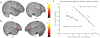Understanding emotions in others: mirror neuron dysfunction in children with autism spectrum disorders - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
Understanding emotions in others: mirror neuron dysfunction in children with autism spectrum disorders
Mirella Dapretto et al. Nat Neurosci. 2006 Jan.
Abstract
To examine mirror neuron abnormalities in autism, high-functioning children with autism and matched controls underwent fMRI while imitating and observing emotional expressions. Although both groups performed the tasks equally well, children with autism showed no mirror neuron activity in the inferior frontal gyrus (pars opercularis). Notably, activity in this area was inversely related to symptom severity in the social domain, suggesting that a dysfunctional 'mirror neuron system' may underlie the social deficits observed in autism.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
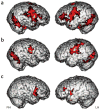
Figure 1. Reliable activity during imitation of emotional expressions
(a,b) Activity in bilateral pars opercularis (stronger in the right) of the inferior frontal gyrus is seen in the typically developing group (a) but not in the ASD group (b). A between-group comparison (c) revealed that this difference was significant (t > 1.83, P < 0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons at the cluster level). RH, right hemisphere; LH, left hemisphere.
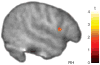
Figure 2
Mirror neuron system activity during observation of emotional expressions. The right pars opercularis showed significantly greater activity in typically developing children than in children with ASD (t > 1.83, P < 0.05, small volume corrected).
Figure 3. Mirror neuron system activity and symptom severity
(a–c) Negative correlations were found in the ASD group between activity in the pars opercularis of the inferior frontal gyrus and scores on the social subscale of both ADOS-G (a,c) and ADI-R (b,c). t > 1.83, P < 0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons at the cluster level.
Similar articles
- [Hemodynamic activities in children with autism while imitating emotional facial expressions: a near-infrared spectroscopy study].
Mori K, Mori T, Goji A, Ito H, Toda Y, Fujii E, Miyazaki M, Harada M, Kagami S. Mori K, et al. No To Hattatsu. 2014 Jul;46(4):281-6. No To Hattatsu. 2014. PMID: 25154225 Japanese. - Mirror neuron dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders.
Perkins T, Stokes M, McGillivray J, Bittar R. Perkins T, et al. J Clin Neurosci. 2010 Oct;17(10):1239-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2010.01.026. Epub 2010 Jul 2. J Clin Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20598548 - Age-related increase in inferior frontal gyrus activity and social functioning in autism spectrum disorder.
Bastiaansen JA, Thioux M, Nanetti L, van der Gaag C, Ketelaars C, Minderaa R, Keysers C. Bastiaansen JA, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2011 May 1;69(9):832-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.11.007. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21310395 - The simulating social mind: the role of the mirror neuron system and simulation in the social and communicative deficits of autism spectrum disorders.
Oberman LM, Ramachandran VS. Oberman LM, et al. Psychol Bull. 2007 Mar;133(2):310-27. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.133.2.310. Psychol Bull. 2007. PMID: 17338602 Review. - Self-other relations in social development and autism: multiple roles for mirror neurons and other brain bases.
Williams JH. Williams JH. Autism Res. 2008 Apr;1(2):73-90. doi: 10.1002/aur.15. Autism Res. 2008. PMID: 19360654 Review.
Cited by
- Perceptual discrimination of action formidableness and friendliness and the impact of autistic traits.
Vlasceanu AM, de la Rosa S, Barraclough NE. Vlasceanu AM, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 26;14(1):25554. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76488-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39462021 Free PMC article. - Task-based functional neural correlates of social cognition across autism and schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
Oliver LD, Moxon-Emre I, Hawco C, Dickie EW, Dakli A, Lyon RE, Szatmari P, Haltigan JD, Goldenberg A, Rashidi AG, Tan V, Secara MT, Desarkar P, Foussias G, Buchanan RW, Malhotra AK, Lai MC, Voineskos AN, Ameis SH. Oliver LD, et al. Mol Autism. 2024 Sep 4;15(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13229-024-00615-3. Mol Autism. 2024. PMID: 39252047 Free PMC article. - Mapping neural correlates of biological motion perception in autistic children using high-density diffuse optical tomography.
Yang D, Svoboda AM, George TG, Mansfield PK, Wheelock MD, Schroeder ML, Rafferty SM, Sherafati A, Tripathy K, Burns-Yocum T, Forsen E, Pruett JR, Marrus NM, Culver JP, Constantino JN, Eggebrecht AT. Yang D, et al. Mol Autism. 2024 Aug 22;15(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13229-024-00614-4. Mol Autism. 2024. PMID: 39175054 Free PMC article. - Relationships between tryptophan-related gut metabolites, brain activity, and autism symptomatology.
Aziz-Zadeh L, Mayer E, Labus J, Ringold S, Jayashankar A, Kilroy E, Butera C, Jacobs J, Tanartkit S, Joshi S, Dapretto M. Aziz-Zadeh L, et al. Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 25:rs.3.rs-4559624. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4559624/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 39108481 Free PMC article. Preprint. - The role of self-representation in emotional contagion.
Wang D, Liu C, Chen W. Wang D, et al. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 May 9;18:1361368. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1361368. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38784524 Free PMC article.
References
- Williams JH, Whiten A, Suddendorf T, Perrett DI. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2001;25:287–295. - PubMed
- Rizzolatti G, Craighero L. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:169–192. - PubMed
- Iacoboni M, et al. Science. 1999;286:2526–2528. - PubMed
- Johnson-Frey SH, et al. Neuron. 2003;39:1053–1058. - PubMed
- Iacoboni M. In: Perspectives on Imitation: From Neuroscience to Social Science. Hurley S, Chater N, editors. MIT Press; Cambridge, Massachusetts: 2005. pp. 77–99.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- RR13642/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR012169/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD055784/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR013642/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD035470/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RR08655/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous