Variation in DISC1 affects hippocampal structure and function and increases risk for schizophrenia - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2005 Jun 14;102(24):8627-32.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500515102. Epub 2005 Jun 6.
Richard E Straub, Lukas Pezawas, Michael F Egan, Venkata S Mattay, Ahmad R Hariri, Beth A Verchinski, Andreas Meyer-Lindenberg, Rishi Balkissoon, Bhaskar Kolachana, Terry E Goldberg, Daniel R Weinberger
Affiliations
- PMID: 15939883
- PMCID: PMC1143583
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0500515102
Variation in DISC1 affects hippocampal structure and function and increases risk for schizophrenia
Joseph H Callicott et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005.
Abstract
Disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) is a promising schizophrenia candidate gene expressed predominantly within the hippocampus. We typed 12 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that covered the DISC1 gene. A three-SNP haplotype [hCV219779 (C)-rs821597 (G)-rs821616 (A)] spanning 83 kb of the gene was associated with schizophrenia in a family-based sample (P = 0.002). A common nonconservative SNP (Ser704Cys) (rs821616) within this haplotype was associated with schizophrenia (P = 0.004). Based on primary expression of DISC1 in hippocampus, we hypothesized that allelic variation at Ser704Cys would have a measurable impact on hippocampal structure and function as assayed via specific hippocampus-related intermediate phenotypes. In addition to overtransmission in schizophrenia, the Ser allele was associated with altered hippocampal structure and function in healthy subjects, including reduced hippocampal gray matter volume and altered engagement of the hippocampus during several cognitive tasks assayed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. These convergent data suggest that allelic variation within DISC1, either at Ser704Cys or haplotypes monitored by it, increases the risk for schizophrenia and that the mechanism of this effect involves structural and functional alterations in the hippocampal formation.
Figures
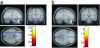
Fig. 1.
“Optimized” VBM and SNP10 (Ser704Cys). DISC1 SNP10 deleteriously effects hippocampal size in healthy subjects (HC) [“optimized” VBM analysis within SPM2, P < 0.05 corrected (see Methods)]. These results were displayed on the standard “MNI305 T1” canonical image within SPM2. (a) HC Ser homozygotes (n = 86) have reduced gray matter volume compared with HC Cys homozygotes (n = 10). (b) HC Ser homozygotes also showed reduced gray matter volume compared with HC Cys carriers (Ser/Cys = 62 + Cys/Cys, n = 10; total n = 72).
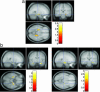
Fig. 2.
BOLD fMRI and SNP10 (Ser704Cys). DISC1 SNP10 affects HF activation during both working memory and declarative memory tasks in healthy subjects [SPM99, P < 0.05 corrected (see Methods)]. (a) For the N-back task, results are displayed on the “MNI305T1” canonical image within SPM99. Healthy Ser homozygotes (n = 18) showed an apparent atypical increase in HF activation during the N-back working memory task relative to Cys carriers (n = 24). (b) During the incidental episodic memory task, (encoding on the left and retrieval on the right). Healthy Ser homozygotes (n = 12) showed decreased HF engagement during both conditions relative to healthy Cys carriers (n = 16).
Similar articles
- Positive association of the Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia-1 gene (DISC1) with schizophrenia in the Chinese Han population.
Qu M, Tang F, Yue W, Ruan Y, Lu T, Liu Z, Zhang H, Han Y, Zhang D, Wang F, Zhang D. Qu M, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2007 Apr 5;144B(3):266-70. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30322. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2007. PMID: 17286247 - Human brain imaging studies of DISC1 in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression: a systematic review.
Duff BJ, Macritchie KAN, Moorhead TWJ, Lawrie SM, Blackwood DHR. Duff BJ, et al. Schizophr Res. 2013 Jun;147(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2013.03.015. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Schizophr Res. 2013. PMID: 23602339 Review. - Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 genotype and positive symptoms in schizophrenia.
DeRosse P, Hodgkinson CA, Lencz T, Burdick KE, Kane JM, Goldman D, Malhotra AK. DeRosse P, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2007 May 15;61(10):1208-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.07.023. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17054920 - Association of the SerCys DISC1 polymorphism with human hippocampal formation gray matter and function during memory encoding.
Di Giorgio A, Blasi G, Sambataro F, Rampino A, Papazacharias A, Gambi F, Romano R, Caforio G, Rizzo M, Latorre V, Popolizio T, Kolachana B, Callicott JH, Nardini M, Weinberger DR, Bertolino A. Di Giorgio A, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Nov;28(10):2129-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06482.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19046394 Free PMC article. - Gene polymorphisms of DISC1 is associated with schizophrenia: Evidence from a meta-analysis.
Wang HY, Liu Y, Yan JW, Hu XL, Zhu DM, Xu XT, Li XS. Wang HY, et al. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 2;81:64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29031911 Review.
Cited by
- Sex-specific deficits in neurite density and white matter integrity are associated with targeted disruption of exon 2 of the Disc1 gene in the rat.
Barnett BR, Torres-Velázquez M, Yi SY, Rowley PA, Sawin EA, Rubinstein CD, Krentz K, Anderson JM, Bakshi VP, Yu JJ. Barnett BR, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Feb 11;9(1):82. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0429-2. Transl Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30745562 Free PMC article. - Neurophysiological modification of CA1 pyramidal neurons in a transgenic mouse expressing a truncated form of disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1.
Booth CA, Brown JT, Randall AD. Booth CA, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Apr;39(7):1074-90. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12549. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24712988 Free PMC article. - Relational memory and hippocampal function in psychotic bipolar disorder.
Avery SN, Williams LE, Woolard AA, Heckers S. Avery SN, et al. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013 Sep 11:10.1007/s00406-013-0442-z. doi: 10.1007/s00406-013-0442-z. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24022592 Free PMC article. - Cortical mapping of genotype-phenotype relationships in schizophrenia.
Bearden CE, van Erp TG, Thompson PM, Toga AW, Cannon TD. Bearden CE, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2007 Jun;28(6):519-32. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20404. Hum Brain Mapp. 2007. PMID: 17437284 Free PMC article. Review. - Are some genetic risk factors common to schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression? Evidence from DISC1, GRIK4 and NRG1.
Blackwood DH, Pickard BJ, Thomson PA, Evans KL, Porteous DJ, Muir WJ. Blackwood DH, et al. Neurotox Res. 2007 Jan;11(1):73-83. doi: 10.1007/BF03033484. Neurotox Res. 2007. PMID: 17449450
References
- Weinberger, D. R. (1999) Biol. Psychiatry 45, 395-402. - PubMed
- Nelson, M. D., Saykin, A. J., Flashman, L. A. & Riordan, H. J. (1998) Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 55, 433-440. - PubMed
- Bertolino, A., Nawroz, S., Mattay, V. S., Barnett, A. S., Duyn, J. H., Moonen, C. T., Frank, J. A., Tedeschi, G. & Weinberger, D. R. (1996) Am. J. Psychiatry 153, 1554-1563. - PubMed
- Freedman, R., Waldo, M., Bickford-Wimer, P. & Nagamoto, H. (1991) Schizophr. Res. 4, 233-243. - PubMed
- Goldberg, T. E., Torrey, E. F., Gold, J. M., Ragland, J. D., Bigelow, L. B. & Weinberger, D. R. (1993) Psychol. Med. 23, 71-85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases