Mitochondria: a target for cancer therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Mitochondria: a target for cancer therapy
Jeffrey S Armstrong. Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Feb.
Abstract
Mitochondria, the cells powerhouses, are essential for maintaining cell life, and they also play a major role in regulating cell death, which occurs upon permeabilization of their membranes. Once mitochondrial membrane permeabilization (MMP) occurs, cells die either by apoptosis or necrosis. Key factors regulating MMP include calcium, the cellular redox status (including levels of reactive oxygen species) and the mobilization and targeting to mitochondria of Bcl-2 family members. Contemporary approaches to targeting mitochondria in cancer therapy use strategies that either modulate the action of Bcl-2 family members at the mitochondrial outer membrane or use specific agents that target the mitochondrial inner membrane and the mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) pore. The aim of this review is to describe the major mechanisms regulating MMP and to discuss, with examples, mitochondrial targeting strategies for potential use in cancer therapy.
Figures
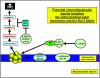
Figure 1
Potential chemotherapeutic approaches targeting the mitochondrial outer membrane and the Bcl-2 family: mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization is regulated by the Bcl-2 family of proteins therefore targeting strategies to induce apoptosis are aimed at either inhibiting Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins or inducing Bax-like proapoptotic proteins. (1) Use of gene silencing technology, for example, Genasense G3139 to downregulate Bcl-2 expression. (2) Bax vectors have been used to deliver Bax and form a pore in the MOM that releases proapoptotic cytochrome c and other factors from the intermembrane space. (3) BH3 stapled peptides (SAHBs) that activate Bax have been employed to induce apoptosis. (4) The caspases are negatively regulated by a family of proteins known as the IAPs including XIAP; however, these themselves are also regulated by the IAP-inhibitor proteins such as Smac/DIABLO, which serves to restore caspase activity. Smac/DIABLO mimics have recently been used to induce apoptosis (see text for references).
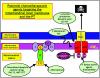
Figure 2
Potential chemotherapeutic approaches targeting the mitochondrial inner membrane and the mitochondrial permeability transition (PT). Mitochondrial inner membrane permeabilization and the PT is regulated by calcium and oxidative stress. Targeting strategies include activating the PT, inhibiting electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation and depleting mtDNA. (1) Agents such as arsenite, lonidamine, betulinic acid and CD437 target the PT and induce loss of Δψm. (2) Delocalized lipophilic cations accumulate in the mitochondria matrix due to the electrochemical gradient and cause loss of respiration and inhibition of electron transport. (3) α Helical peptides such as mastoparan and Vpr permeabilize mitochondrial membranes and induce PT. (4) Redox modulating compound such as diamide deplete GSH stores and oxidize and crosslink critical mitochondrial redox-sensitive thiol groups at the matrix surface of the PT. (5) mtDNA depleting agents such as ditercalinium inhibit respiration, electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation (see text for references).
Similar articles
- Transient mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening after neonatal cardioplegic arrest.
Leung CH, Wang L, Fu YY, Yuen W, Caldarone CA. Leung CH, et al. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011 Apr;141(4):975-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.08.030. Epub 2010 Sep 29. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011. PMID: 20884027 - Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization: the sine qua non for cell death.
Armstrong JS. Armstrong JS. Bioessays. 2006 Mar;28(3):253-60. doi: 10.1002/bies.20370. Bioessays. 2006. PMID: 16479581 Review. - The role of the mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death.
Armstrong JS. Armstrong JS. Mitochondrion. 2006 Oct;6(5):225-34. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2006.07.006. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Mitochondrion. 2006. PMID: 16935572 Review. - Changes in specific lipids regulate BAX-induced mitochondrial permeability transition.
Martínez-Abundis E, García N, Correa F, Franco M, Zazueta C. Martínez-Abundis E, et al. FEBS J. 2007 Dec;274(24):6500-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06166.x. Epub 2007 Nov 17. FEBS J. 2007. PMID: 18028444 - Mitochondria as decision-makers in cell death.
Borutaite V. Borutaite V. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2010 Jun;51(5):406-16. doi: 10.1002/em.20564. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2010. PMID: 20209625 Review.
Cited by
- Mitochondrial targeted peptides for cancer therapy.
Farsinejad S, Gheisary Z, Ebrahimi Samani S, Alizadeh AM. Farsinejad S, et al. Tumour Biol. 2015 Aug;36(8):5715-25. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3719-1. Epub 2015 Jul 5. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 26142734 Review. - The antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 negatively regulates autophagy and growth arrest induced by the anticancer redox agent mitoquinone.
Rao VA, Klein SR, Bonar SJ, Zielonka J, Mizuno N, Dickey JS, Keller PW, Joseph J, Kalyanaraman B, Shacter E. Rao VA, et al. J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 5;285(45):34447-59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.133579. Epub 2010 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20805228 Free PMC article. - Chemical-genetic profiling of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines and -pyrimidines reveals target pathways conserved between yeast and human cells.
Yu L, Lopez A, Anaflous A, El Bali B, Hamal A, Ericson E, Heisler LE, McQuibban A, Giaever G, Nislow C, Boone C, Brown GW, Bellaoui M. Yu L, et al. PLoS Genet. 2008 Nov;4(11):e1000284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000284. Epub 2008 Nov 28. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 19043571 Free PMC article. - The cytotoxic properties and preferential toxicity to tumour cells displayed by some 2,4-bis(benzylidene)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1] octan-3-ones and 3,5-bis(benzylidene)-1-methyl-4-piperidones.
Pati HN, Das U, Das S, Bandy B, De Clercq E, Balzarini J, Kawase M, Sakagami H, Quail JW, Stables JP, Dimmock JR. Pati HN, et al. Eur J Med Chem. 2009 Jan;44(1):54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2008.03.015. Epub 2008 Mar 29. Eur J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 18468733 Free PMC article. - Hirsutine induces mPTP-dependent apoptosis through ROCK1/PTEN/PI3K/GSK3β pathway in human lung cancer cells.
Zhang R, Li G, Zhang Q, Tang Q, Huang J, Hu C, Liu Y, Wang Q, Liu W, Gao N, Zhou S. Zhang R, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2018 May 22;9(6):598. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0641-7. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29789524 Free PMC article.
References
- ACKERMANN E.J., TAYLOR J.K., NARAYANA R., BENNETT C.F. The role of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members in endothelial apoptosis elucidated with antisense oligonucleotides. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:11245–11252. - PubMed
- ADACHI M., HIGUCHI H., MIURA S., AZUMA T., INOKUCHI S., SAITO H., KATO S., ISHII H. Bax interacts with the voltage-dependent anion channel and mediates ethanol-induced apoptosis in rat hepatocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004;287:G695–G705. - PubMed
- ANDERSON K.S. The molecular basis of inhibition and toxicity of modified cytosine analogues targeting HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2001;12 (Suppl 1):13–17. - PubMed
- AQEILAN R., YARKONI S., LORBERBOUM-GALSKI H. Interleukin 2-Bax: a novel prototype of human chimeric proteins for targeted therapy. FEBS Lett. 1999;457:271–276. - PubMed
- ARDAIL D., PRIVAT J.P., EGRET-CHARLIER M., LEVRAT C., LERME F., LOUISOT P. Mitochondrial contact sites. Lipid composition and dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:18797–18802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources