Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Uruguay - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.3201/eid1106.041059.
Antonio Galiana, Walter Pedreira, Martin Mowszowicz, Inés Christophersen, Silvia Machiavello, Liliana Lope, Sara Benaderet, Fernanda Buela, Walter Vincentino, Maria Albini, Olivier Bertaux, Irene Constenla, Homero Bagnulo, Luis Llosa, Teruyo Ito, Keiichi Hiramatsu
Affiliations
- PMID: 15963301
- PMCID: PMC3367603
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1106.041059
Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Uruguay
Xiao Xue Ma et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Jun.
Erratum in
- Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Aug;11(8):1329
Abstract
A novel, methicillin-resistant [corrected] Staphylococcus aureus clone (Uruguay clone) with a non-multidrug-resistant phenotype caused a large outbreak, including 7 deaths, in Montevideo, Uruguay. The clone was distinct from the highly virulent community clone represented by strain MW2, although both clones carried Panton-Valentine leukocidin gene and cna gene.
Figures
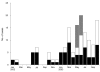
Figure 1
The monthly accumulation of cases of infections due to non–multidrug-resistant MRSA strains from January 2002 to October 2003. Black blocks indicate numbers of strains that were isolated from patients in the public hospital (Hospital Maciel), white indicates strains from a private hospital (Centro de Asistencia del Sindicato Médico del Uruguay), and gray indicates strains from 2 prisons (Libertad and Comcar).
Figure 2
Dendrogram of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) banding pattern of representative Uruguay clone. Pulsotypes of representative Uruguay strains, a CA-MRSA strain isolated in the United States (MW2), 3 CA-MRSA strains isolated in Australia (A803355, A823549, and E802537), and a Japanese strain isolated from an outpatient (81/108) were compared by using a BioNumerics software program (Applied Maths, Sint-Martens-Latem, Belgium). Similarity coefficient was calculated by using Pearson correlation with position tolerance of 5%, and cluster analysis was performed by the unweighted pair-group method. Pulsotypes in parentheses indicate the types previously reported (7). PFGE was performed for 22 h with a CHEF MAPPER (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) with a pulse time of 5 s to 40 s. _Sma_I-restriction patterns of the tested strains and reference strains were compared by using BioNumerics software. Genotypes of representative strains were determined by multilocus sequence typing as described by Enright et al. (9). Sequence type (ST) and clonal complex were assigned using programs in the S. aureus multilocus sequence typing database (
).
Similar articles
- Molecular characterization and susceptibility of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates from hospitals and the community in Vladivostok, Russia.
Baranovich T, Zaraket H, Shabana II, Nevzorova V, Turcutyuicov V, Suzuki H. Baranovich T, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010 Jun;16(6):575-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02891.x. Epub 2009 Aug 4. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010. PMID: 19681959 - Polymorphism of the Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes and its possible link with the fitness of community-associated methicillin-resistant S. aureus.
Dumitrescu O, Tristan A, Meugnier H, Bes M, Gouy M, Etienne J, Lina G, Vandenesch F. Dumitrescu O, et al. J Infect Dis. 2008 Sep 1;198(5):792-4. doi: 10.1086/590914. J Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18694339 No abstract available. - Adult methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in Taiwan: clinical significance of non-multi-resistant antibiogram and Panton-Valentine leukocidin gene.
Wang JL, Wang JT, Chen SY, Hsueh PR, Kung HC, Chen YC, Chang SC. Wang JL, et al. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007 Dec;59(4):365-71. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2007.06.021. Epub 2007 Sep 18. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17878063 - Community-associated Staphylococcus aureus infections in children.
Rojo P, Barrios M, Palacios A, Gomez C, Chaves F. Rojo P, et al. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010 May;8(5):541-54. doi: 10.1586/eri.10.34. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010. PMID: 20455683 Review. - [Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) -- diagnosis].
Linde H, Lehn N. Linde H, et al. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2005 Mar 18;130(11):582-5; quiz 589-92. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-865066. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2005. PMID: 15761787 Review. German. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Characterization of resistance and virulence factors in livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Beshiru A, Igbinosa IH, Akinnibosun O, Ogofure AG, Dunkwu-Okafor A, Uwhuba KE, Igbinosa EO. Beshiru A, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 9;14(1):13235. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63963-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38853154 Free PMC article. - Detection of Vancomycin Resistance among Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains Recovered from Children with Invasive Diseases in a Reference Pediatric Hospital.
Pardo L, Mota MI, Parnizari A, Varela A, Algorta G, Varela G. Pardo L, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Mar 26;13(4):298. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13040298. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38666974 Free PMC article. - Genomic epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bloodstream infections in South America during 2019 supports regional surveillance.
Di Gregorio S, Vielma J, Haim MS, Rago L, Campos J, Kekre M, Abrudan M, Famiglietti Á, Canigia LF, Rubinstein G, Helena von Specht M, Herrera M, Aro C, Galas M, Yarhui NB, Figueiredo A, Lincopan N, Falcon M, Guillén R, Camou T, Varela G, Aanensen DM, Argimón S, Mollerach M, On Behalf Of StaphNET-Sa Consortium. Di Gregorio S, et al. Microb Genom. 2023 May;9(5):mgen001020. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001020. Microb Genom. 2023. PMID: 37227244 Free PMC article. - Prevalence, multiple antibiotic resistance and virulence profile of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in retail poultry meat from Edo, Nigeria.
Igbinosa EO, Beshiru A, Igbinosa IH, Ogofure AG, Ekundayo TC, Okoh AI. Igbinosa EO, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 2;13:1122059. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1122059. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36936767 Free PMC article. - Staphylococcus aureus ST59: Concurrent but Separate Evolution of North American and East Asian Lineages.
McClure JA, Lakhundi S, Niazy A, Dong G, Obasuyi O, Gordon P, Chen S, Conly JM, Zhang K. McClure JA, et al. Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 10;12:631845. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.631845. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33643261 Free PMC article.
References
- Galiana VA. Infecciones por Staphylococcus aureus adquiridos en la comunidad. Arch Pediatr Urug. 2003;74:26–9.
- Annual report: National Committee of Hospital Infection Control. Montevideo, Uruguay: Ministry of Public Health; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical