Orbitofrontal cortex, associative learning, and expectancies - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Orbitofrontal cortex, associative learning, and expectancies
Geoffrey Schoenbaum et al. Neuron. 2005.
Abstract
Orbitofrontal cortex is characterized by its unique pattern of connections with subcortical areas, such as basolateral amygdala. Here we distinguish between the critical role of these areas in associative learning and the pivotal contribution of OFC to the manipulation of this information to control behavior. This contribution reflects the ability of OFC to signal the desirability of expected outcomes, which requires the integration of associative information with information concerning internal states and goals in representational memory.
Figures
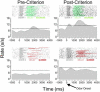
Figure 1. Neural Correlates of Outcome Expectancies in OFC
Single-unit activity is shown in raster format and perievent time histogram, synchronized to odor onset (100 ms bins; dotted line is 99% CI; top panels, Odor 1+; bottom panels, Odor 2−; odor sampling, gray shading). After odor sampling, the rat had to respond at the fluid well. On odor 1 and 2 trials, the response produced sucrose and quinine, respectively. A delay (pre-sucrose, green; pre-quinine, red) interposed between a response at the well and fluid delivery serves to isolate neural activity signaling the expected outcome.
Figure 2. OFC-ABL Interactions in Establishing Neural Representations
ABL lesions have no effect on outcome-expectant activity in OFC but abolish the activation of these cells during cue sampling. By contrast, OFC lesions disrupt outcome-expectant activity in ABL. C, cue; D, delay before outcome; O, outcome.
Similar articles
- Orbitofrontal cortex, decision-making and drug addiction.
Schoenbaum G, Roesch MR, Stalnaker TA. Schoenbaum G, et al. Trends Neurosci. 2006 Feb;29(2):116-24. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2005.12.006. Epub 2006 Jan 6. Trends Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16406092 Free PMC article. Review. - Orbitofrontal cortex inactivation impairs between- but not within-session Pavlovian extinction: an associative analysis.
Panayi MC, Killcross S. Panayi MC, et al. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Feb;108:78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 23954805 - Identity-specific coding of future rewards in the human orbitofrontal cortex.
Howard JD, Gottfried JA, Tobler PN, Kahnt T. Howard JD, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 21;112(16):5195-200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1503550112. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25848032 Free PMC article. - Rapid associative encoding in basolateral amygdala depends on connections with orbitofrontal cortex.
Saddoris MP, Gallagher M, Schoenbaum G. Saddoris MP, et al. Neuron. 2005 Apr 21;46(2):321-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.02.018. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 15848809 - The orbitofrontal cortex.
Rolls ET. Rolls ET. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996 Oct 29;351(1346):1433-43; discussion 1443-4. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1996.0128. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996. PMID: 8941955 Review.
Cited by
- Measuring extrastriatal dopamine release during a reward learning task.
Vrieze E, Ceccarini J, Pizzagalli DA, Bormans G, Vandenbulcke M, Demyttenaere K, Van Laere K, Claes S. Vrieze E, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2013 Mar;34(3):575-86. doi: 10.1002/hbm.21456. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Hum Brain Mapp. 2013. PMID: 22109979 Free PMC article. - Alteration of functional connectivity in autism spectrum disorder: effect of age and anatomical distance.
Long Z, Duan X, Mantini D, Chen H. Long Z, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 May 19;6:26527. doi: 10.1038/srep26527. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27194227 Free PMC article. - Amygdala neural encoding of the absence of reward during extinction.
Tye KM, Cone JJ, Schairer WW, Janak PH. Tye KM, et al. J Neurosci. 2010 Jan 6;30(1):116-25. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4240-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20053894 Free PMC article. - A new perspective on the role of the orbitofrontal cortex in adaptive behaviour.
Schoenbaum G, Roesch MR, Stalnaker TA, Takahashi YK. Schoenbaum G, et al. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009 Dec;10(12):885-92. doi: 10.1038/nrn2753. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19904278 Free PMC article. Review. - Encoding of Multiple Reward-Related Computations in Transient and Sustained High-Frequency Activity in Human OFC.
Saez I, Lin J, Stolk A, Chang E, Parvizi J, Schalk G, Knight RT, Hsu M. Saez I, et al. Curr Biol. 2018 Sep 24;28(18):2889-2899.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.07.045. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 30220499 Free PMC article.
References
- Camille N, Coricelli G, Sallet J, Pradat-Diehl P, Duhamel J-R, Sirigu A. Science. 2004;304:1168–1170. - PubMed
- Cousens GA, Otto T. Integr. Physiol. Behav. Sci. 2003;38:272–294. - PubMed
- Dickinson A. In: Contemporary Learning Theories: Pavlovian Conditioning and the Status of Traditional Learning Theory. Klein SB, Mowrer RR, editors. Erlbaum; Hillsdale, NJ: 1989. pp. 279–308.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01-DA015718/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32-NS07375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA015718/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA015718-03/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources