Schramm. 2003. In situ distribution and activity of nitrifying bacteria in freshwater sediment. Environ. Microbiol. 5:798-803. - PubMed
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases