Evolutionary regulation of the blind subterranean mole rat, Spalax, revealed by genome-wide gene expression - PubMed (original) (raw)
Evolutionary regulation of the blind subterranean mole rat, Spalax, revealed by genome-wide gene expression
L I Brodsky et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005.
Abstract
We applied genome-wide gene expression analysis to the evolutionary processes of adaptive speciation of the Israeli blind subterranean mole rats of the Spalax ehrenbergi superspecies. The four Israeli allospecies climatically and adaptively radiated into the cooler, mesic northern domain (N) and warmer, xeric southern domain (S). The kidney and brain mRNAs of two N and two S animals were examined through cross-species hybridizations with two types of Affymetrix arrays (mouse and rat) and muscle mRNA of six N and six S animals with spotted cDNA mouse arrays. The initial microarray analysis was hypothesis-free, i.e., conducted without reference to the origin of animals. Principal component analysis revealed that 20-30% of the expression signal variability could be explained by the differentiation of N-S species. Similar N-S effects were obtained for all tissues and types of arrays: two Affymetrix microarrays using probe oligomer signals and the spotted array. Likewise, ANOVA and t test statistics demonstrated significant N-S ecogeographic divergence and region-tissue specificity in gene expression. Analysis of differential gene expression between species corroborates previous results deduced by allozymes and DNA molecular polymorphisms. Functional categories show significant N-S ecologic putative adaptive divergent up-regulation of genes highlighting a higher metabolism in N, and potential adaptive brain activity and kidney urine cycle pathways in S. The present results confirm ecologic-genomic separation of blind mole rats into N and S. Gene expression regulation appears to be central to the evolution of blind mole rats.
Figures
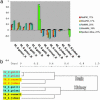
Fig. 1.
PCA and cluster analysis of probe oligomer (Affymetrix arrays) and gene signals (spotted array). Profiles of the second PC of PM and MM log signals for mouse and rat Affymetrix microarray experiments and mouse spotted-array experiment. (a) PC2 reflects the general signal difference between N and S animals for two types of Affymetrix microarrays [PM (red bars) and MM (blue bars) signals] and for the spotted array experiment (green bars). This PC2 component explains 20-30% of total signal variability. (b) The dendrogram of correlation distances between Affymetrix hybridizations (average linkage) after the cleaning of artifacts. All nonpatterned probe oligomers with average signals of >300 according to all eight hybridizations were taken. Clear N-S (S. galili plus S. golani vs. S. carmeli plus S. judaei) separation is seen for both tissues as in all other evolutionary discrimination of Spalax species based on diverse molecular markers and morphological criteria (figures 16, 17, 19, 20-22, 23 a and b, 31, and 33 in ref. 7).
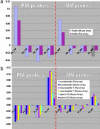
Fig. 2.
The estimated expression profiles of several proteins that have ecogeography-tissue specificity (see the description of proteins in the text). The log values of averaged gene expression for four factor combinations were calculated through estimated parameters of the ANOVA model according to all PM and MM probes. The same type of gene expression regulation was detected by mouse and rat array hybridizations. (a) N kidney up-regulated ferritin. The strong N up-regulation of this gene for muscle was detected by spotted array hybridizations. (b) S brain up-regulated genes: somatostatin, neuropeptide Y, and ephrin.
Similar articles
- Adaptation of pelage color and pigment variations in Israeli subterranean blind mole rats, Spalax ehrenbergi [corrected].
Singaravelan N, Raz S, Tzur S, Belifante S, Pavlicek T, Beiles A, Ito S, Wakamatsu K, Nevo E. Singaravelan N, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Jul 25;8(7):e69346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069346. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23935991 Free PMC article. - Differential expression profiling of the blind subterranean mole rat Spalax ehrenbergi superspecies: bioprospecting for hypoxia tolerance.
Avivi A, Brodsky L, Nevo E, Band MR. Avivi A, et al. Physiol Genomics. 2006 Oct 3;27(1):54-64. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00001.2006. Epub 2006 Jun 20. Physiol Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16788006 - Sympatric speciation revealed by genome-wide divergence in the blind mole rat Spalax.
Li K, Hong W, Jiao H, Wang GD, Rodriguez KA, Buffenstein R, Zhao Y, Nevo E, Zhao H. Li K, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 22;112(38):11905-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1514896112. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26340990 Free PMC article. - p53--a key player in tumoral and evolutionary adaptation: a lesson from the Israeli blind subterranean mole rat.
Avivi A, Ashur-Fabian O, Amariglio N, Nevo E, Rechavi G. Avivi A, et al. Cell Cycle. 2005 Mar;4(3):368-72. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.3.1534. Epub 2005 Mar 11. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15701965 Review. - Cancer-free aging: Insights from Spalax ehrenbergi superspecies.
Lagunas-Rangel FA. Lagunas-Rangel FA. Ageing Res Rev. 2018 Nov;47:18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2018.06.004. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Ageing Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29913210 Review.
Cited by
- Genome-Wide Microarray Analysis Suggests Transcriptomic Response May Not Play a Major Role in High- to Low-Altitude Acclimation in Harvest Mouse (Micromys minutus).
Chen TH, Ma GC, Lin WH, Lee DJ, Wu SH, Liao BY, Chen M, Lin LK. Chen TH, et al. Animals (Basel). 2019 Mar 13;9(3):92. doi: 10.3390/ani9030092. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30871279 Free PMC article. - Reorganization of the Y Chromosomes Enhances Divergence in Israeli Mole Rats Nannospalax ehrenbergi (Spalacidae, Rodentia): Comparative Analysis of Meiotic and Mitotic Chromosomes.
Matveevsky S, Ivanitskaya E, Spangenberg V, Bakloushinskaya I, Kolomiets O. Matveevsky S, et al. Genes (Basel). 2018 May 24;9(6):272. doi: 10.3390/genes9060272. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29794981 Free PMC article. - Impact of high predation risk on genome-wide hippocampal gene expression in snowshoe hares.
Lavergne SG, McGowan PO, Krebs CJ, Boonstra R. Lavergne SG, et al. Oecologia. 2014 Nov;176(3):613-24. doi: 10.1007/s00442-014-3053-0. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Oecologia. 2014. PMID: 25234370 - Evolution under environmental stress at macro- and microscales.
Nevo E. Nevo E. Genome Biol Evol. 2011;3:1039-52. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evr052. Genome Biol Evol. 2011. PMID: 21979157 Free PMC article.
References
- Hoffman, A. R. & Parsons, P. (1991) Environmental Stress (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford).
- Nevo, E. (1998) Heredity 81, 591-593.
- Darwin, C. (1859) On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection (Murray, London).
- Brown, P. O. & Botstein, D. (1999) Nat. Genet. 21, 33-37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous