Activation of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell attenuates context-induced relapse to heroin seeking - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
. 2006 Oct;31(10):2197-209.
doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300977. Epub 2005 Dec 7.
Affiliations
- PMID: 16341024
- PMCID: PMC1570155
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300977
Comparative Study
Activation of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell attenuates context-induced relapse to heroin seeking
Jennifer M Bossert et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Oct.
Abstract
Using a rat relapse model, we previously reported that re-exposing rats to a drug-associated context, following extinction of operant responding in a different context, reinstates heroin seeking. In an initial pharmacological characterization, we found that the mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268, which acts centrally to reduce evoked glutamate release, attenuates context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking when injected systemically or into the ventral tegmental area, the cell body region of the mesolimbic dopamine system. Here, we tested whether injections of LY379268 into the nucleus accumbens (NAc), a terminal region of the mesolimbic dopamine system, would also attenuate context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. Rats were trained to self-administer heroin; drug infusions were paired with a discrete tone-light cue. Subsequently, lever pressing was extinguished in the presence of the discrete cue in a context that differed from the drug self-administration context in terms of visual, auditory, tactile, and circadian cues. After extinction of responding, LY379268 was injected to different groups of rats into the NAc core or shell or into the caudate-putamen, a terminal region of the nigrastriatal dopamine system. Injections of LY379268 into the NAc shell (0.3 or 1.0 microg) dose-dependently attenuated context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. Injections of 1.0 microg of LY379268 into the NAc core had no effect, while a higher dose (3.0 microg) decreased this reinstatement. Injections of LY379268 (3.0 microg) 1.5 mm dorsal from the NAc core into the caudate-putamen were ineffective. Results suggest an important role of glutamate transmission in the NAc shell in context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking.
Figures
Figure 1
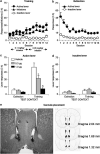
Effects of intra-NAc shell LY379268 injections on context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. (a) Training: mean ± SEM infusions, and active and inactive lever responses during the 12 days of heroin self-administration training. Rats were trained on an FR-1 schedule with a 2.3 s timeout period; active lever responses reflect infusion + timeout responses. The unit dose of heroin was 0.1 mg/kg for the first six sessions and 0.05 mg/kg for the last six sessions (n = 25, three groups). (b) Extinction: mean responses on the previously active lever and on the inactive lever during extinction sessions conducted in the absence of heroin and in a context different from the training context (n = 25). (c) Test for reinstatement: active lever: mean responses on the active lever after bilateral intra-NAc shell injections of vehicle, 0.3 or 1.0 μg of LY379268 in the training or the extinction context. *Different from the vehicle condition, p 0.05 (n = 8-9/group). (d) Test for reinstatement: inactive lever: mean responses on the inactive lever after intra-NAc shell injections of vehicle or LY379268. (e) A representative picture of NAc shell injector tip and the approximate placements of the injectors' tip of the rats (Paxinos and Watson, 2005).
Figure 2
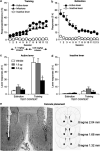
Effects of intra-NAc core LY379268 injections on context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. (a) Training: mean ± SEM infusions, and active and inactive lever responses during the 12 days of heroin self-administration training. Rats were trained on an FR-1 schedule with a 2.3 s timeout period; active lever responses reflect infusion + timeout responses. The unit dose of heroin was 0.1 mg/kg for the first six sessions and 0.05 mg/kg for the last six sessions (n = 29, three groups). (b) Extinction: mean responses on the previously active lever and on the inactive lever during extinction sessions conducted in the absence of heroin and in a context different from the training context (n = 29). (c) Test for reinstatement: active lever: mean responses on the active lever after bilateral injections of vehicle, 1.0, or 3.0 μg of LY379268 in the training or the extinction context. *Different from the vehicle condition, p < 0.05 (n = 9-10/group). (d) Test for reinstatement: inactive lever: mean responses on the inactive lever after injections of vehicle or LY379268. (e) A representative picture of NAc core injector tip and the approximate placements of the injectors' tip of the rats (Paxinos and Watson, 2005).
Figure 3
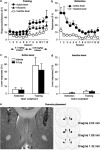
Effects of intracaudate-putamen LY379268 injections on context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. (a) Training: mean ± SEM infusions, and active and inactive lever responses during the 12 days of heroin self-administration training. Rats were trained on an FR-1 schedule with a 2.3 s timeout period; active lever responses reflect infusion + timeout responses. The unit dose of heroin was 0.1 mg/kg for the first six sessions and 0.05 mg/kg for the last six sessions (n = 15, two groups). (b) Extinction: Mean responses on the previously active lever and on the inactive lever during extinction sessions conducted in the absence of heroin in a context different from the training context (n = 15). (c) Test for reinstatement: active lever: mean responses on the active lever after bilateral injections of vehicle or 3.0 μg of LY379268 in the training or the extinction context (n = 7-8/group). (d) Test for reinstatement: inactive lever: mean responses on the inactive lever after injections of vehicle or LY379268. (e) A representative picture of caudate-putamen injector tip and the approximate placements of the injectors' tip of the rats (Paxinos and Watson, 2005).
Figure 4
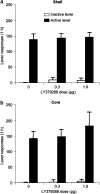
Effect of intra-NAc shell or core injections of LY379268 on sucrose self-administration. mean ± SEM responses on the active and the inactive levers after bilateral injections of vehicle or LY379268 into the NAc shell (a) (0.3 and 1.0 μg; n = 5) or into the NAc core (b) (1.0 and 3.0 μg; n = 7). No significant effects were observed.
Similar articles
- Differential effects of blockade of dopamine D1-family receptors in nucleus accumbens core or shell on reinstatement of heroin seeking induced by contextual and discrete cues.
Bossert JM, Poles GC, Wihbey KA, Koya E, Shaham Y. Bossert JM, et al. J Neurosci. 2007 Nov 14;27(46):12655-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3926-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18003845 Free PMC article. - A role of ventral tegmental area glutamate in contextual cue-induced relapse to heroin seeking.
Bossert JM, Liu SY, Lu L, Shaham Y. Bossert JM, et al. J Neurosci. 2004 Nov 24;24(47):10726-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3207-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15564590 Free PMC article. - The novel mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268 attenuates cue-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking.
Bossert JM, Busch RF, Gray SM. Bossert JM, et al. Neuroreport. 2005 Jun 21;16(9):1013-6. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200506210-00026. Neuroreport. 2005. PMID: 15931079 - Review. Context-induced relapse to drug seeking: a review.
Crombag HS, Bossert JM, Koya E, Shaham Y. Crombag HS, et al. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2008 Oct 12;363(1507):3233-43. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0090. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18640922 Free PMC article. Review. - Metabotropic glutamate 7 (mGlu7) receptor: a target for medication development for the treatment of cocaine dependence.
Li X, Xi ZX, Markou A. Li X, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2013 Mar;66:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.04.010. Epub 2012 Apr 21. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 22546614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Gq-DREADD Selectively Initiates Glial Glutamate Release and Inhibits Cue-induced Cocaine Seeking.
Scofield MD, Boger HA, Smith RJ, Li H, Haydon PG, Kalivas PW. Scofield MD, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Oct 1;78(7):441-51. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.02.016. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25861696 Free PMC article. - Exaggerated cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking but not incubation of cocaine craving in a developmental rat model of schizophrenia.
Karlsson RM, Kircher DM, Shaham Y, O'Donnell P. Karlsson RM, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Mar;226(1):45-51. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2882-y. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23010798 Free PMC article. - Signals from the Fourth Dimension Regulate Drug Relapse.
Mulholland PJ, Chandler LJ, Kalivas PW. Mulholland PJ, et al. Trends Neurosci. 2016 Jul;39(7):472-485. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 May 10. Trends Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27173064 Free PMC article. Review. - Metabotropic group II glutamate receptors mediate cue-triggered increases in reward-seeking behaviour.
Garceau C, Marsault J, Robinson MJF, Samaha AN. Garceau C, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2023 Mar;240(3):515-529. doi: 10.1007/s00213-022-06101-z. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2023. PMID: 35230468 - The preclinical properties of a novel group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist LY379268.
Imre G. Imre G. CNS Drug Rev. 2007 Winter;13(4):444-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2007.00024.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2007. PMID: 18078428 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: electrophysiological properties and role in plasticity. Brain Res Rev. 1999;29:83–120. - PubMed
- Bardo MT, Bevins RA. Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharmacology. 2000;153:31–43. - PubMed
- Bast T, Zhang WN, Feldon J. The ventral hippocampus and fear conditioning in rats. Different anterograde amnesias of fear after tetrodotoxin inactivation and infusion of the GABA(A) agonist muscimol. Exp Brain Res. 2001;139:39–52. - PubMed
- Bossert JM, Busch RF, Gray SM. The novel mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268 attenuates cue-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. Neuroreport. 2005;16:1013–1016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical