Gene expression profiling in single cells from the pancreatic islets of Langerhans reveals lognormal distribution of mRNA levels - PubMed (original) (raw)
Gene expression profiling in single cells from the pancreatic islets of Langerhans reveals lognormal distribution of mRNA levels
Martin Bengtsson et al. Genome Res. 2005 Oct.
Abstract
The transcriptional machinery in individual cells is controlled by a relatively small number of molecules, which may result in stochastic behavior in gene activity. Because of technical limitations in current collection and recording methods, most gene expression measurements are carried out on populations of cells and therefore reflect average mRNA levels. The variability of the transcript levels between different cells remains undefined, although it may have profound effects on cellular activities. Here we have measured gene expression levels of the five genes ActB, Ins1, Ins2, Abcc8, and Kcnj11 in individual cells from mouse pancreatic islets. Whereas Ins1 and Ins2 expression show a strong cell-cell correlation, this is not the case for the other genes. We further found that the transcript levels of the different genes are lognormally distributed. Hence, the geometric mean of expression levels provides a better estimate of gene activity of the typical cell than does the arithmetic mean measured on a cell population.
Figures
Figure 1.
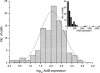
Histograms showing the expression levels of 96 cells expressing ActB in logarithmic and linear scale (inset). Logarithms of transcript levels are mean-centered for the two glucose concentrations. Solid line describes lognormal distribution centered on the geometric mean (2.06) of the ActB expression levels. Inset shows histogram of the expression levels in linear scale.
Figure 2.
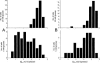
(A) Histograms of Ins1 expression levels in cells incubated in 5 mM (bottom) and 20 mM (top) glucose. Horizontal axis has logarithmic scale, which is identical in the two histograms. Scale on the vertical axis indicates the cell count in each histogram bin. (B) Corresponding histograms for Ins2 expression levels.
Similar articles
- Prolactin-modulated gene expression profiles in pancreatic islets from adult female rats.
Bordin S, Amaral ME, Anhê GF, Delghingaro-Augusto V, Cunha DA, Nicoletti-Carvalho JE, Boschero AC. Bordin S, et al. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2004 May 31;220(1-2):41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2004.04.001. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15196698 - Gene expression profiling in insulinomas of Men1 beta-cell mutant mice reveals early genetic and epigenetic events involved in pancreatic beta-cell tumorigenesis.
Fontanière S, Tost J, Wierinckx A, Lachuer J, Lu J, Hussein N, Busato F, Gut I, Wang ZQ, Zhang CX. Fontanière S, et al. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006 Dec;13(4):1223-36. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01294. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006. PMID: 17158767 - Differentiation phenotypes of pancreatic islet beta- and alpha-cells are closely related with homeotic genes and a group of differentially expressed genes.
Mizusawa N, Hasegawa T, Ohigashi I, Tanaka-Kosugi C, Harada N, Itakura M, Yoshimoto K. Mizusawa N, et al. Gene. 2004 Apr 28;331:53-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.01.016. Gene. 2004. PMID: 15094191 - The role of interferon regulatory factor-1 in cytokine-induced mRNA expression and cell death in murine pancreatic beta-cells.
Pavlovic D, Chen MC, Gysemans CA, Mathieu C, Eizirik DL. Pavlovic D, et al. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1999 Sep;10(3):403-12. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1999. PMID: 10477397 - Isosteviol increases insulin sensitivity and changes gene expression of key insulin regulatory genes and transcription factors in islets of the diabetic KKAy mouse.
Nordentoft I, Jeppesen PB, Hong J, Abudula R, Hermansen K. Nordentoft I, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008 Sep;10(10):939-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2007.00836.x. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008. PMID: 18201205
Cited by
- The MEK1/2 Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma.
Chesnokov MS, Khan I, Park Y, Ezell J, Mehta G, Yousif A, Hong LJ, Buckanovich RJ, Takahashi A, Chefetz I. Chesnokov MS, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;13(6):1369. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061369. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803586 Free PMC article. - Initial Molecular Mechanisms of the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease in a Mouse Neurotoxic Model of the Earliest Preclinical Stage of This Disease.
Kolacheva A, Pavlova E, Bannikova A, Bogdanov V, Ugrumov M. Kolacheva A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 22;25(2):1354. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021354. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279354 Free PMC article. - A Combinatorial Single-cell Approach to Characterize the Molecular and Immunophenotypic Heterogeneity of Human Stem and Progenitor Populations.
Sommarin MNE, Warfvinge R, Safi F, Karlsson G. Sommarin MNE, et al. J Vis Exp. 2018 Oct 25;(140):57831. doi: 10.3791/57831. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 30417863 Free PMC article. - Low protein expression enhances phenotypic evolvability by intensifying selection on folding stability.
Karve S, Dasmeh P, Zheng J, Wagner A. Karve S, et al. Nat Ecol Evol. 2022 Aug;6(8):1155-1164. doi: 10.1038/s41559-022-01797-w. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Nat Ecol Evol. 2022. PMID: 35798838 Free PMC article. - Quantification of circadian rhythms in single cells.
Westermark PO, Welsh DK, Okamura H, Herzel H. Westermark PO, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009 Nov;5(11):e1000580. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000580. Epub 2009 Nov 26. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009. PMID: 19956762 Free PMC article.
References
- Barg, S., Galvanovskis, J., Gopel, S.O., Rorsman, P., and Eliasson, L. 2000. Tight coupling between electrical activity and exocytosis in mouse glucagon-secreting α-cells. Diabetes 49: 1500-1510. - PubMed
- Bishop, A.E. and Polak, J.M. 1997. The anatomy, organisation and ultrastructure of the islets of Langerhans. In Textbook of diabetes (eds. J. Pickup and G. Williams), pp. 6.1-6.16. Blackwell Science, Oxford, UK.
- Blake, W.J., Kaern, M., Cantor, C.R., and Collins, J.J. 2003. Noise in eukaryotic gene expression. Nature 422: 633-637. - PubMed
- Bustin, S.A. 2000. Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 25: 169-193. - PubMed
- Castano, J.P., Kineman, R.D., and Frawley, L.S. 1996. Dynamic monitoring and quantification of gene expression in single, living cells: A molecular basis for secretory cell heterogeneity. Mol. Endocrinol. 10: 599-605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous