Bistability in the Bacillus subtilis K-state (competence) system requires a positive feedback loop - PubMed (original) (raw)
Bistability in the Bacillus subtilis K-state (competence) system requires a positive feedback loop
Hédia Maamar et al. Mol Microbiol. 2005 May.
Abstract
High expression of the transcriptional activator ComK occurs in 10-20% of the cells in stationary phase cultures of Bacillus subtilis strain 168. ComK drives the expression of more than 100 genes constituting the semidormant K-state, distinct from sporulation and vegetative growth. Among the genes so activated are those that permit competence for genetic transformation. We have addressed the origin of bistability in expression of ComK. We show that bistability requires positive autoregulation at the promoter of comK, but not a potential toggle switch, in which ComK represses the promoter of rok and Rok represses the promoter of comK. We further address the source of the noise that results in the stochastic selection of cells that will express comK. A revised model for the regulation of comK expression is proposed that partially explains bistability.
Figures
Fig. 1
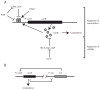
Regulation of competence. A. Summary of competence regulation. Arrows and perpendiculars represent positive and negative regulation respectively. ComK binds to its promoter as a dimer of dimers. B. Illustration of the putative toggle switch, in which ComK represses the transcription of rok and Rok represses the transcription of comK.
Fig. 2
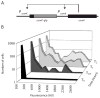
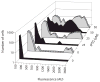
Bistability during the development of competence. A. The construction (BD2711) used to demonstrate bistability. The arrows represent positive regulation. B. The frequency distributions of fluorescence intensities in cells carrying comK-gfp (strain BD2711) are plotted at various times during the development of competence. T0 refers to the time of departure from exponential growth. At each time point, the fluorescent intensities of 500 cells were evaluated.
Fig. 3
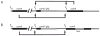
Constructs used to test the requirement for the autoregulatory loop for bistability. The arrowheads indicate positive regulation. A. Construct containing the loop (strain BD4010). B. Construct lacking the loop (strain BD4011).
Fig. 4
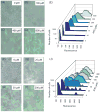
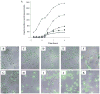
Distributions of ComK-GFP in cells without (A–E, strain BD4011) and with (F–J, strain BD4010) the ComK autoregulatory loop. The representative micrographs consist of fluorescent images overlaid with bright field images. All of the micrographs were recorded just before T0. In panel F, the arrow points to a rare cell expressing comK-gfp. The concentrations of IPTG used for each panel are indicated. For each IPTG concentration, the fluorescent intensities of 250 cells were determined.
Fig. 5
Effect of competence regulatory mutations on the expression of _comK-_lacZ (A) and of comK-gfp (B–K). In A, the following strains are shown: wild-type (○; strain BD1991), multicopy degU (■; strain BD4017), codY (▲; strain BD2607), rok (□; strain BD4016) and multicopy comS (△; strain BD4018). B–F exhibit cells taken at T0 and G–K exhibit cells taken at T2. The strains used were wild-type for regulatory genes (B, G; strain BD2711), carried a multicopy plasmid with degU (C, H; strain BD4013), were codY (D, I; strain BD4014), rok (E, J; strain BD4012) or carried a multicopy plasmid with comS (F, K; strain BD4015).
Fig. 6
Effect of rok knockout mutation on bistability in the strain BD4010 background (Fig. 3A). The distributions for the rok (BD4019, shaded) and rok+ (BD4010, black) strains are shown. The fluorescent intensities of 250 cells were evaluated for each IPTG concentration.
Similar articles
- Rok (YkuW) regulates genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis by directly repressing comK.
Hoa TT, Tortosa P, Albano M, Dubnau D. Hoa TT, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2002 Jan;43(1):15-26. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02727.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11849533 - A Novel Feedback Loop That Controls Bimodal Expression of Genetic Competence.
Gamba P, Jonker MJ, Hamoen LW. Gamba P, et al. PLoS Genet. 2015 Jun 25;11(6):e1005047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005047. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26110430 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of Bacillus subtilis natural competence by a native, conjugative plasmid-encoded comK repressor protein.
Singh PK, Ramachandran G, Durán-Alcalde L, Alonso C, Wu LJ, Meijer WJ. Singh PK, et al. Environ Microbiol. 2012 Oct;14(10):2812-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02819.x. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22779408 - A complex path for domestication of B. subtilis sociality.
Pollak S, Omer Bendori S, Eldar A. Pollak S, et al. Curr Genet. 2015 Nov;61(4):493-6. doi: 10.1007/s00294-015-0479-9. Epub 2015 Feb 14. Curr Genet. 2015. PMID: 25680358 Review. - Genetic networks controlling the initiation of sporulation and the development of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis.
Grossman AD. Grossman AD. Annu Rev Genet. 1995;29:477-508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.29.120195.002401. Annu Rev Genet. 1995. PMID: 8825484 Review.
Cited by
- Plasmid-encoded ComI inhibits competence in the ancestral 3610 strain of Bacillus subtilis.
Konkol MA, Blair KM, Kearns DB. Konkol MA, et al. J Bacteriol. 2013 Sep;195(18):4085-93. doi: 10.1128/JB.00696-13. Epub 2013 Jul 8. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23836866 Free PMC article. - A GFP-lacZ bicistronic reporter system for promoter analysis in environmental gram-negative bacteria.
Silva-Rocha R, de Lorenzo V. Silva-Rocha R, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034675. Epub 2012 Apr 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22493710 Free PMC article. - Density-Dependent Differentiation of Bacteria in Spatially Structured Open Systems.
Ribbe J, Maier B. Ribbe J, et al. Biophys J. 2016 Apr 12;110(7):1648-1660. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.03.007. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27074689 Free PMC article. - A bistable switch and anatomical site control Vibrio cholerae virulence gene expression in the intestine.
Nielsen AT, Dolganov NA, Rasmussen T, Otto G, Miller MC, Felt SA, Torreilles S, Schoolnik GK. Nielsen AT, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2010 Sep 16;6(9):e1001102. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001102. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20862321 Free PMC article. - Buffering and Amplifying Transcriptional Noise During Cell Fate Specification.
Urban EA, Johnston RJ Jr. Urban EA, et al. Front Genet. 2018 Nov 29;9:591. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00591. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30555516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Balaban NQ, Merrin J, Chait R, Kowalik L, Leibler S. Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch. Science. 2004;305:1622–1625. - PubMed
- Berka RM, Hahn J, Albano M, Draskovic I, Persuh M, Cui X, et al. Microarray analysis of the Bacillus subtilis K-state: genome-wide expression changes dependent on ComK. Mol Microbiol. 2002;43:1331–1345. - PubMed
- Elowitz MB, Levine AJ, Siggia ED, Swain PS. Stochastic gene expression in a single cell. Science. 2002;297:1183–1186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases