Recognition of Staphylococcus aureus by the innate immune system - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Recognition of Staphylococcus aureus by the innate immune system
Bénédicte Fournier et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005 Jul.
Abstract
The gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus is a major pathogen responsible for a variety of diseases ranging from minor skin infections to life-threatening conditions such as sepsis. Cell wall-associated and secreted proteins (e.g., protein A, hemolysins, and phenol-soluble modulin) and cell wall components (e.g., peptidoglycan and alanylated lipoteichoic acid) have been shown to be inflammatory, and these staphylococcal components may contribute to sepsis. On the host side, many host factors have been implicated in the innate detection of staphylococcal components. One class of pattern recognition molecules, Toll-like receptor 2, has been shown to function as the transmembrane component involved in the detection of staphylococcal lipoteichoic acid and phenol-soluble modulin and is involved in the synthesis of inflammatory cytokines by monocytes/macrophages in response to these components. Nod2 (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 2) is the intracellular sensor for muramyl dipeptide, the minimal bioactive structure of peptidoglycan, and it may contribute to the innate immune defense against S. aureus. The staphylococcal virulence factor protein A was recently shown to interact directly with tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 in airway epithelium and to reproduce the effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha. Finally, peptidoglycan recognition protein L is an amidase that inactivates the proinflammatory activities of peptidoglycan. However, peptidoglycan recognition protein L probably plays a minor role in the innate immune response to S. aureus. Thus, several innate immunity receptors may be implicated in host defense against S. aureus.
Figures
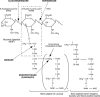
FIG. 1.
Structures of teichoic acid (A) and lipoteichoic acid (B) of S. aureus (data from references and 163). NAG, _N_-acetylglucosamine.
FIG. 2.
Structure of peptidoglycan of S. aureus and several other bacteria. The peptidoglycan of gram-negative bacteria and gram-positive bacilli is indicated on the right. Digestion by different enzymes (glucosaminidase, muramidase, amidase, and endopeptidase) is shown by dotted arrows. MDP structure is indicated in the dotted square. NAG, _N_-acetylglucosamine; NAM, _N_-acetylmuramic acid; m-DAP, _m_-diaminopimelic acid.
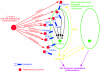
FIG. 3.
Action of staphylococcal components to promote immune responses from immune cells (data from reference 63). FPR, formylated peptide receptor.
FIG. 4.
Domain structure of TLR2 (A) and Nod2 (B). Numbers correspond to amino acid residues. A. TLR2 structure (data from references and 118). ECD, extracellular domain; TMD, transmembrane domain; ICD, intracellular domain; TIR, Toll/IL-1 receptor domain. The regions homologous to LRRs are indicated by square boxes, and LRR-like motifs are indicated by boxes with an asterisk. B. Nod2 structure (data from reference 141). CARD, caspase-activating and recruitment domain; NBS, nucleotide binding site and LRR domain.
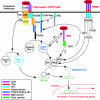
FIG. 5.
Different signaling pathways of TLR2, Nod, and TNFR1 in response to ligand, resulting in activation of NF-κB, the nuclear transcriptional factor responsible for regulation of the immune response genes (data from references , , and 194). RIP1, receptor-interacting protein 1; FADD, Fas-associated death domain protein; TRAF2, TNF receptor-associated factor 2; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase composed of two subunits (p85 and p110).
Similar articles
- Alanylation of teichoic acids protects Staphylococcus aureus against Toll-like receptor 2-dependent host defense in a mouse tissue cage infection model.
Kristian SA, Lauth X, Nizet V, Goetz F, Neumeister B, Peschel A, Landmann R. Kristian SA, et al. J Infect Dis. 2003 Aug 1;188(3):414-23. doi: 10.1086/376533. Epub 2003 Jul 10. J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12870123 - Bacterial evasion of innate host defenses--the Staphylococcus aureus lesson.
Fedtke I, Götz F, Peschel A. Fedtke I, et al. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004 Sep;294(2-3):189-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2004.06.016. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15493829 Review. - Cutting edge: recognition of Gram-positive bacterial cell wall components by the innate immune system occurs via Toll-like receptor 2.
Yoshimura A, Lien E, Ingalls RR, Tuomanen E, Dziarski R, Golenbock D. Yoshimura A, et al. J Immunol. 1999 Jul 1;163(1):1-5. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10384090 - Biochemical characterization of evasion from peptidoglycan recognition by Staphylococcus aureus D-alanylated wall teichoic acid in insect innate immunity.
Kurokawa K, Gong JH, Ryu KH, Zheng L, Chae JH, Kim MS, Lee BL. Kurokawa K, et al. Dev Comp Immunol. 2011 Aug;35(8):835-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2011.03.001. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Dev Comp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21453720 - The anti-inflammatory activities of Staphylococcus aureus.
Chavakis T, Preissner KT, Herrmann M. Chavakis T, et al. Trends Immunol. 2007 Sep;28(9):408-18. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2007.07.002. Epub 2007 Aug 2. Trends Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17681885 Review.
Cited by
- The Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan protects mice against the pathogen and eradicates experimentally induced infection.
Capparelli R, Nocerino N, Medaglia C, Blaiotta G, Bonelli P, Iannelli D. Capparelli R, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028377. Epub 2011 Dec 1. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22145040 Free PMC article. - In Staphylococcus aureus, the Particulate State of the Cell Envelope Is Required for the Efficient Induction of Host Defense Responses.
Kim B, Jiang T, Bae JH, Yun HS, Jang SH, Kim JH, Kim JD, Hur JH, Shibata K, Kurokawa K, Jung Y, Peschel A, Bae T, Lee BL. Kim B, et al. Infect Immun. 2019 Nov 18;87(12):e00674-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00674-19. Print 2019 Dec. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31548327 Free PMC article. - Two-photon intravital imaging of leukocyte migration during inflammation in the respiratory system.
Kim YM, Jeong S, Choe YH, Hyun YM. Kim YM, et al. Acute Crit Care. 2019 May;34(2):101-107. doi: 10.4266/acc.2019.00542. Epub 2019 May 31. Acute Crit Care. 2019. PMID: 31723914 Free PMC article. Review. - Non-spa-typeable clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains are naturally occurring protein A mutants.
Baum C, Haslinger-Löffler B, Westh H, Boye K, Peters G, Neumann C, Kahl BC. Baum C, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Nov;47(11):3624-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00941-09. Epub 2009 Sep 16. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19759222 Free PMC article. - Global transcriptome analysis of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in response to innate immune cells.
Scherr TD, Roux CM, Hanke ML, Angle A, Dunman PM, Kielian T. Scherr TD, et al. Infect Immun. 2013 Dec;81(12):4363-76. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00819-13. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 24042108 Free PMC article.
References
- Abachin, E., C. Poyart, E. Pellegrini, E. Milohanic, F. Fiedler, P. Berche, and P. Trieu-Cuot. 2002. Formation of d-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid is required for adhesion and virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Mol. Microbiol. 43:1-14. - PubMed
- Abraham, E. 2002. Anti-cytokine therapy, p. 719-728. In J. L. Vincent, J. Carlet, and S. M. Opal (ed.), The sepsis text. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
- Aderem, A., and R. J. Ulevitch. 2000. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 406:782-787. - PubMed
- Akira, S., K. Takeda, and T. Kaisho. 2001. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2:675-680. - PubMed
- Alberti, C., C. Brun-Buisson, S. V. Goodman, D. Guidici, J. Granton, R. Moreno, M. Smithies, O. Thomas, A. Artigas, and J. R. Le Gall. 2003. Influence of systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis on outcome of critically ill infected patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 168:77-84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical