Animal virus replication and RNAi-mediated antiviral silencing in Caenorhabditis elegans - PubMed (original) (raw)
Animal virus replication and RNAi-mediated antiviral silencing in Caenorhabditis elegans
R Lu et al. Nature. 2005.
Abstract
The worm Caenorhabditis elegans is a model system for studying many aspects of biology, including host responses to bacterial pathogens, but it is not known to support replication of any virus. Plants and insects encode multiple Dicer enzymes that recognize distinct precursors of small RNAs and may act cooperatively. However, it is not known whether the single Dicer of worms and mammals is able to initiate the small RNA-guided RNA interference (RNAi) antiviral immunity as occurs in plants and insects. Here we show complete replication of the Flock house virus (FHV) bipartite, plus-strand RNA genome in C. elegans. We show that FHV replication in C. elegans triggers potent antiviral silencing that requires RDE-1, an Argonaute protein essential for RNAi mediated by small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) but not by microRNAs. This immunity system is capable of rapid virus clearance in the absence of FHV B2 protein, which acts as a broad-spectrum RNAi inhibitor upstream of rde-1 by targeting the siRNA precursor. This work establishes a C. elegans model for genetic studies of animal virus-host interactions and indicates that mammals might use a siRNA pathway as an antiviral response.
Figures
Fig. 1
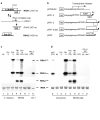
Replication and silencing of FHV in C. elegans. a, Structure, replication and expression of FHV genome. b, Structure of FHV transgenes. HIP- heat inducible promoter. The junction region between HIP (lower case) and FHV cDNA (upper case) is shown. Transcriptional initiation sites from HIP were indicated. Rz — a self-cleaving ribozyme used to reduce non-viral extensions at the 3'-termini of heat-induced transcripts. Northern blot detection of FHV RNA accumulation in C. elegans (c) and fruit fly S2 cells (d). Four μg total RNA was loaded per lane in both c and d, except for lane 8 of c.
Fig. 2
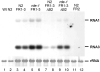
FHV RNAi suppressor is active in rde-1 worms. Total RNA was extracted from worms of either wild type or rde-1 genotype carrying an integrated FR1-3 or FR1-3ΔB2 transgene two days after transcriptional induction. Northern blot hybridizations were carried out as in upper panels of Fig. 1c/d.
Fig. 3
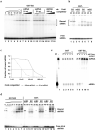
FHV B2 is a dsRNA-binding protein and inhibits siRNA production in vitro. a — d. GST-tagged B2 protein (GST-B2) binds both 21-nt siRNA duplex (a and d) and 44-nt dsRNA (d) in vitro. Volumes of the top siRNA/B2 band in lanes 7-10 and 15-18 were quantified by phosphoimager and plotted against the concentrations of the cold competitor RNAs (c). Note the presence of non-specific signals in lanes 1, 8, 13 and 16 of d. e. B2 inhibits in vitro processing of a labeled long dsRNA by the Dicer extracts from fruit fly S2 cells. Concentration gradients of GST or GST-B2 used were 50, 200, 800, 3,200 or 10,000 nM. A labeled 21-nt siRNA was used as a marker (M) at left.
Similar articles
- A low-abundance class of Dicer-dependent siRNAs produced from a variety of features in C. elegans.
Knittel TL, Montgomery BE, Tate AJ, Deihl EW, Nawrocki AS, Hoerndli FJ, Montgomery TA. Knittel TL, et al. Genome Res. 2024 Dec 23;34(12):2203-2216. doi: 10.1101/gr.279083.124. Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 39622635 - RNA interference is an antiviral defence mechanism in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Wilkins C, Dishongh R, Moore SC, Whitt MA, Chow M, Machaca K. Wilkins C, et al. Nature. 2005 Aug 18;436(7053):1044-7. doi: 10.1038/nature03957. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16107852 - Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.
Salisbury L, Baraitser L. Salisbury L, et al. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Caenorhabditis elegans inositol hexaphosphate pathways couple to RNA interference and pathogen defense.
Xu W, Sun Y, Breen P, Ruvkun G, Mao K. Xu W, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Dec 3;121(49):e2416982121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2416982121. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39602251 Free PMC article. - Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.
Bryant A, Hiu S, Kunonga PT, Gajjar K, Craig D, Vale L, Winter-Roach BA, Elattar A, Naik R. Bryant A, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Key Mechanistic Principles and Considerations Concerning RNA Interference.
Svoboda P. Svoboda P. Front Plant Sci. 2020 Aug 13;11:1237. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01237. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32903622 Free PMC article. Review. - Restriction of vaccinia virus replication by a ced-3 and ced-4-dependent pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Liu WH, Lin YL, Wang JP, Liou W, Hou RF, Wu YC, Liao CL. Liu WH, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Mar 14;103(11):4174-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506442103. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16537504 Free PMC article. - Dissection of double-stranded RNA binding protein B2 from betanodavirus.
Fenner BJ, Goh W, Kwang J. Fenner BJ, et al. J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):5449-59. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00009-07. Epub 2007 Mar 21. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17376906 Free PMC article. - Arabidopsis DRB4, AGO1, AGO7, and RDR6 participate in a DCL4-initiated antiviral RNA silencing pathway negatively regulated by DCL1.
Qu F, Ye X, Morris TJ. Qu F, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 23;105(38):14732-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805760105. Epub 2008 Sep 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18799732 Free PMC article. - Gene regulation by non-coding RNAs.
Patil VS, Zhou R, Rana TM. Patil VS, et al. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Jan-Feb;49(1):16-32. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2013.844092. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24164576 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Mahajan-Miklos S, Tan MW, Rahme LG, Ausubel FM. Molecular mechanisms of bacterial virulence elucidated using a Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Caenorhabditis elegans pathogenesis model. Cell. 1999;96:47–56. - PubMed
- Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 1999;286:950–952. - PubMed
- Li HW, Li WX, Ding SW. Induction and suppression of RNA silencing by an animal virus. Science. 2002;296:1319–1321. - PubMed
- Fire A, et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources