Genomic DNA amplification from a single bacterium - PubMed (original) (raw)
Genomic DNA amplification from a single bacterium
Arumugham Raghunathan et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jun.
Abstract
Genomic DNA was amplified about 5 billion-fold from single, flow-sorted bacterial cells by the multiple displacement amplification (MDA) reaction, using phi 29 DNA polymerase. A 662-bp segment of the 16S rRNA gene could be accurately sequenced from the amplified DNA. MDA methods enable new strategies for studying non-culturable microorganisms.
Figures
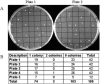
FIG. 1.
Verification of single-cell isolation by flow sorting. (A) Two examples of the five plates (42 squares per plate grid). (B) Colonies growing from each well were counted after an overnight incubation.
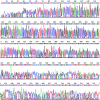
FIG. 2.
DNA sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene by direct primer annealing to DNA amplified from a single cell. Five microliters of DNA amplified from a single cell was sequenced on an Applied Biosystems 3730 capillary DNA analyzer.
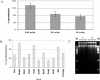
FIG. 3.
Analysis of amplified DNA by quantitative PCR. (A) Each bar is the average of results for four different loci and 10 replicate MDA reactions for approximately 100, 50, and 10 flow-sorted E. coli cells. Error bars are 1 standard deviation. (B) Single cells were sorted into 84 microtiter plate wells, lysed, and subjected to whole-genome amplification by MDA. Average locus representation (n = 84) is plotted on the y axis for 10 individual loci in the E. coli genome. The average of all 10 loci is represented in the last bar. (C) Amplified DNA (negative controls and single-cell samples) resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis. Lanes M, molecular size markers.
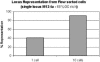
FIG. 4.
Whole-genome amplification from 1 or 10 M. xanthus cells. Results of a quantitative assay for a representative locus are shown.
Similar articles
- Multiple displacement amplification as a pre-polymerase chain reaction (pre-PCR) to process difficult to amplify samples and low copy number sequences from natural environments.
Gonzalez JM, Portillo MC, Saiz-Jimenez C. Gonzalez JM, et al. Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jul;7(7):1024-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00779.x. Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15946299 - Whole-metagenome amplification of a microbial community associated with scleractinian coral by multiple displacement amplification using phi29 polymerase.
Yokouchi H, Fukuoka Y, Mukoyama D, Calugay R, Takeyama H, Matsunaga T. Yokouchi H, et al. Environ Microbiol. 2006 Jul;8(7):1155-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01005.x. Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16817924 - Decontamination of MDA reagents for single cell whole genome amplification.
Woyke T, Sczyrba A, Lee J, Rinke C, Tighe D, Clingenpeel S, Malmstrom R, Stepanauskas R, Cheng JF. Woyke T, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26161. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026161. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22028825 Free PMC article. - Genomic DNA amplification by the multiple displacement amplification (MDA) method.
Lasken RS. Lasken RS. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Apr;37(Pt 2):450-3. doi: 10.1042/BST0370450. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19290880 Review. - Nucleic acid isothermal amplification technologies: a review.
Gill P, Ghaemi A. Gill P, et al. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2008 Mar;27(3):224-43. doi: 10.1080/15257770701845204. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2008. PMID: 18260008 Review.
Cited by
- Ecology of uncultured Prochlorococcus clades revealed through single-cell genomics and biogeographic analysis.
Malmstrom RR, Rodrigue S, Huang KH, Kelly L, Kern SE, Thompson A, Roggensack S, Berube PM, Henn MR, Chisholm SW. Malmstrom RR, et al. ISME J. 2013 Jan;7(1):184-98. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2012.89. Epub 2012 Aug 16. ISME J. 2013. PMID: 22895163 Free PMC article. - Virtual microfluidics for digital quantification and single-cell sequencing.
Xu L, Brito IL, Alm EJ, Blainey PC. Xu L, et al. Nat Methods. 2016 Sep;13(9):759-62. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3955. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Nat Methods. 2016. PMID: 27479330 Free PMC article. - Prevalent genome streamlining and latitudinal divergence of planktonic bacteria in the surface ocean.
Swan BK, Tupper B, Sczyrba A, Lauro FM, Martinez-Garcia M, González JM, Luo H, Wright JJ, Landry ZC, Hanson NW, Thompson BP, Poulton NJ, Schwientek P, Acinas SG, Giovannoni SJ, Moran MA, Hallam SJ, Cavicchioli R, Woyke T, Stepanauskas R. Swan BK, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 9;110(28):11463-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304246110. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23801761 Free PMC article. - The dynamic genetic repertoire of microbial communities.
Wilmes P, Simmons SL, Denef VJ, Banfield JF. Wilmes P, et al. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009 Jan;33(1):109-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00144.x. Epub 2008 Nov 24. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19054116 Free PMC article. Review. - Plasmid DNA contaminant in molecular reagents.
Wally N, Schneider M, Thannesberger J, Kastner MT, Bakonyi T, Indik S, Rattei T, Bedarf J, Hildebrand F, Law J, Jovel J, Steininger C. Wally N, et al. Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 7;9(1):1652. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38733-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30733546 Free PMC article.
References
- Dean, F. B., S. Hosono, L. Fang, X. Wu, A. F. Faruqi, P. Bray-Ward, Z. Sun, Q. Zong, Y. Du, J. Du, M. Driscoll, W. Song, S. F. Kingsmore, M. Egholm, and R. S. Lasken. 2002. Comprehensive human genome amplification using multiple displacement amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:5261-5266. - PMC - PubMed
- Detter, J. C., J. M. Jett, S. M. Lucas, E. Dalin, A. R. Arellano, M. Wang, J. R. Nelson, J. Chapman, Y. Lou, D. Rokhsar, T. L. Hawkins, and P. M. Richardson. 2002. Isothermal strand-displacement amplification applications for high-throughput genomics. Genomics 80:691-698. - PubMed
- Handyside, A. H., M. D. Robinson, R. J. Simpson, M. Omar, Marie-Anne Shaw, J. G. Grudzinskas, and A. Rutherford. 2004. Isothermal whole genome amplification from single and small numbers of cells: a new era for preimplantation genetic diagnosis of inherited disease. Mol. Hum. Reprod. Epub 20 August 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources