Efficacy of cefepime and imipenem in experimental murine pneumonia caused by porin-deficient Klebsiella pneumoniae producing CMY-2 beta-Lactamase - PubMed (original) (raw)
Efficacy of cefepime and imipenem in experimental murine pneumonia caused by porin-deficient Klebsiella pneumoniae producing CMY-2 beta-Lactamase
Cristina Pichardo et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Aug.
Abstract
Previous studies have shown decreased in vitro activity of zwitterionic cephalosporins and carbapenems against porin-deficient Klebsiella pneumoniae expressing a plasmid-mediated AmpC-type beta-lactamase (PACBL). The in vitro and in vivo activities of cefepime and imipenem were evaluated against the porin-deficient strain K. pneumoniae C2 and its CMY-2-producing derivative [K. pneumoniae C2(pMG248)]. The MICs (in micrograms/milliliter) of cefepime and imipenem against K. pneumoniae C2 were 0.125 and 0.25, respectively, while the corresponding values against K. pneumoniae C2(pMG248) were 8 and 16. Cefepime showed a greater inoculum effect than imipenem against both strains. Imipenem showed a significant postantibiotic effect (>2 h) against K. pneumoniae C2(pMG248) at 1x, 2x, 4x, 6x, and 8x MIC. The maximum concentrations of drug in serum of cefepime and imipenem in a pneumonia model using mice were 124.1 and 16.9 mug/ml, respectively. DeltaT/MIC for K. pneumoniae C2 and C2(pMG248) were 1.29 h and 0.34 h for imipenem and 2.96 h and 1.27 h for cefepime. Both imipenem (30 mg/kg of body weight every 3 h) and cefepime (60 mg/kg every 4 h), administered for 72 h, increased the survival rate (86.6% and 100%) compared with untreated control animals (26.6%, P < 0.003) infected with K. pneumoniae C2. For the CMY-2-producing strain, imipenem, but not cefepime, increased the survival rate compared to the controls (86.6% and 40% versus 40%, P < 0.01). Bacterial concentration of the lungs was significantly decreased by both antimicrobials. In conclusion, imipenem was more active in terms of survival than cefepime for the treatment of murine pneumonia caused by a porin-deficient K. pneumoniae expressing PACBL CMY-2.
Figures
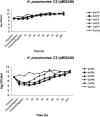
FIG. 1.
PAE of imipenem and cefepime against K. pneumoniae C2(pMG248) after 1.5 h of exposure to 1×, 2×, 4×, 6×, and 8× MIC of cefepime (FEP) and imipenem (IPM).
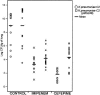
FIG. 2.
Effect of antibiotic therapy on the clearance of K. pneumoniae from mice lungs.
Similar articles
- Effect of porins and plasmid-mediated AmpC beta-lactamases on the efficacy of beta-lactams in rat pneumonia caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Padilla E, Alonso D, Doménech-Sánchez A, Gomez C, Pérez JL, Albertí S, Borrell N. Padilla E, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Jun;50(6):2258-60. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01513-05. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16723600 Free PMC article. - Activity of cefepime and carbapenems in experimental pneumonia caused by porin-deficient Klebsiella pneumoniae producing FOX-5 beta-lactamase.
Pichardo C, del Carmen Conejo M, Bernabéu-Wittel M, Pascual A, Jiménez-Mejías ME, de Cueto M, Pachón-Ibáñez ME, García I, Pachón J, Martínez-Martínez L. Pichardo C, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2005 Jan;11(1):31-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.01018.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2005. PMID: 15649301 - Cefepime and the inoculum effect in tests with Klebsiella pneumoniae producing plasmid-mediated AmpC-type beta-lactamase.
Kang CI, Pai H, Kim SH, Kim HB, Kim EC, Oh MD, Choe KW. Kang CI, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004 Dec;54(6):1130-3. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkh462. Epub 2004 Oct 14. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15486080 - Diagnosis and treatment of extended-spectrum and AmpC beta-lactamase-producing organisms.
Yang K, Guglielmo BJ. Yang K, et al. Ann Pharmacother. 2007 Sep;41(9):1427-35. doi: 10.1345/aph.1K213. Epub 2007 Jul 31. Ann Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17666573 Free PMC article. Review. - Cefepime and its role in pediatric infections.
Shahid SK. Shahid SK. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2008 Jun;3(2):145-8. doi: 10.2174/157489108784746614. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2008. PMID: 18673128 Review.
Cited by
- Effect of porins and plasmid-mediated AmpC beta-lactamases on the efficacy of beta-lactams in rat pneumonia caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Padilla E, Alonso D, Doménech-Sánchez A, Gomez C, Pérez JL, Albertí S, Borrell N. Padilla E, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Jun;50(6):2258-60. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01513-05. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16723600 Free PMC article. - Sensitive screening tests for suspected class A carbapenemase production in species of Enterobacteriaceae.
Pasteran F, Mendez T, Guerriero L, Rapoport M, Corso A. Pasteran F, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Jun;47(6):1631-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00130-09. Epub 2009 Apr 22. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19386850 Free PMC article. - Inoculum effect of β-lactam antibiotics.
Lenhard JR, Bulman ZP. Lenhard JR, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019 Oct 1;74(10):2825-2843. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkz226. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31170287 Free PMC article. Review. - AmpC beta-lactamases.
Jacoby GA. Jacoby GA. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009 Jan;22(1):161-82, Table of Contents. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00036-08. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19136439 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bauernfeind, A., Y. Chong, and S. Schweighart. 1989. Extended broad spectrum β-lactamase in Klebsiella pneumoniae including resistance to cephamycins. Infection 17:316-321. - PubMed
- Bradford, P. A., C. Urban, N. Mariano, S. J. Projan, J. J. Rahal, and K. Bush. 1997. Imipenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae is associated with the combination of ACT-1, a plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamase, and the loss of an outer membrane protein. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:563-569. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous