A randomized controlled trial of vitamin D3 supplementation in African American women - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
A randomized controlled trial of vitamin D3 supplementation in African American women
John F Aloia et al. Arch Intern Med. 2005.
Abstract
Background: We conducted a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial to test the hypothesis that vitamin D(3) supplementation would prevent bone loss in calcium-replete, African American postmenopausal women.
Methods: Two hundred eight healthy black postmenopausal women, 50 to 75 years of age, were assigned to receive either placebo or 20 microg/d (800 IU) of vitamin D(3). Calcium supplements were provided to ensure a total calcium intake of 1200 to 1500 mg/d. After 2 years, the vitamin D(3) dose was increased to 50 microg/d (2000 IU) in the active group, and the study continued for an additional year. Bone mineral density (BMD) was measured every 6 months. Markers of bone turnover, vitamin D metabolites, and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels were measured in serum.
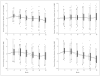
Results: There were no significant differences in BMD between the active and control groups throughout the study. There was also no relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels attained and rates of bone loss. There was an increase in BMD of the total body, hip, and radius at 1 year in both groups. Over the 3 years, BMD declined at these sites by 0.26% to 0.55% per year. The BMD of the lumbar spine increased slightly in the placebo and active groups. There were no persistent changes in serum PTH levels or the markers of bone turnover, although there was a transient decline in PTH in both groups at 3 months. No significant adverse events were attributed to vitamin D supplementation.
Conclusions: There was no observed effect of vitamin D(3) supplementation on bone loss or bone turnover markers in calcium-replete, postmenopausal African American women. Further studies are needed to determine if these findings are applicable to women of other ethnic groups.
Figures
Figure 1
Flowchart of subject progress through trial. HT indicates hormone therapy; AEs, adverse events.
Figure 2
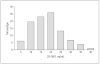
Distribution of baseline 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD) among African American postmenopausal women (n = 208). To convert 25-OHD to nanomoles per liter, multiply by 2.496.
Figure 3
Box and whisker plots of the percent change from baseline for 4 body sites. There were no significant differences between groups. BMD indicates bone mineral density.
Similar articles
- Supplementation with oral vitamin D3 and calcium during winter prevents seasonal bone loss: a randomized controlled open-label prospective trial.
Meier C, Woitge HW, Witte K, Lemmer B, Seibel MJ. Meier C, et al. J Bone Miner Res. 2004 Aug;19(8):1221-30. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.040511. Epub 2004 May 24. J Bone Miner Res. 2004. PMID: 15231008 Clinical Trial. - Hip bone loss is attenuated with 1000 IU but not 400 IU daily vitamin D3: a 1-year double-blind RCT in postmenopausal women.
Macdonald HM, Wood AD, Aucott LS, Black AJ, Fraser WD, Mavroeidi A, Reid DM, Secombes KR, Simpson WG, Thies F. Macdonald HM, et al. J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Oct;28(10):2202-13. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1959. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 23585346 Clinical Trial. - Effect of isolated vitamin D supplementation on bone turnover markers in younger postmenopausal women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Nahas-Neto J, Cangussu LM, Orsatti CL, Bueloni-Dias FN, Poloni PF, Schmitt EB, Nahas EAP. Nahas-Neto J, et al. Osteoporos Int. 2018 May;29(5):1125-1133. doi: 10.1007/s00198-018-4395-y. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Osteoporos Int. 2018. PMID: 29450585 Clinical Trial. - Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.
Cranney A, Horsley T, O'Donnell S, Weiler H, Puil L, Ooi D, Atkinson S, Ward L, Moher D, Hanley D, Fang M, Yazdi F, Garritty C, Sampson M, Barrowman N, Tsertsvadze A, Mamaladze V. Cranney A, et al. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article. Review. - Existing and potentially novel functional markers of vitamin D status: a systematic review.
Seamans KM, Cashman KD. Seamans KM, et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 Jun;89(6):1997S-2008S. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.27230D. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19403634 Review.
Cited by
- Therapeutic Effects of Vitamin D on Vaginal, Sexual, and Urological Functions in Postmenopausal Women.
Hassanein MM, Huri HZ, Abduelkarem AR, Baig K. Hassanein MM, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Aug 30;15(17):3804. doi: 10.3390/nu15173804. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37686835 Free PMC article. Review. - Scientific opinion on the tolerable upper intake level for vitamin D, including the derivation of a conversion factor for calcidiol monohydrate.
EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and FoodAllergens (NDA); Turck D, Bohn T, Castenmiller J, de Henauw S, Hirsch-Ernst KI, Knutsen HK, Maciuk A, Mangelsdorf I, McArdle HJ, Pentieva K, Siani A, Thies F, Tsabouri S, Vinceti M, Lanham-New S, Passeri G, Craciun I, Fabiani L, De Sousa RF, Martino L, Martínez SV, Naska A. EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and FoodAllergens (NDA), et al. EFSA J. 2023 Aug 8;21(8):e08145. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2023.8145. eCollection 2023 Aug. EFSA J. 2023. PMID: 37560437 Free PMC article. - The effects of vitamin D on all-cause mortality in different diseases: an evidence-map and umbrella review of 116 randomized controlled trials.
Cao M, He C, Gong M, Wu S, He J. Cao M, et al. Front Nutr. 2023 Jun 22;10:1132528. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1132528. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37426183 Free PMC article. - Vitamin D Supplementation and Its Impact on Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 80 Randomized Clinical Trials.
Ruiz-García A, Pallarés-Carratalá V, Turégano-Yedro M, Torres F, Sapena V, Martin-Gorgojo A, Martin-Moreno JM. Ruiz-García A, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Apr 7;15(8):1810. doi: 10.3390/nu15081810. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37111028 Free PMC article.
References
- Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. NIH Consens Statement. 2000;17:1–45. - PubMed
- Heaney RP. Lessons for nutritional science from vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;69:825–826. - PubMed
- Burckhardt P. Calcium and vitamin D in osteoporosis: supplementation or treatment? Calcif Tissue Int. 2002;70:74–77. - PubMed
- Chapuy MC, Preziosi P, Maamer M, et al. Prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in an adult normal population. Osteoporos Int. 1997;7:439–443. - PubMed
- Guillemant J, Le HT, Maria A, Allemandou A, Peres G, Guillemant S. Wintertime vitamin D deficiency in male adolescents: effect on parathyroid function and response to vitamin D3 supplements. Osteoporos Int. 2001;12:875–879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical