Use of a novel panel of nine short tandem repeats for exact and high-resolution fingerprinting of Aspergillus fumigatus isolates - PubMed (original) (raw)
Use of a novel panel of nine short tandem repeats for exact and high-resolution fingerprinting of Aspergillus fumigatus isolates
Hanneke A de Valk et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Aug.
Abstract
Here we describe a new panel of short tandem repeats (STRs) for a novel exact typing assay that can be used to discriminate between Aspergillus fumigatus isolates. A total of nine STR markers were selected from available genomic A. fumigatus sequences and were divided into three multicolor multiplex PCRs. Each multiplex reaction amplified three di-, tri-, or tetranucleotide repeats, respectively. All nine STR markers were used to analyze 100 presumably unrelated A. fumigatus isolates. For each marker, between 11 and 37 alleles were found in this population. One isolate proved to be a mixture of at least two different isolates. With the remaining 99 isolates, 96 different fingerprinting profiles were obtained. The Simpson's diversity index for the individual markers ranged from 0.77 to 0.97. The diversity index for the multiplex combination of di-, tri-, and tetranucleotide repeats ranged from 0.9784 to 0.9968. The combination of all nine markers yielded a Simpson's diversity index of 0.9994, indicative of the high discriminatory power of these new loci. In theory, this panel of markers is able to discriminate between no less than 27 x 10(9) different genotypes. The multicolor multiplex approach allows large numbers of markers to be tested in a short period of time. The exact nature of the assay combines high reproducibility with the easy exchange of results and makes it a very suitable tool for large-scale epidemiological studies.
Figures
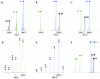
FIG.1.
Examples of amplification results. The principle peak used for analysis is indicated with a colored dot. Blue traces represent the FAM label, black traces represent the HEX label, and green traces represent the TET label. Typical results obtained with the dinucleotide repeats (A), trinucleotide repeats (B), and tetranucleotide repeats (C) are shown. (D) Typical example of amplification artifacts obtained with a dinucleotide repeat. The principle peak is indicated with an “n.” A second peak exactly 1 bp shorter is the result of incomplete A addition (hence, n − a). A stutter peak one repeat shorter is indicated with n − 1. Other artifact peaks are indicated accordingly. (E) Multiple stutter peaks with a trinucleotide repeat do not influence the ability to identify the principle peak in a sample. (F) A typical result obtained with a mixed sample.
FIG. 2.
Determination of repeat numbers by DNA sequencing. Examples are shown for a dinucleotide repeat (A), trinucleotide repeat (B), and tetranucleotide repeat (C).
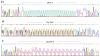
FIG. 3.
Dendrogram based on profiles of nine STR_Af_ markers from 99 presumably unrelated A. fumigatus isolates. The dendrogram was created by using BioNumerics, version 3.5, software (Applied Maths) and the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic averages method with the multistate categorical similarity coefficient. See the text for further details.
Similar articles
- Microsatellite Stability in STR Analysis Aspergillus fumigatus Depends on Number of Repeat Units.
de Groot T, Meis JF. de Groot T, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Mar 29;9:82. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00082. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30984630 Free PMC article. - Utility of a microsatellite assay for identifying clonally related outbreak isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus.
Balajee SA, de Valk HA, Lasker BA, Meis JF, Klaassen CH. Balajee SA, et al. J Microbiol Methods. 2008 Jun;73(3):252-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2008.02.011. Epub 2008 Feb 23. J Microbiol Methods. 2008. PMID: 18375005 - Comparison of two highly discriminatory molecular fingerprinting assays for analysis of multiple Aspergillus fumigatus isolates from patients with invasive aspergillosis.
de Valk HA, Meis JF, de Pauw BE, Donnelly PJ, Klaassen CH. de Valk HA, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2007 May;45(5):1415-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02423-06. Epub 2007 Mar 21. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17376887 Free PMC article. - MLST versus microsatellites for typing Aspergillus fumigatus isolates.
Klaassen CH. Klaassen CH. Med Mycol. 2009;47 Suppl 1:S27-33. doi: 10.1080/13693780802382244. Epub 2009 Feb 28. Med Mycol. 2009. PMID: 19255901 Review. - [The unusual typing of short tandem repeats].
Lu DJ, Chen YC, Lu HL. Lu DJ, et al. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2002 May;18(2):118-20, 123. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 12596600 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
- Pharmacodynamics of isavuconazole in an Aspergillus fumigatus mouse infection model.
Seyedmousavi S, Brüggemann RJ, Meis JF, Melchers WJ, Verweij PE, Mouton JW. Seyedmousavi S, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 May;59(5):2855-66. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04907-14. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25753636 Free PMC article. - Five-Year Survey (2014 to 2018) of Azole Resistance in Environmental Aspergillus fumigatus Isolates from China.
Cao D, Wu R, Dong S, Wang F, Ju C, Yu S, Xu S, Fang H, Yu Y. Cao D, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Sep 21;64(10):e00904-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00904-20. Print 2020 Sep 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32718960 Free PMC article. - Optimization and Validation of Candida auris Short Tandem Repeat Analysis.
de Groot T, Spruijtenburg B, Parnell LA, Chow NA, Meis JF. de Groot T, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0264522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02645-22. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36190407 Free PMC article. - A New Aspergillus fumigatus Typing Method Based on Hypervariable Tandem Repeats Located within Exons of Surface Protein Coding Genes (TRESP).
Garcia-Rubio R, Gil H, Monteiro MC, Pelaez T, Mellado E. Garcia-Rubio R, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Oct 4;11(10):e0163869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163869. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27701437 Free PMC article. - The Transcriptome Response to Azole Compounds in Aspergillus fumigatus Shows Differential Gene Expression across Pathways Essential for Azole Resistance and Cell Survival.
Hokken MWJ, Coolen JPM, Steenbreker H, Zoll J, Baltussen TJH, Verweij PE, Melchers WJG. Hokken MWJ, et al. J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jul 30;9(8):807. doi: 10.3390/jof9080807. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37623579 Free PMC article.
References
- Bart-Delabesse, E., J. Sarfati, J.-P. Debeaupuis, W. van Leeuwen, A. van Belkum, S. Bretagne, and J.-P. Latge. 2001. Comparison of restriction fragment length polymorphism, microsatellite length polymorphism, and random amplification of polymorphic DNA analyses for fingerprinting Aspergillus fumigatus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:2683-2686. - PMC - PubMed
- Bertout, S., F. Renaud, R. Barton, F. Symoens, J. Burnod, M.-A. Piens, B. Lebeau, M.-A. Viviani, F. Chapuis, J.-M. Bastide, R. Grillot, M. Mallie, and The European Research Group on Biotype and Genotype of Aspergillus. 2001. Genetic polymorphism of Aspergillus fumigatus in clinical samples from patients with invasive aspergillosis: investigation using multiple typing methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:1731-1737. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources