Impaired early B cell tolerance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Impaired early B cell tolerance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Jonathan Samuels et al. J Exp Med. 2005.
Abstract
Autoantibody production is a characteristic of most autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The role of these autoantibodies in the pathogenesis of RA remains elusive, but they appear in the serum many years before the onset of clinical disease suggesting an early break in B cell tolerance. The stage of B cell development at which B cell tolerance is broken in RA remains unknown. We previously established in healthy donors that most polyreactive developing B cells are silenced in the bone marrow, and additional autoreactive B cells are removed in the periphery. B cell tolerance in untreated active RA patients was analyzed by testing the specificity of recombinant antibodies cloned from single B cells. We find that autoreactive B cells fail to be removed in all six RA patients and represent 35-52% of the mature naive B cell compartment compared with 20% in healthy donors. In some patients, RA B cells express an increased proportion of polyreactive antibodies that can recognize immunoglobulins and cyclic citrullinated peptides, suggesting early defects in central B cell tolerance. Thus, RA patients exhibit defective B cell tolerance checkpoints that may favor the development of autoimmunity.
Figures
Figure 1.
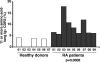
RA B cells express antibodies with unusually long CDR3s. Increased frequency of Igκ genes with unusually long ≥11−amino acid CDR3s in new emigrant B cells from RA patients. Differences in frequency of Igκ genes with ≥11−amino acid CDR3s between healthy donors and RA patients were found to be statistically significant (P = 0.008).
Figure 2.
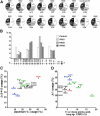
RA B cells can express an antibody repertoire consistent with either decreased or increased secondary V(D)J recombination. (A) Increased Jκ1 usage in new emigrant B cells from RA01, RA02, and RA08 patients. Pie charts show the proportion of different Jκ genes. The number of sequences analyzed in each fraction is indicated below the pie charts. Control healthy donor new emigrant B cells from HD01, HD02, and HD03 were previously reported (13, 14). *, Indicates statistically significant difference (RA01: 53.1%, P = 0.025; RA02: 51.4%, P = 0.02; and RA08: 47.9%, P = 0.027). (B) Decreased upstream (5′) Vκ usage in RA01, RA02, and RA08 new emigrant B cells. The proximal Vκ locus involved in 95% of Vκ−Jκ rearrangements is shown clustered into four groups of Vκ genes. Genes from the distal locus were combined to the upstream Vκ group. The percent of each Vκ group is indicated on the Y axis. *, Indicates statistically significant difference (RA02: P = 0.044; combined RA01, RA02, RA08: P = 0.0042). (C) The new emigrant B cell Igκ repertoire in RA06 is consistent with increased secondary V(D)J recombination in developing B cells. Patients' and healthy donor controls' upstream Vκ usage frequency was plotted against that of downstream Jκ3-4-5 usage. Increased upstream Vκ usage in RA06 was found to be statistically significant (P = 0.033). (D) Increased Jκ1 usage in some RA patients is associated with a lower frequency of ≥11–amino acid–long Igκ CDR3s in new emigrant B cells. Patients' and healthy donor controls' Jκ1 usage frequency was plotted against that of ≥11–amino acid–long Igκ CDR3s.
Figure 3.
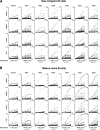
Increased frequency of HEp-2–reactive antibodies in mature naive B cells from RA patients. Data shown are from ELISAs for anti–HEp-2 cell reactivity of recombinant antibodies cloned from (A) new emigrant and (B) mature naive B cells from RA patients. Dotted lines show ED38 positive control (13, 17). The percentage of autoreactive clones for each fraction and their p-values for differences with controls are indicated. *, The controls for new emigrant and mature naive B cells isolated from HD01, HD02, HD03, and HD04 were previously reported (13, 14).
Figure 4.
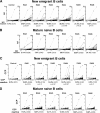
RA B cells express polyreactive antibodies. Antibodies from (A) new emigrant and (B) mature naive B cells from RA patients were tested by ELISAs for reactivity with single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), insulin, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Dotted lines show ED38-positive control (13, 17). Percentages represent frequency of polyreactive antibodies in each fraction. *, The controls for new emigrant and mature naive B cells isolated from HD01, HD02, HD03, and HD04 were previously reported (13, 14).
Figure 5.
RA peripheral B cells contain rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP clones. Antibodies from new emigrant and mature naive B cells from RA patients were tested by ELISAs for reactivity against IgG (A and B) and CCP (C and D). Dotted lines show either ED38-positive control (A and B) or serum anti-CCP IgG-positive control (C and D). Percentages represent frequency of anti-CCP antibodies in each fraction. P-values are in comparison to control new emigrant B cells (13, 14).
Similar articles
- Human B cell tolerance and its failure in rheumatoid arthritis.
Samuels J, Ng YS, Coupillaud C, Paget D, Meffre E. Samuels J, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Dec;1062:116-26. doi: 10.1196/annals.1358.014. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16461794 Review. - B cells in rheumatoid arthritis.
Bugatti S, Codullo V, Caporali R, Montecucco C. Bugatti S, et al. Autoimmun Rev. 2007 Dec;7(2):137-42. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2007.02.017. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Autoimmun Rev. 2007. PMID: 18035324 Review. - Defects in the regulation of B cell apoptosis are required for the production of citrullinated peptide autoantibodies in mice.
López-Hoyos M, Marquina R, Tamayo E, González-Rojas J, Izui S, Merino R, Merino J. López-Hoyos M, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Aug;48(8):2353-61. doi: 10.1002/art.11107. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 12905491 - Serum autoantibodies that bind citrullinated fibrinogen are frequently found in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Hill JA, Al-Bishri J, Gladman DD, Cairns E, Bell DA. Hill JA, et al. J Rheumatol. 2006 Nov;33(11):2115-9. Epub 2006 Aug 15. J Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 16924693 - Isotype distribution of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in undifferentiated arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis reflects an ongoing immune response.
Verpoort KN, Jol-van der Zijde CM, Papendrecht-van der Voort EA, Ioan-Facsinay A, Drijfhout JW, van Tol MJ, Breedveld FC, Huizinga TW, Toes RE. Verpoort KN, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Dec;54(12):3799-808. doi: 10.1002/art.22279. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 17133560
Cited by
- Comparative Analysis on Abnormal Methylome of Differentially Expressed Genes and Disease Pathways in the Immune Cells of RA and SLE.
Fang Q, Li T, Chen P, Wu Y, Wang T, Mo L, Ou J, Nandakumar KS. Fang Q, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 May 17;12:668007. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.668007. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34079550 Free PMC article. - The Role of the Intestinal Microbiome in Multiple Sclerosis-Lessons to Be Learned from Hippocrates.
El-Sayed MM, Mohak S, Gala D, Fabian R, Peterfi Z, Fabian Z. El-Sayed MM, et al. Biology (Basel). 2023 Nov 24;12(12):1463. doi: 10.3390/biology12121463. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132289 Free PMC article. Review. - Current State of Knowledge on Primary Sjögren's Syndrome, an Autoimmune Exocrinopathy.
Parisis D, Chivasso C, Perret J, Soyfoo MS, Delporte C. Parisis D, et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Jul 20;9(7):2299. doi: 10.3390/jcm9072299. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32698400 Free PMC article. Review. - Autoimmune host-microbiota interactions at barrier sites and beyond.
Ruff WE, Kriegel MA. Ruff WE, et al. Trends Mol Med. 2015 Apr;21(4):233-44. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2015.02.006. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Trends Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25771098 Free PMC article. Review. - Single-cell approaches to investigate B cells and antibodies in autoimmune neurological disorders.
Zou A, Ramanathan S, Dale RC, Brilot F. Zou A, et al. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021 Feb;18(2):294-306. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0510-z. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32728203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Feldmann, M., F.M. Brennan, and R.N. Maini. 1996. Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. 85:307–310. - PubMed
- Smolen, J.S., and G. Steiner. 2001. Rheumatoid arthritis is more than cytokines: autoimmunity and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 44:2218–2220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical