Effect of domain interaction on apolipoprotein E levels in mouse brain - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Effect of domain interaction on apolipoprotein E levels in mouse brain
Gayathri Ramaswamy et al. J Neurosci. 2005.
Abstract
Apolipoprotein (apo) E4 is a risk factor for heart disease, Alzheimer's disease, and other forms of neurodegeneration, but the underlying mechanisms are unknown. Domain interaction, a structural property that distinguishes apoE4 from apoE2 and apoE3, results in more rapid turnover and lower plasma levels of apoE4. To determine whether domain interaction affects brain apoE levels, we analyzed brain homogenates from human apoE3 and apoE4 knock-in mice, wild-type mice, and Arg-61 apoE mice, in which domain interaction was introduced by gene targeting. As determined on Western blots, the hemibrain, cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum of knock-in mice had 30-40% lower levels of apoE4 than apoE3, and Arg-61 mice had 25-50% lower apoE levels than wild-type mice. In the CSF, Arg-61 apoE level was 40% lower than the wild-type level. Arg-61 apoE mRNA levels were similar to or slightly higher than wild-type apoE mRNA levels. Thus, the lower Arg-61 apoE levels were not attributable to decreased mRNA levels. In culture medium from heterozygous Arg-61/wild-type and apoE4/apoE3 primary astrocytes, Arg-61 apoE and apoE4 levels were lower than wild-type apoE and apoE3, respectively, suggesting that primary astrocytes secrete lower amounts of Arg-61 apoE and apoE4. These results demonstrate that domain interaction is responsible for the lower levels of both human apoE4 and mouse Arg-61 apoE in mouse brain. Cells may recognize apoE4 and Arg-61 apoE as misfolded proteins and target them for degradation or accumulation. Thus, degradation/accumulation or lower levels of apoE4 may contribute to the association of apoE4 with Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
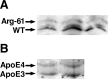
Figure 1.
Specificity of mouse apoE antibody for wild-type (WT) and Arg-61 apoE. Purified mouse WT and Arg-61 apoE (250 and 500 ng) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with an antibody against full-length mouse apoE.
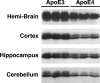
Figure 2.
ApoE levels in human apoE knock-in mouse brains. The hemibrain, cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum from 5-month-old female human apoE3 and apoE4 knock-in mice were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with an antibody against full-length human apoE.
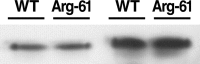
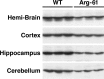
Figure 3.
ApoE levels in wild-type (WT) and Arg-61 apoE mouse brains. The hemibrain, cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum from 5-month-old WT and Arg-61 apoE homozygous female mice were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with an antibody against fulllength WT mouse apoE.
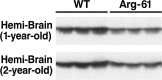
Figure 4.
ApoE levels in 1- and 2-year-old wild-type (WT) and Arg-61 apoE mouse brains. The hemibrains from 1- and 2-year-old WT and Arg-61 apoE homozygous female mice were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with an antibody to full-length mouse apoE.
Figure 5.
ApoE levels in CSF. CSF from 5-month-old heterozygous Arg-61/wild-type (WT) apoE heterozygous mice was subjected to isoelectric focusing and Western blotting.
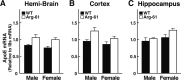
Figure 6.
ApoE mRNA levels in mouse brain. Total RNA from the hemibrain (A), cortex (B), and hippocampus (C) was extracted from 5-month-old male and female wild-type (WT) and Arg-61 apoE homozygous mice (n = 6 each) and analyzed for apoE mRNA levels by reverse transcription, followed by real-time PCR. The apoE mRNA levels were normalized to 18s mRNA. Error bars represent values ± SEM.
Figure 7.
ApoE levels in conditioned medium from primary astrocytes. Primary astrocytes from 3-d-old Arg-61/wild-type (WT) apoE (A) and apoE4/apoE3 (B) heterozygous pups were cultured in serum-free medium for 72 h, and the conditioned medium was subjected to isoelectric focusing and Western blotting.
Similar articles
- Introduction of human apolipoprotein E4 "domain interaction" into mouse apolipoprotein E.
Raffai RL, Dong LM, Farese RV Jr, Weisgraber KH. Raffai RL, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Sep 25;98(20):11587-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.201279298. Epub 2001 Sep 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11553788 Free PMC article. - Neuron-specific apolipoprotein e4 proteolysis is associated with increased tau phosphorylation in brains of transgenic mice.
Brecht WJ, Harris FM, Chang S, Tesseur I, Yu GQ, Xu Q, Dee Fish J, Wyss-Coray T, Buttini M, Mucke L, Mahley RW, Huang Y. Brecht WJ, et al. J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 10;24(10):2527-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4315-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15014128 Free PMC article. - Plasma ApoE4 Levels Are Lower than ApoE2 and ApoE3 Levels, and Not Associated with Plasma Aβ40/42 Ratio as a Biomarker of Amyloid-β Amyloidosis in Alzheimer's Disease.
Nakamura T, Kawarabayashi T, Ueda T, Shimomura S, Hoshino M, Itoh K, Ihara K, Nakaji S, Takatama M, Ikeda Y, Shoji M. Nakamura T, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;93(1):333-348. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220996. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 36970894 - Apolipoprotein E isoforms in Alzheimer's disease pathology and etiology.
Baum L, Chen L, Ng HK, Pang CP. Baum L, et al. Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Aug 15;50(4):278-81. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20000815)50:4<278::AID-JEMT5>3.0.CO;2-T. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10936880 Review. - Understanding the basis for the association of apoE4 with Alzheimer's disease: opening the door for therapeutic approaches.
Zhong N, Weisgraber KH. Zhong N, et al. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2009 Oct;6(5):415-8. doi: 10.2174/156720509789207921. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2009. PMID: 19874264 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- An Integrative Overview of Non-Amyloid and Non-Tau Pathologies in Alzheimer's Disease.
Menta BW, Swerdlow RH. Menta BW, et al. Neurochem Res. 2019 Jan;44(1):12-21. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2603-y. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 30084096 Free PMC article. Review. - Apolipoprotein E level and cholesterol are associated with reduced synaptic amyloid beta in Alzheimer's disease and apoE TR mouse cortex.
Arold S, Sullivan P, Bilousova T, Teng E, Miller CA, Poon WW, Vinters HV, Cornwell LB, Saing T, Cole GM, Gylys KH. Arold S, et al. Acta Neuropathol. 2012 Jan;123(1):39-52. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0892-1. Epub 2011 Oct 22. Acta Neuropathol. 2012. PMID: 22020632 Free PMC article. - Understanding the association of apolipoprotein E4 with Alzheimer disease: clues from its structure.
Zhong N, Weisgraber KH. Zhong N, et al. J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 6;284(10):6027-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800009200. Epub 2008 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 18948255 Free PMC article. Review. - Illuminating Neural Circuits: From Molecules to MRI.
Lee JH, Kreitzer AC, Singer AC, Schiff ND. Lee JH, et al. J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 8;37(45):10817-10825. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2569-17.2017. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29118210 Free PMC article. Review. - Insight on the molecular envelope of lipid-bound apolipoprotein E from electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Hatters DM, Voss JC, Budamagunta MS, Newhouse YN, Weisgraber KH. Hatters DM, et al. J Mol Biol. 2009 Feb 13;386(1):261-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.12.040. Epub 2008 Dec 24. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19124026 Free PMC article.
References
- Bao F, Arai H, Matsushita S, Higuchi S, Sasaki H (1996) Expression of apolipoprotein E in normal and diverse neurodegenerative disease brain. NeuroReport 7: 1733-1739. - PubMed
- Beffert U, Cohn JS, Petit-Turcotte C, Tremblay M, Aumont N, Ramassamy C, Davignon J, Poirier J (1999) Apolipoprotein E and β-amyloid levels in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of Alzheimer's disease subjects are disease-related and apolipoprotein E genotype dependent. Brain Res 843: 87-94. - PubMed
- Bertrand P, Poirier J, Oda T, Finch CE, Pasinetti GM (1995) Association of apolipoprotein E genotype with brain levels of apolipoprotein E and apolipoprotein J (clusterin) in Alzheimer disease. Mol Brain Res 33: 174-178. - PubMed
- Boschert U, Merlo-Pich E, Higgins G, Roses AD, Catsicas S (1999) Apolipoprotein E expression by neurons surviving excitotoxic stress. Neurobiol Dis 6: 508-514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- C06 RR018928/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL037063/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020235/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL37063/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG20235/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous