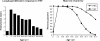Shingles Immunity and Health Functioning in the Elderly: Tai Chi Chih as a Behavioral Treatment - PubMed (original) (raw)
Shingles Immunity and Health Functioning in the Elderly: Tai Chi Chih as a Behavioral Treatment
Michael Irwin et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2004 Dec.
Abstract
Both the incidence and severity of herpes zoster (HZ) or shingles increase markedly with increasing age in association with a decline in varicella zoster virus (VZV)-specific immunity. Considerable evidence shows that behavioral stressors, prevalent in older adults, correlate with impairments of cellular immunity. Moreover, the presence of depressive symptoms in older adults is associated with declines in VZV-responder cell frequency (VZV-RCF), an immunological marker of shingles risk. In this review, we discuss recent findings that administration of a relaxation response-based intervention, tai chi chih (TCC), results in improvements in health functioning and immunity to VZV in older adults as compared with a control group. TCC is a slow moving meditation consisting of 20 separate standardized movements which can be readily used in elderly and medically compromised individuals. TCC offers standardized training and practice schedules, lending an important advantage over prior relaxation response-based therapies. Focus on older adults at increased risk for HZ and assay of VZV-specific immunity have implications for understanding the impact of behavioral factors and a behavioral intervention on a clinically relevant end-point and on the response of the immune system to infectious pathogens.
Figures
**Figure 1
Varicella zoster virus specific cellular immunity and age. The relationship between human age, level of lymphocyte proliferative response to varicella zoster virus antigen and phytohemagglutinin (PHA), and delayed-type hypersensitivity response to varicella zoster virus antigen skin challenge. There is a marked attenuation of varicella zoster-specific cellular immunity in persons over the age of 60 years. Reprinted from Burke et al. (13).
**Figure 2
Pathogenesis of herpes zoster. Reprinted with permission from Oxman (111).
**Figure 3
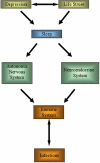
Relationship between depression, life stress, sleep and the autonomic, neuroendocrine and immune systems. The evidence for the relationship between life stress and depression and varicella zoster-specific immunity and herpes zoster risk is the subject of this review. Possible mechanisms for these effects including alterations in behavioral responses such as disordered sleep or abnormal activation of the sympathetic nervous system are also considered.
**Figure 4
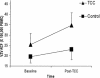
VZV-specific CMI (VZV-RCF) at baseline and at 1 week post-intervention in the intent-to-treat sample. VZV-RCF increased from baseline to 1 week post-intervention in the TCC group [F(1,31) = 4.4, P < 0.05] but not in the control group. Data are mean ± SEM values. Reprinted with permission from Irwin et al. (70).
**Figure 5
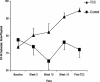
SF-36 scale score role-physical at baseline, during the itnervention at weeks 5, 10 and 15, and 1 week post-intervention in the completer sample, TCC (n = 14) and control group (n = 17). SF-36 role-physical scores were higher in the TCC group compared with controls [F(1,2) = 5.1] at post-intervention. Data are mean = SEM scores. Reprinted with permission from Irwin et al. (70).
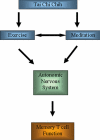
**Figure 6
Hypothesized mediators of the effects of tai chi chih on varicella zoster virus memory T-cell responses. The evidence for the pathway components of exercise and relaxation or meditation with changes of sympathovagal balance are considered.
Similar articles
- Effects of a behavioral intervention, Tai Chi Chih, on varicella-zoster virus specific immunity and health functioning in older adults.
Irwin MR, Pike JL, Cole JC, Oxman MN. Irwin MR, et al. Psychosom Med. 2003 Sep-Oct;65(5):824-30. doi: 10.1097/01.psy.0000088591.86103.8f. Psychosom Med. 2003. PMID: 14508027 Clinical Trial. - Major depressive disorder and immunity to varicella-zoster virus in the elderly.
Irwin MR, Levin MJ, Carrillo C, Olmstead R, Lucko A, Lang N, Caulfield MJ, Weinberg A, Chan IS, Clair J, Smith JG, Marchese RD, Williams HM, Beck DJ, McCook PT, Johnson G, Oxman MN. Irwin MR, et al. Brain Behav Immun. 2011 May;25(4):759-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.02.001. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Brain Behav Immun. 2011. PMID: 21329753 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Breadth and Functionality of Varicella-Zoster Virus Glycoprotein-Specific Antibodies Identified after Zostavax Vaccination in Humans.
Sullivan NL, Reuter-Monslow MA, Sei J, Durr E, Davis CW, Chang C, McCausland M, Wieland A, Krah D, Rouphael N, Mehta AK, Mulligan MJ, Pulendran B, Ahmed R, Vora KA. Sullivan NL, et al. J Virol. 2018 Jun 29;92(14):e00269-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00269-18. Print 2018 Jul 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29743372 Free PMC article. - Vaccines for preventing herpes zoster in older adults.
Gagliardi AM, Andriolo BN, Torloni MR, Soares BG. Gagliardi AM, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 3;3(3):CD008858. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008858.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26937872 Free PMC article. Updated. Review. - Animal models of varicella zoster virus infection.
Haberthur K, Messaoudi I. Haberthur K, et al. Pathogens. 2013 May 13;2(2):364-82. doi: 10.3390/pathogens2020364. Pathogens. 2013. PMID: 25437040 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Shaolin dan tian breathing fosters relaxed and attentive mind: a randomized controlled neuro-electrophysiological study.
Chan AS, Cheung MC, Sze SL, Leung WW, Shi D. Chan AS, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:180704. doi: 10.1155/2011/180704. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. PMID: 20976126 Free PMC article. - A pilot study exploring the effects of a 12-week t'ai chi intervention on somatic symptoms of depression in patients with heart failure.
Redwine LS, Tsuang M, Rusiewicz A, Pandzic I, Cammarata S, Rutledge T, Hong S, Linke S, Mills PJ. Redwine LS, et al. J Altern Complement Med. 2012 Aug;18(8):744-8. doi: 10.1089/acm.2011.0314. Epub 2012 Jul 30. J Altern Complement Med. 2012. PMID: 22845485 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Mind-Body Therapies for Late-Life Mental and Cognitive Health.
Laird KT, Paholpak P, Roman M, Rahi B, Lavretsky H. Laird KT, et al. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2018 Jan 25;20(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s11920-018-0864-4. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2018. PMID: 29372339 Review. - CAM and cell fate targeting: molecular and energetic insights into cell growth and differentiation.
Ventura C. Ventura C. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2005 Sep;2(3):277-83. doi: 10.1093/ecam/neh100. Epub 2005 Jul 20. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2005. PMID: 16136206 Free PMC article. - A review focused on the psychological effectiveness of tai chi on different populations.
Zhang L, Layne C, Lowder T, Liu J. Zhang L, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:678107. doi: 10.1155/2012/678107. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 21792371 Free PMC article.
References
- Ader R, Felten DL, Cohen N. Interactions between the brain and the immune system. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:561–602. - PubMed
- Maier SF, Watkins LR, Fleshner M. Psychoneuroimmunology: the interface between behavior, brain, and immunity. Am Psychol. 1994;49:1004–1017. - PubMed
- Glaser R, Rabin B, Chesney M, Cohen S, Natelson B. Stress-induced immunomodulation: implications for infectious diseases? J Am Med Assoc. 1999;281:2266–2270. - PubMed
- Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Glaser R. Psychoneuroimmunology: can psychological interventions modulate immunity. J Consult Clin Psychiatry. 1992;60:569–575. - PubMed
- Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Glaser R, Williger D, et al. Psychosocial enhancement of immunocompetence in a geriatric population. Health Psychol. 1985;4:25–41. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- R01 AG018367/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH019925/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA016541/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR049840/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH055253/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013239/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources