Correlations between apolipoprotein E epsilon4 gene dose and brain-imaging measurements of regional hypometabolism - PubMed (original) (raw)
Correlations between apolipoprotein E epsilon4 gene dose and brain-imaging measurements of regional hypometabolism
Eric M Reiman et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005.
Abstract
Patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) have abnormally low positron emission tomography (PET) measurements of the cerebral metabolic rate for glucose (CMRgl) in regions of the precuneus and the posterior cingulate, parietotemporal, and frontal cortex. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) epsilon4 gene dose (i.e., the number of epsilon4 alleles in a person's APOE genotype) is associated with a higher risk of AD and a younger age at dementia onset. We previously found that cognitively normal late-middle-aged APOE epsilon4 carriers have abnormally low CMRgl in the same brain regions as patients with probable Alzheimer's dementia. In a PET study of 160 cognitively normal subjects 47-68 years of age, including 36 epsilon4 homozygotes, 46 heterozygotes, and 78 epsilon4 noncarriers who were individually matched for their gender, age, and educational level, we now find that epsilon4 gene dose is correlated with lower CMRgl in each of these brain regions. This study raises the possibility of using PET as a quantitative presymptomatic endophenotype to help evaluate the individual and aggregate effects of putative genetic and nongenetic modifiers of AD risk.
Figures
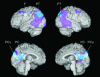
Fig. 1.
Correlations between APOE ε4 gene dose and lower CMRgl (shown in blue, P < 0.005, uncorrected for multiple comparisons) in cognitively normal late-middle-aged persons are projected onto the lateral and medial surfaces of the left and right cerebral hemispheres and shown in relationship to CMRgl reductions (purple and dark blue) found in previously described patients with Alzheimer's dementia (2) (purple and dark blue). Significant correlations were observed bilaterally in the precuneus (PCu), posterior cingulate (PC), left and right parietotemporal (PT), and left frontal (F) regions preferentially affected by AD (dark blue), and in adjacent PC, PCu, PT, and F regions (light blue).
Similar articles
- Declining brain activity in cognitively normal apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 heterozygotes: A foundation for using positron emission tomography to efficiently test treatments to prevent Alzheimer's disease.
Reiman EM, Caselli RJ, Chen K, Alexander GE, Bandy D, Frost J. Reiman EM, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Mar 13;98(6):3334-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.061509598. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11248079 Free PMC article. - Hypometabolism in Alzheimer-affected brain regions in cognitively healthy Latino individuals carrying the apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele.
Langbaum JB, Chen K, Caselli RJ, Lee W, Reschke C, Bandy D, Alexander GE, Burns CM, Kaszniak AW, Reeder SA, Corneveaux JJ, Allen AN, Pruzin J, Huentelman MJ, Fleisher AS, Reiman EM. Langbaum JB, et al. Arch Neurol. 2010 Apr;67(4):462-8. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.30. Arch Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20385913 Free PMC article. - Functional brain abnormalities in young adults at genetic risk for late-onset Alzheimer's dementia.
Reiman EM, Chen K, Alexander GE, Caselli RJ, Bandy D, Osborne D, Saunders AM, Hardy J. Reiman EM, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 6;101(1):284-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2635903100. Epub 2003 Dec 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14688411 Free PMC article. - Linking brain imaging and genomics in the study of Alzheimer's disease and aging.
Reiman EM. Reiman EM. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Feb;1097:94-113. doi: 10.1196/annals.1379.011. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17413015 Review. - Cerebral blood flow and metabolic abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease.
Matsuda H. Matsuda H. Ann Nucl Med. 2001 Apr;15(2):85-92. doi: 10.1007/BF02988596. Ann Nucl Med. 2001. PMID: 11448080 Review.
Cited by
- Apolipoprotein E ε4 Allele-Based Differences in Brain Volumes Are Largely Uniform Across Late Middle Aged and Older Hispanic/Latino- and Non-Hispanic/Latino Whites Without Dementia.
Stickel AM, McKinnon AC, Matijevic S, Grilli MD, Ruiz J, Ryan L. Stickel AM, et al. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Feb 26;13:627322. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.627322. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33716715 Free PMC article. - Correlations between FDG PET glucose uptake-MRI gray matter volume scores and apolipoprotein E ε4 gene dose in cognitively normal adults: a cross-validation study using voxel-based multi-modal partial least squares.
Chen K, Ayutyanont N, Langbaum JB, Fleisher AS, Reschke C, Lee W, Liu X, Alexander GE, Bandy D, Caselli RJ, Reiman EM. Chen K, et al. Neuroimage. 2012 May 1;60(4):2316-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.02.005. Epub 2012 Feb 12. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22348880 Free PMC article. - Precision Nutrition for Alzheimer's Prevention in ApoE4 Carriers.
Norwitz NG, Saif N, Ariza IE, Isaacson RS. Norwitz NG, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Apr 19;13(4):1362. doi: 10.3390/nu13041362. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33921683 Free PMC article. Review. - Apolipoprotein E4 effects in Alzheimer's disease are mediated by synaptotoxic oligomeric amyloid-β.
Koffie RM, Hashimoto T, Tai HC, Kay KR, Serrano-Pozo A, Joyner D, Hou S, Kopeikina KJ, Frosch MP, Lee VM, Holtzman DM, Hyman BT, Spires-Jones TL. Koffie RM, et al. Brain. 2012 Jul;135(Pt 7):2155-68. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws127. Epub 2012 May 26. Brain. 2012. PMID: 22637583 Free PMC article. - Sex modifies APOE ε4 dose effect on brain tau deposition in cognitively impaired individuals.
Yan S, Zheng C, Paranjpe MD, Li Y, Li W, Wang X, Benzinger TLS, Lu J, Zhou Y. Yan S, et al. Brain. 2021 Nov 29;144(10):3201-3211. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab160. Brain. 2021. PMID: 33876815 Free PMC article.
References
- Gottesman, I. I. & Gould, T. D. (2003) Am. J. Psychiatry 160, 636-645. - PubMed
- Alexander, G. E., Chen, K., Pietrini, P., Rapoport, S. I. & Reiman, E. M. (2002) Am. J. Psychiatry 159, 738-745. - PubMed
- Minoshima, S., Frey, K. A., Koeppe, R. A., Foster, N. L. & Kuhl, D. E. (1995) J. Nucl. Med. 36, 1238-1248. - PubMed
- Silverman, D. H., Small, G. W., Chang, C. Y., Lu, C. S., Kung De Aburto, M. A., Chen, W., Czernin, J., Rapoport, S. I., Pietrini, P., Alexander, G. E., et al. (2001) J. Am. Med. Assoc. 286, 2120-2127. - PubMed
- Arnaiz, E., Jelic, V., Almkvist, O., Wahlund, L. O., Winblad, B., Valind, S. & Nordberg, A. (2001) NeuroReport 12, 851-855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous