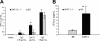Siglec-H is an IPC-specific receptor that modulates type I IFN secretion through DAP12 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Siglec-H is an IPC-specific receptor that modulates type I IFN secretion through DAP12
Amanda L Blasius et al. Blood. 2006.
Abstract
Natural interferon (IFN)-producing cells are the primary cell type responsible for production of type I IFN in response to viruses. Herein we report the identification of the first molecular marker of mouse natural interferon-producing cells (IPCs), a novel member of the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin (Ig)-like lectin (Siglec) family termed Siglec-H. Siglec-H is expressed exclusively on IPCs and is unique among Siglec proteins in that it associates with the adaptor protein DAP12. Moreover, we show that DAP12 modulates the type I IFN response of IPCs to a Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) agonist. This observation explains our previous finding that stimulation of IPCs with 440c, a Siglec-H-specific antibody, reduces IPC secretion of type I IFN. Moreover, it supports a model in which engagement of DNAX-activation protein 12 (DAP12)-associated receptors with antibodies or low avidity endogenous ligands interferes with TLR-mediated cellular activation.
Figures
Figure 1.
Antibody 440c recognizes Siglec-H. (A) Total splenocytes from WT (C57BL/6), DAP12-/-, DAP10-/-, or FcRγ-/- mice (all on C57BL/6 background) were stained with phycoerythrin (PE)-labeled mAb anti-B220 and biotinylated mAbs 440c or mPDCA1, followed by streptavidin-APC and analyzed by 2-color flow cytometry. Percentages of 440+ and mPDCA1+ IPCs are indicated. IPCs appear to be less abundant in WT mice than in DAP12-/- mice. It is possible that the lack of 440c Ag expression in the DAP12-/- mice influences IPC homing to the spleen, IPC development, or IPC survival. (B) 293T cells expressing murine DAP12 (293T-DAP12) and 293T cells were transiently transfected with a Siglec-H-encoding cDNA, stained with mAb 440c, and analyzed by flow cytometry. FSC, forward scatter. (C) Alignment of V-type Ig domains of Siglec-H and mouse CD33. Identical residues are darkly shaded, similar residues are lightly shaded. Residues likely involved in sialic acid binding are boxed. (D) Alignment of transmembrane regions of mouse Siglec-H, mouse CD33, and chimpanzee Siglec-13. The conserved lysine residue that may allow for DAP12 association is indicated with an asterisk.
Figure 2.
**DAP12-deficient IPC secrete more IFN-**α than WT IPC in vitro and in vivo. (A) Splenic CD11c+B220+CD11b-Ly6C+ IPCs from WT C57BL/6 and DAP12-/- mice were sorted by flow cytometry. Cells were stimulated with CpG oligonucleotide 2216 for 16 hours. Data are compiled from 6 independent experiments. (B) Mice received intravenous injections of 5 μg CpG 2216 in DOTAP and serum was collected after 6 hours. Representative data of 1 of 3 independent experiments are shown, each with 3 mice per group. IFN-α was measured in cell culture supernatants (A) or mouse serum by ELISA (B). Error bars show one standard deviation. *P < .05 versus B6 by Student t test.
Similar articles
- Sampling and signaling in plasmacytoid dendritic cells: the potential roles of Siglec-H.
Blasius AL, Colonna M. Blasius AL, et al. Trends Immunol. 2006 Jun;27(6):255-60. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2006.04.005. Epub 2006 May 6. Trends Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16679063 Review. - Siglec-H-Deficient Mice Show Enhanced Type I IFN Responses, but Do Not Develop Autoimmunity After Influenza or LCMV Infections.
Szumilas N, Corneth OBJ, Lehmann CHK, Schmitt H, Cunz S, Cullen JG, Chu T, Marosan A, Mócsai A, Benes V, Zehn D, Dudziak D, Hendriks RW, Nitschke L. Szumilas N, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 23;12:698420. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.698420. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34497606 Free PMC article. - Siglec-15 regulates osteoclast differentiation by modulating RANKL-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and Erk pathways in association with signaling Adaptor DAP12.
Kameda Y, Takahata M, Komatsu M, Mikuni S, Hatakeyama S, Shimizu T, Angata T, Kinjo M, Minami A, Iwasaki N. Kameda Y, et al. J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Dec;28(12):2463-75. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1989. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 23677868 - Siglec-H protects from virus-triggered severe systemic autoimmunity.
Schmitt H, Sell S, Koch J, Seefried M, Sonnewald S, Daniel C, Winkler TH, Nitschke L. Schmitt H, et al. J Exp Med. 2016 Jul 25;213(8):1627-44. doi: 10.1084/jem.20160189. Epub 2016 Jul 4. J Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 27377589 Free PMC article. - Siglecs that Associate with DAP12.
Angata T. Angata T. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1204:215-230. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1580-4_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32152949 Review.
Cited by
- Targeting TREM2 signaling shows limited impact on cerebrovascular calcification.
Sridhar S, Zhou Y, Ibrahim A, Bertazzo S, Wyss T, Swain A, Maheshwari U, Huang SF, Colonna M, Keller A. Sridhar S, et al. Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Oct 28;8(1):e202402796. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202402796. Print 2025 Jan. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39467636 Free PMC article. - The dualistic role of Lyn tyrosine kinase in immune cell signaling: implications for systemic lupus erythematosus.
L'Estrange-Stranieri E, Gottschalk TA, Wright MD, Hibbs ML. L'Estrange-Stranieri E, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 28;15:1395427. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395427. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39007135 Free PMC article. Review. - Tolerogenic pDCs Turn the Inflammatory Tide and Protect Against Acute Liver Failure.
Ling GS. Ling GS. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;18(3):101370. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2024.101370. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38991653 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - The role of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) in immunity during viral infections and beyond.
Ngo C, Garrec C, Tomasello E, Dalod M. Ngo C, et al. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024 Sep;21(9):1008-1035. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01167-5. Epub 2024 May 22. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38777879 Free PMC article. Review. - In vivo single-cell high-dimensional mass cytometry analysis to track the interactions between Klebsiella pneumoniae and myeloid cells.
Calderon-Gonzalez R, Dumigan A, Sá-Pessoa J, Kissenpfennig A, Bengoechea JA. Calderon-Gonzalez R, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2024 Apr 5;20(4):e1011900. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011900. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38578798 Free PMC article.
References
- Colonna M, Trinchieri G, Liu YJ. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells in immunity. Nat Immunol. 2004;5: 1219-1226. - PubMed
- Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2004;5: 987-995. - PubMed
- Siegal FP, Kadowaki N, Shodell M, et al. The nature of the principal type 1 interferon-producing cells in human blood. Science. 1999;284: 1835-1837. - PubMed
- Cella M, Facchetti F, Lanzavecchia A, Colonna M. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells activated by influenza virus and CD40L drive a potent TH1 polarization. Nat Immunol. 2000;1: 305-310. - PubMed
- Asselin-Paturel C, Boonstra A, Dalod M, et al. Mouse type I IFN-producing cells are immature APCs with plasmacytoid morphology. Nat Immunol. 2001;2: 1144-1150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous