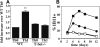A crucial role for T-bet in selectin ligand expression in T helper 1 (Th1) cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
A crucial role for T-bet in selectin ligand expression in T helper 1 (Th1) cells
Greg H Underhill et al. Blood. 2005.
Abstract
Proinflammatory T helper 1 (Th1) cells express high levels of carbohydrate ligands for the endothelial selectins, but the molecular basis for this phenotype is incompletely understood. We document here a significant role in selectin ligand formation for the recently described Th1 transcription factor T-bet. Th1 cells generated from T-bet-/- mice showed significantly lower levels of ligands for both E-selectin and P-selectin, compared with wild-type (WT) Th1 cells. Enforced expression of T-bet in WT Th0 cells only modestly up-regulated P-selectin ligands and had no effect on E-selectin ligands. To define a mechanism for the defects observed in T-bet-/- mice, we examined expression of glycosyltransferases involved in selectin ligand biosynthesis. T-bet-/- Th1 cells expressed significantly lower levels of core 2 beta1,6 N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I (C2GlcNAcT-I), but no differences in levels of alpha 2,3-sialyltransferase IV (ST3Gal-IV). Further, we show that T-bet is responsible for the signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (Stat4)-independent increase in Th1 cells of fucosyltransferase VII (FucT-VII). We also identify ST3Gal-VI, which is thought to play an important role in E- and P-selectin ligand formation, as an interleukin 12 (IL-12)-regulated, T-bet-dependent gene. These data show that T-bet controls selectin ligand formation in Th1 cells via control of expression of multiple key enzymes in response to IL-12 signaling and establishes an independent transcriptional pathway for control of Th1 cell traffic.
Figures
Figure 1.
Defective induction of selectin ligands in T-bet-/- Th1 cells. Purified CD4+ T cells were cultured under either Th1 (IL-2 plus IL-12 plus anti–IL-4) or Th0 (IL-2 only) conditions and analyzed on day 8 for rolling on (A) E-selectin and (B) P-selectin. One representative of at least 2 experiments. **Significantly different (P < .05) from all other groups; *significantly different (P < .05).
Figure 2.
Kinetics of expression of selectin ligands is not altered by the absence of T-bet. Cells from T-cell activation cultures as in Figure 1 were also analyzed over time by FACS with selectin chimeras to determine the fraction which expressed ligands for (A) E-selectin or (B) P-selectin. Filled symbols, Th1; open symbols, Th0; squares, WT; circles, T-bet-/-. One of at least 5 experiments.
Figure 3.
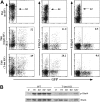
Direct and indirect effects of T-bet on selectin ligand induction. (A) Enforced overexpression of T-bet in WT Th0 cells fails to induce maximal levels of selectin ligands. WT CD4+ T cells were activated under Th0 conditions, infected with retroviruses (RVs) expressing no cDNA (empty) or T-bet, and cultured under Th0 conditions. Cells were then stained with P- or E-selectin chimeras or 1B11. Uninfected WT Th1 cells were included side-by-side for comparison. Numbers given for retrovirally transduced cells are the percentage of the GFP+ cells which stain for either 1B11 (first column), P-selectin ligands (second column), or E-selectin ligands (third column). One representative of 3 similar experiments. (B) T-bet deficiency inhibits functional expression of the IL12R. WT and T-bet-/- CD4 cells were cultured under Th1 conditions for 6 days, washed, and restimulated with IL-12. At the indicated time points, cells were harvested, lysed, and subjected to Western blotting for tyrosine phosphorylated, and total Stat4. Results are representative of 2 experiments. KO indicates knock-out.
Figure 4.
T-bet is required for up-regulation of C2GlcNAcT-I and FucT-VII in Th1 cells. (A) qRT-PCR of FucT-VII mRNA levels of WT and T-bet-/- Th0 and Th1 cells. Levels are normalized to pgk mRNA levels and expressed as fold induction over WT Th0 cells. Error bars indicate SD. (B) Expression of the C2GlcNAcT-I reporter epitope defined by the 1B11 mAb on WT and T-bet-/- Th0 and Th1 cells over time. Results are representative of at least 3 experiments. Filled symbols, Th1; open symbols, Th0; squares, WT; circles, T-bet-/-, as in Figure 2. **Significantly different from all other groups.
Figure 5.
Role of ST3Gal-IV in selectin ligand formation in Th1 cells. Rolling of WT and ST3Gal-IV-/- Th0 and Th1 cells on (A) E-selectin and (B) P-selectin reveals significantly decreased rolling of ST3Gal-IV-/- Th1 cells, compared with WT Th1 cells. (C) qRT-PCR shows no significant difference in ST3Gal-IV-/- mRNA levels between WT or T-bet-/- Th0 or Th1 cells. (D) qRT-PCR also shows no significant difference in ST3Gal-IV mRNA levels between WT and Stat4-/- Th0 or Th1 cells. Data are depicted as in Figure 4A. Results are representative of at least 3 experiments. **Significantly different from all other groups.
Figure 6.
Possible role of ST3Gal-VI in selectin ligand formation. WT and ST3Gal-IV-/- Th1 cells were either untreated or treated with neuraminidase, and rolling on (A) E-selectin or (B) P-selectin was measured. Neuraminidase blocked rolling of cells of both genotypes on both selectins. (A-B) **Significantly different from the corresponding group without neuraminidase treatment. (C) qRT-PCR reveals significant induction of ST3Gal-VI mRNA by IL-12 in WT cells but virtually no effect of IL-12 in T-bet-/- cells. (D) A similar effect on ST3Gal-VI induction is observed with CD4 cells from Stat4-/- mice, although the magnitude of the effect of Stat4 deficiency is smaller than that for T-bet (note different scales). (C-D) **Significantly different from all other groups.
Figure 7.
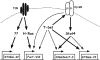
Pathways controlling expression of glycosyltransferases in Th1 cells. Naive T cells express little or no FucT-VII, C2GlcNAcT-I, or ST3Gal-VI. T-cell activation through the TCR leads to activation of H-Ras and induction of FucT-VII, as well as induction or maintenance of constitutive levels of ST3Gal-IV. Whether ST3Gal-IV expression requires H-Ras is unknown. In addition, T-cell activation is associated with induction of the IL12R, particularly the IL12Rβ2 chain, and the IL12R is essential for activation of Stat4, which plays a major role in induction of C2GlcNAcT-I and a minor role in induction of ST3Gal-VI. T-bet plays a role through induction/maintenance of the IL12Rβ2, allowing up-regulation of C2GlcNAcT-I by Stat4; through direct up-regulation of C2GlcNAcT-I and ST3Gal-VI; and through up-regulation of FucT-VII by an as yet undetermined mechanism. Bold lines represent strong, presumably or known to be direct, effects; thin lines represent weak effects.
Similar articles
- Cutting edge: differential requirements for Stat4 in expression of glycosyltransferases responsible for selectin ligand formation in Th1 cells.
White SJ, Underhill GH, Kaplan MH, Kansas GS. White SJ, et al. J Immunol. 2001 Jul 15;167(2):628-31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.2.628. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11441063 - Core 2 ß1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-I, crucial for P-selectin ligand expression is controlled by a distal enhancer regulated by STAT4 and T-bet in CD4+ T helper cells 1.
Mardahl M, Schröter MF, Engelbert D, Pink M, Sperandio M, Hamann A, Syrbe U. Mardahl M, et al. Mol Immunol. 2016 Sep;77:132-40. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Aug 6. Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27505708 - Differential requirements for the O-linked branching enzyme core 2 beta1-6-N-glucosaminyltransferase in biosynthesis of ligands for E-selectin and P-selectin.
Snapp KR, Heitzig CE, Ellies LG, Marth JD, Kansas GS. Snapp KR, et al. Blood. 2001 Jun 15;97(12):3806-11. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.12.3806. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11389020 - Selectins and glycosyltransferases in leukocyte rolling in vivo.
Sperandio M. Sperandio M. FEBS J. 2006 Oct;273(19):4377-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05437.x. Epub 2006 Sep 5. FEBS J. 2006. PMID: 16956372 Review. - [Control of T cell fate by galectins and their ligand-through regulation of the expression of glycosyltransferases].
Amano M. Amano M. Seikagaku. 2004 Sep;76(9):1203-6. Seikagaku. 2004. PMID: 15524108 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
- More than just a T-box: the role of T-bet as a possible biomarker and therapeutic target in autoimmune diseases.
Ji N, Sosa RA, Forsthuber TG. Ji N, et al. Immunotherapy. 2011 Mar;3(3):435-41. doi: 10.2217/imt.10.111. Immunotherapy. 2011. PMID: 21395384 Free PMC article. Review. - T helper 1 effector memory CD4+ T cells protect the skin from poxvirus infection.
Harbour JC, Abdelbary M, Schell JB, Fancher SP, McLean JJ, Nappi TJ, Liu S, Nice TJ, Xia Z, Früh K, Nolz JC. Harbour JC, et al. Cell Rep. 2023 May 30;42(5):112407. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112407. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37083328 Free PMC article. - Glycosyltransferase-programmed stereosubstitution (GPS) to create HCELL: engineering a roadmap for cell migration.
Sackstein R. Sackstein R. Immunol Rev. 2009 Jul;230(1):51-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00792.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19594629 Free PMC article. Review. - Skin-homing receptors on effector leukocytes are differentially sensitive to glyco-metabolic antagonism in allergic contact dermatitis.
Gainers ME, Descheny L, Barthel SR, Liu L, Wurbel MA, Dimitroff CJ. Gainers ME, et al. J Immunol. 2007 Dec 15;179(12):8509-18. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.12.8509. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18056398 Free PMC article. - T-bet regulates Th1 responses through essential effects on GATA-3 function rather than on IFNG gene acetylation and transcription.
Usui T, Preiss JC, Kanno Y, Yao ZJ, Bream JH, O'Shea JJ, Strober W. Usui T, et al. J Exp Med. 2006 Mar 20;203(3):755-66. doi: 10.1084/jem.20052165. Epub 2006 Mar 6. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 16520391 Free PMC article.
References
- Ley K, Kansas GS. Selectins in T cell recruitment to non-lymphoid tissues and sites of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4: 325-335. - PubMed
- Austrup F, Vestweber D, Borges E, et al. P- and E-selectin mediate recruitment of T helper 1 but not T helper 2 cells into inflamed tissues. Nature. 1997;385: 81-83. - PubMed
- van Wely CA, Blanchard AD, Britten CJ. Differential expression of alpha3 fucosyltransferases in Th1 and Th2 cells correlates with their ability to bind P-selectin. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 1998;18: 307-311. - PubMed
- Knibbs RN, Craig RA, Maly P, et al. α1,3-fucosyltransferase VII dependent synthesis of P- and E-selectin ligands on cultured T lymphoblasts. J Immunol. 1998;161: 6305-6315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous