Magnocellular contributions to impaired motion processing in schizophrenia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Magnocellular contributions to impaired motion processing in schizophrenia
Dongsoo Kim et al. Schizophr Res. 2006.
Abstract
Patients with schizophrenia show impairments in motion processing, along with deficits in lower level processing primarily involving the magnocellular visual pathway. The present study investigates potential magnocellular contributions to impaired motion processing in schizophrenia using a combined neurophysiological and behavioral approach. As compared to prior motion studies in schizophrenia, thresholds were determined for both incoherent and coherent visual motion. In this study, velocity discrimination thresholds were measured for schizophrenia patients (n=14) and age-matched normal control subjects (n=16) using a staircase procedure. Early visual processing was evaluated using steady-state visual evoked potentials (ssVEP), with stimuli biased toward activation of either the magnocellular or parvocellular visual pathways through luminance contrast manipulation. Patients with schizophrenia showed poor velocity discrimination for both incoherent and coherent motion, with no significant group x task interaction. Further, when coherent motion performance was measured at individually determined incoherent motion thresholds, accuracy levels for patients were similar to controls, also indicating similarity of deficit for incoherent vs. coherent motion discrimination. Impairments in velocity discrimination correlated significantly with reduced amplitude of ssVEP elicited by magnocellular -- but not parvocellular -- selective stimuli. This study demonstrates that deficits in motion processing in schizophrenia are significantly related to reduced activation of the magnocellular visual system. Further, this study supports and extends prior reports of impaired motion processing in schizophrenia, and indicates significant bottom-up contributions to higher-order cognitive impairments.
Figures
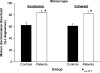
Fig. 1
Bar chart showing mean (±sem) thresholds for detecting differences in velocity of coherent (left) and incoherent (right) motion stimuli for patients with schizophrenia (n = 14) vs. controls (n = 16).
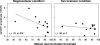
Fig. 2
Correlation between average coherent/incoherent motion discrimination threshold and steady-state visual evoked potential (ssVEP) amplitude measured as signal-to-noise (SNR) ratio to magnocellularly (left) and parvocellularly (right) biased stimuli.
Similar articles
- Impairments in generation of early-stage transient visual evoked potentials to magno- and parvocellular-selective stimuli in schizophrenia.
Schechter I, Butler PD, Zemon VM, Revheim N, Saperstein AM, Jalbrzikowski M, Pasternak R, Silipo G, Javitt DC. Schechter I, et al. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005 Sep;116(9):2204-15. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2005.06.013. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 16055375 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Dysfunction of early-stage visual processing in schizophrenia.
Butler PD, Schechter I, Zemon V, Schwartz SG, Greenstein VC, Gordon J, Schroeder CE, Javitt DC. Butler PD, et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2001 Jul;158(7):1126-33. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.158.7.1126. Am J Psychiatry. 2001. PMID: 11431235 - Early-stage visual processing and cortical amplification deficits in schizophrenia.
Butler PD, Zemon V, Schechter I, Saperstein AM, Hoptman MJ, Lim KO, Revheim N, Silipo G, Javitt DC. Butler PD, et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005 May;62(5):495-504. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.5.495. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15867102 Free PMC article. - Perception measurement in clinical trials of schizophrenia: promising paradigms from CNTRICS.
Green MF, Butler PD, Chen Y, Geyer MA, Silverstein S, Wynn JK, Yoon JH, Zemon V. Green MF, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2009 Jan;35(1):163-81. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbn156. Epub 2008 Nov 20. Schizophr Bull. 2009. PMID: 19023123 Free PMC article. Review. - Abnormal visual motion processing in schizophrenia: a review of research progress.
Chen Y. Chen Y. Schizophr Bull. 2011 Jul;37(4):709-15. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbr020. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Schizophr Bull. 2011. PMID: 21436317 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Efference copy failure during smooth pursuit eye movements in schizophrenia.
Spering M, Dias EC, Sanchez JL, Schütz AC, Javitt DC. Spering M, et al. J Neurosci. 2013 Jul 17;33(29):11779-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0578-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23864667 Free PMC article. - Normal Face Detection Over a Range of Luminance Contrasts in Adolescents With Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Norton DJ, McBain RK, Murray GE, Khang J, Zong Z, Bollacke HR, Maher S, Levy DL, Ongur D, Chen Y. Norton DJ, et al. Front Psychol. 2021 Jul 16;12:667359. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.667359. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34335378 Free PMC article. - An fMRI study of language processing in people at high genetic risk for schizophrenia.
Li X, Branch CA, Bertisch HC, Brown K, Szulc KU, Ardekani BA, DeLisi LE. Li X, et al. Schizophr Res. 2007 Mar;91(1-3):62-72. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2006.12.016. Epub 2007 Feb 16. Schizophr Res. 2007. PMID: 17306963 Free PMC article. - Compromised speed discrimination among schizophrenia patients when viewing smooth pursuit targets.
Clementz BA, McDowell JE, Dobkins KR. Clementz BA, et al. Schizophr Res. 2007 Sep;95(1-3):61-4. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2007.05.043. Epub 2007 Jul 12. Schizophr Res. 2007. PMID: 17628436 Free PMC article. - An fMRI study of visual attention and sensorimotor function before and after antipsychotic treatment in first-episode schizophrenia.
Keedy SK, Rosen C, Khine T, Rajarethinam R, Janicak PG, Sweeney JA. Keedy SK, et al. Psychiatry Res. 2009 Apr 30;172(1):16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2008.06.003. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Psychiatry Res. 2009. PMID: 19243925 Free PMC article.
References
- Abi-Saab WM, D'Souza DC, Moghaddam B, Krystal JH. The NMDA antagonist model for schizophrenia: promise and pitfalls. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1998;31(Suppl 2):104–109. - PubMed
- Bisley JW, Pasternak T. The multiple roles of visual cortical areas MT/MST in remembering the direction of visual motion. Cereb. Cortex. 2000;10:1053–1065. - PubMed
- Braus DF, Weber-Fahr W, Tost H, Ruf M, Henn FA. Sensory information processing in neuroleptic-naive first-episode schizophrenic patients: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2002;59:696–701. - PubMed
- Brenner CA, Wilt MA, Lysaker PH, Koyfman A, O'Donnell BF. Psychometrically matched visual-processing tasks in schizophrenia spectrum disorders. J. Abnorm. Psychology. 2003;112:28–37. - PubMed
- Butler PD, Schechter I, Zemon V, Schwartz SG, Greenstein VC, Gordon J, Schroeder CE, Javitt DC. Dysfunction of early stage visual processing in schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2001;158:1126–1133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH049334/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH49334/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH049334/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH066374/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K02 MH01439/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- K02 MH001439/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials