Effects of DNA mass on multiple displacement whole genome amplification and genotyping performance - PubMed (original) (raw)
Effects of DNA mass on multiple displacement whole genome amplification and genotyping performance
Andrew W Bergen et al. BMC Biotechnol. 2005.
Abstract
Background: Whole genome amplification (WGA) promises to eliminate practical molecular genetic analysis limitations associated with genomic DNA (gDNA) quantity. We evaluated the performance of multiple displacement amplification (MDA) WGA using gDNA extracted from lymphoblastoid cell lines (N = 27) with a range of starting gDNA input of 1-200 ng into the WGA reaction. Yield and composition analysis of whole genome amplified DNA (wgaDNA) was performed using three DNA quantification methods (OD, PicoGreen and RT-PCR). Two panels of N = 15 STR (using the AmpFlSTR Identifiler panel) and N = 49 SNP (TaqMan) genotyping assays were performed on each gDNA and wgaDNA sample in duplicate. gDNA and wgaDNA masses of 1, 4 and 20 ng were used in the SNP assays to evaluate the effects of DNA mass on SNP genotyping assay performance. A total of N = 6,880 STR and N = 56,448 SNP genotype attempts provided adequate power to detect differences in STR and SNP genotyping performance between gDNA and wgaDNA, and among wgaDNA produced from a range of gDNA templates inputs.
Results: The proportion of double-stranded wgaDNA and human-specific PCR amplifiable wgaDNA increased with increased gDNA input into the WGA reaction. Increased amounts of gDNA input into the WGA reaction improved wgaDNA genotyping performance. Genotype completion or genotype concordance rates of wgaDNA produced from all gDNA input levels were observed to be reduced compared to gDNA, although the reduction was not always statistically significant. Reduced wgaDNA genotyping performance was primarily due to the increased variance of allelic amplification, resulting in loss of heterozygosity or increased undetermined genotypes. MDA WGA produces wgaDNA from no template control samples; such samples exhibited substantial false-positive genotyping rates.
Conclusion: The amount of gDNA input into the MDA WGA reaction is a critical determinant of genotyping performance of wgaDNA. At least 10 ng of lymphoblastoid gDNA input into MDA WGA is required to obtain wgaDNA TaqMan SNP assay genotyping performance equivalent to that of gDNA. Over 100 ng of lymphoblastoid gDNA input into MDA WGA is required to obtain optimal STR genotyping performance using the AmpFlSTR Identifiler panel from wgaDNA equivalent to that of gDNA.
Figures
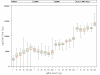
Figure 1
Yield of DNA components of wgaDNA by gDNA input into WGA. Mean ("+"), Median (middle bar), lower and upper quartile (lower and upper end of box), and minimum and maximum of BRCA1 locus equivalents, ssDNA, dsDNA and total DNA.
Similar articles
- Comparison of yield and genotyping performance of multiple displacement amplification and OmniPlex whole genome amplified DNA generated from multiple DNA sources.
Bergen AW, Haque KA, Qi Y, Beerman MB, Garcia-Closas M, Rothman N, Chanock SJ. Bergen AW, et al. Hum Mutat. 2005 Sep;26(3):262-70. doi: 10.1002/humu.20213. Hum Mutat. 2005. PMID: 16086324 - Reliability of high-throughput genotyping of whole genome amplified DNA in SNP genotyping studies.
Berthier-Schaad Y, Kao WH, Coresh J, Zhang L, Ingersoll RG, Stephens R, Smith MW. Berthier-Schaad Y, et al. Electrophoresis. 2007 Aug;28(16):2812-7. doi: 10.1002/elps.200600674. Electrophoresis. 2007. PMID: 17702060 - Effects of electron-beam irradiation on whole genome amplification.
Bergen AW, Qi Y, Haque KA, Welch RA, Garcia-Closas M, Chanock SJ, Vaught J, Castle PE. Bergen AW, et al. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005 Apr;14(4):1016-9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-04-0686. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005. PMID: 15824182 - Multiple displacement amplification to create a long-lasting source of DNA for genetic studies.
Lovmar L, Syvänen AC. Lovmar L, et al. Hum Mutat. 2006 Jul;27(7):603-14. doi: 10.1002/humu.20341. Hum Mutat. 2006. PMID: 16786504 Review. - Single-Cell DNA-Seq and RNA-Seq in Cancer Using the C1 System.
Seki M, Suzuki A, Sereewattanawoot S, Suzuki Y. Seki M, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1129:27-50. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-6037-4_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30968359 Review.
Cited by
- Use of multiple displacement amplification to increase the detection and genotyping of trypanosoma species samples immobilized on FTA filters.
Morrison LJ, McCormack G, Sweeney L, Likeufack AC, Truc P, Turner CM, Tait A, MacLeod A. Morrison LJ, et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007 Jun;76(6):1132-7. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007. PMID: 17556624 Free PMC article. - Whole genome amplification and real-time PCR in forensic casework.
Giardina E, Pietrangeli I, Martone C, Zampatti S, Marsala P, Gabriele L, Ricci O, Solla G, Asili P, Arcudi G, Spinella A, Novelli G. Giardina E, et al. BMC Genomics. 2009 Apr 14;10:159. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-159. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19366436 Free PMC article. - Single molecule transcription profiling with AFM.
Reed J, Mishra B, Pittenger B, Magonov S, Troke J, Teitell MA, Gimzewski JK. Reed J, et al. Nanotechnology. 2007 May 9;18(4):44032. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/18/4/044032. Nanotechnology. 2007. PMID: 20721301 Free PMC article. - Fluorescence in situ hybridization-flow cytometry-cell sorting-based method for separation and enrichment of type I and type II methanotroph populations.
Kalyuzhnaya MG, Zabinsky R, Bowerman S, Baker DR, Lidstrom ME, Chistoserdova L. Kalyuzhnaya MG, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Jun;72(6):4293-301. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00161-06. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16751544 Free PMC article. - Preparation of Phi29 DNA polymerase free of amplifiable DNA using ethidium monoazide, an ultraviolet-free light-emitting diode lamp and trehalose.
Takahashi H, Yamazaki H, Akanuma S, Kanahara H, Saito T, Chimuro T, Kobayashi T, Ohtani T, Yamamoto K, Sugiyama S, Kobori T. Takahashi H, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Feb 5;9(2):e82624. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082624. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24505243 Free PMC article.
References
- Risch N, Merikangas K. The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science. 1996;273:1516–1517. - PubMed
- Matsuzaki H, Loi H, Dong S, Tsai YY, Fang J, Law J, Di X, Liu WM, Yang G, Liu G, Huang J, Kennedy GC, Ryder TB, Marcus GA, Walsh PS, Shriver MD, Puck JM, Jones KW, Mei R. Parallel genotyping of over 10,000 SNPs using a one-primer assay on a high-density oligonucleotide array. Genome Res. 2004;14:414–425. doi: 10.1101/gr.2014904. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources