Sleeping sickness in Uganda: a thin line between two fatal diseases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Sleeping sickness in Uganda: a thin line between two fatal diseases
Kim Picozzi et al. BMJ. 2005.
Abstract
Objective: To determine, through the use of molecular diagnostic tools, whether the two species of parasite that cause human African trypanosomiasis have become sympatric.
Design: Blood sampling of all available patients between June 2001 and June 2005 in central Uganda and between July and September 2003 in northwest Uganda and analysis of subcounty sleeping sickness records in Uganda between 1985 and 2005.
Setting: Sleeping sickness treatment centres in central and northwest Uganda and in south Sudan.
Participants: Patients presenting at the treatment centres and diagnosed as having sleeping sickness.
Main outcome measure: Classification of parasites from patients from each disease focus as either Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense (acute form) or T b gambiense (chronic form).
Results: Blood from 231 patients with sleeping sickness in central Uganda and from 91 patients with sleeping sickness in northwest Uganda and south Sudan were screened for T b rhodesiense (detection of SRA gene) and T b gambiense (detection of TgsGP gene). All samples from central Uganda were classified as T b rhodesiense, and all samples from northwest Uganda and south Sudan were identified as T b gambiense.
Conclusions: The two focuses of human African trypanosomiasis remain discrete, but the area of Uganda affected by the acute form of human sleeping sickness has increased 2.5-fold since 1985, spreading to three new districts within the past five years through movement of infected livestock. Without preventive action targeted at the livestock reservoir of this zoonotic disease, it is likely that the two disease focuses will converge. This will have a major impact on diagnosis and treatment of this neglected disease. Real time monitoring is recommended, using molecular diagnostic tools (at a regional surveillance centre, for example) targeted at both livestock and human patients.
Figures
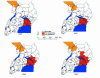
Figure 1
Sequential maps of areas of Uganda affected by sleeping sickness. T b gambiense (in orange) occurs in south Sudan and northwest Uganda, where substantial human population movements have occurred as a result of civil instability. T b rhodesiense (in red) has been spreading since the mid-1980s, and its transmission is now occurring within 150 km of the T b gambiense active focus. The tsetse belt for Glossina fuscipes fuscipes extends right across the region
Comment in
- Sleeping sickness--a growing problem?
Jannin JG. Jannin JG. BMJ. 2005 Nov 26;331(7527):1242. doi: 10.1136/bmj.331.7527.1242. BMJ. 2005. PMID: 16308384 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Impact of mass chemotherapy in domestic livestock for control of zoonotic T. b. rhodesiense human African trypanosomiasis in Eastern Uganda.
Fyfe J, Picozzi K, Waiswa C, Bardosh KL, Welburn SC. Fyfe J, et al. Acta Trop. 2017 Jan;165:216-229. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.08.022. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Acta Trop. 2017. PMID: 27570206 - Identification of human-infective trypanosomes in animal reservoir of sleeping sickness in Uganda by means of serum-resistance-associated (SRA) gene.
Welburn SC, Picozzi K, Fèvre EM, Coleman PG, Odiit M, Carrington M, Maudlin I. Welburn SC, et al. Lancet. 2001 Dec 15;358(9298):2017-9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(01)07096-9. Lancet. 2001. PMID: 11755607 - Cattle movements and trypanosomes: restocking efforts and the spread of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense sleeping sickness in post-conflict Uganda.
Selby R, Bardosh K, Picozzi K, Waiswa C, Welburn SC. Selby R, et al. Parasit Vectors. 2013 Sep 27;6(1):281. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-281. Parasit Vectors. 2013. PMID: 24289452 Free PMC article. - Priorities for the elimination of sleeping sickness.
Welburn SC, Maudlin I. Welburn SC, et al. Adv Parasitol. 2012;79:299-337. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-398457-9.00004-4. Adv Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22726645 Review. - A co-evolutionary arms race: trypanosomes shaping the human genome, humans shaping the trypanosome genome.
Capewell P, Cooper A, Clucas C, Weir W, Macleod A. Capewell P, et al. Parasitology. 2015 Feb;142 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S108-19. doi: 10.1017/S0031182014000602. Parasitology. 2015. PMID: 25656360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Human and animal Trypanosomes in Côte d'Ivoire form a single breeding population.
Capewell P, Cooper A, Duffy CW, Tait A, Turner CM, Gibson W, Mehlitz D, Macleod A. Capewell P, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Jul 2;8(7):e67852. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067852. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23844111 Free PMC article. - Spatial predictions of Rhodesian Human African Trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) prevalence in Kaberamaido and Dokolo, two newly affected districts of Uganda.
Batchelor NA, Atkinson PM, Gething PW, Picozzi K, Fèvre EM, Kakembo AS, Welburn SC. Batchelor NA, et al. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009 Dec 15;3(12):e563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000563. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009. PMID: 20016846 Free PMC article. - The Atlas of human African trypanosomiasis: a contribution to global mapping of neglected tropical diseases.
Simarro PP, Cecchi G, Paone M, Franco JR, Diarra A, Ruiz JA, Fèvre EM, Courtin F, Mattioli RC, Jannin JG. Simarro PP, et al. Int J Health Geogr. 2010 Nov 1;9:57. doi: 10.1186/1476-072X-9-57. Int J Health Geogr. 2010. PMID: 21040555 Free PMC article. - Incorporating scale dependence in disease burden estimates: the case of human African trypanosomiasis in Uganda.
Hackett F, Berrang Ford L, Fèvre E, Simarro P. Hackett F, et al. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Feb 13;8(2):e2704. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002704. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24551264 Free PMC article. - Factors associated with persistence of African animal trypanosomiasis in Lango subregion, northern Uganda.
Wangoola RM, Kevin B, Acup CA, Welburn S, Waiswa C, Bugeza J. Wangoola RM, et al. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2019 Sep;51(7):2011-2018. doi: 10.1007/s11250-019-01900-7. Epub 2019 May 3. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2019. PMID: 31054060
References
- Welburn SC, Odiit M. Recent developments in human African trypanosomiasis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2002;15: 477-84. - PubMed
- Welburn SC, Fèvre EM, Coleman PG, Odiit M, Maudlin I. Sleeping sickness: a tale of two diseases. Trends Parasitol 2001;17: 19-24. - PubMed
- Hutchinson OC, Fèvre EM, Carrington M, Welburn SC. Lessons learned from the emergence of a new Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense sleeping sickness focus in Uganda. Lancet Infect Dis 2003;3: 42-5. - PubMed
- Paquet C, Castilla J, Mbulamberi D, Beaulieu MF, Etchegorry MG, Moren A. [Trypanosomiasis from Trypanosoma brucei gambiense in the center of north-west Uganda: evaluation of 5 years of control (1987-1991).] Bull Soc Pathol Exot 1995;88: 38-41. - PubMed
- Okiria R. The prevalence of human trypanosomiasis in Uganda, 1970 to 1983. East Afr Med J 1985;62: 813-6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous