Anti-viral RNA silencing: do we look like plants? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Anti-viral RNA silencing: do we look like plants?
Anne Saumet et al. Retrovirology. 2006.
Abstract
The anti-viral function of RNA silencing was first discovered in plants as a natural manifestation of the artificial 'co-suppression', which refers to the extinction of endogenous gene induced by homologous transgene. Because silencing components are conserved among most, if not all, eukaryotes, the question rapidly arose as to determine whether this process fulfils anti-viral functions in animals, such as insects and mammals. It appears that, whereas the anti-viral process seems to be similarly conserved from plants to insects, even in worms, RNA silencing does influence the replication of mammalian viruses but in a particular mode: micro(mi)RNAs, endogenous small RNAs naturally implicated in translational control, rather than virus-derived small interfering (si)RNAs like in other organisms, are involved. In fact, these recent studies even suggest that RNA silencing may be beneficial for viral replication. Accordingly, several large DNA mammalian viruses have been shown to encode their own miRNAs. Here, we summarize the seminal studies that have implicated RNA silencing in viral infection and compare the different eukaryotic responses.
Figures
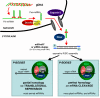
Figure 1
miRNA biogenesis and action. Long primary transcripts (pri-miRNAs) containing one or several miRNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II and cleaved by the Microprocessor Complex, containing at least Drosha (RNAase III endonuclease) and DGCR8/Pasha in human (a double-stranded RNA binding protein). This complex recognizes the double stranded RNA structure of the pri-miRNA and specifically cleaves at the base of the stem loop, hence releasing a 60- to 70-nucleotide precursor(pre)-miRNA. This pre-miRNA is then exported through the Exportin-5 pathway into the cytoplasm where it is further processed into a mature miR/miR* duplex by Dicer, a second RNase III endonuclease. The miR/miR* duplex is then loaded into a multi-component complex, the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), constituted of at least TRBP (TAR Binding Protein), Dicer, and one Argonaute (Ago2 in human). The miR serves as a guide for target recognition while the miR* passenger strand is cleaved by Ago2. In contrast to siRNAs (small interfering RNA) and plant miRNAs, which induced the cleavage of the targeted mRNA, most of animal miRNAs harbour an imperfect homology with their targets and, therefore, inhibit translation by a RISC-dependent mechanism that probably interferes with the mRNA cap recognition. This step occurs in cytoplasmic foci called P-bodies (for processing bodies), which contain untranslated mRNAs and can serve as specific sites for mRNA degradation.
Similar articles
- [Micro RNA and viral infections in mammals].
Pfeffer S. Pfeffer S. J Soc Biol. 2007;201(4):377-84. doi: 10.1051/jbio:2007908. Epub 2008 Mar 5. J Soc Biol. 2007. PMID: 18533098 Review. French. - Viral induction and suppression of RNA silencing in plants.
Shimura H, Pantaleo V. Shimura H, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov-Dec;1809(11-12):601-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.04.005. Epub 2011 Apr 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21550428 - Viral suppression of RNA silencing.
Jiang L, Wei C, Li Y. Jiang L, et al. Sci China Life Sci. 2012 Feb;55(2):109-18. doi: 10.1007/s11427-012-4279-x. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Sci China Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22415681 Review. - Viral and subviral derived small RNAs as pathogenic determinants in plants and insects.
Leonetti P, Miesen P, van Rij RP, Pantaleo V. Leonetti P, et al. Adv Virus Res. 2020;107:1-36. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2020.04.001. Epub 2020 May 27. Adv Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32711727
Cited by
- Improving model predictions for RNA interference activities that use support vector machine regression by combining and filtering features.
Peek AS. Peek AS. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Jun 6;8:182. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-182. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17553157 Free PMC article. - The silent defense: micro-RNA directed defense against HIV-1 replication.
Kumar A. Kumar A. Retrovirology. 2007 Apr 12;4:26. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-4-26. Retrovirology. 2007. PMID: 17430590 Free PMC article. - Interactions between the HIV-1 Unspliced mRNA and Host mRNA Decay Machineries.
Toro-Ascuy D, Rojas-Araya B, Valiente-Echeverría F, Soto-Rifo R. Toro-Ascuy D, et al. Viruses. 2016 Nov 23;8(11):320. doi: 10.3390/v8110320. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27886048 Free PMC article. Review. - Meta-transcriptomic analysis reveals the geographical expansion of known sugarbeet-infecting viruses and the occurrence of a novel virus in sugarbeet in the United States.
Chinnadurai C, Wyatt NA, Weiland JJ, Neher OT, Hastings J, Bloomquist MW, Chu C, Chanda AK, Khan M, Bolton MD, Ramachandran V. Chinnadurai C, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2024 Aug 30;15:1429402. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1429402. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39290724 Free PMC article. - A systematic approach to virus-virus interactions.
DaPalma T, Doonan BP, Trager NM, Kasman LM. DaPalma T, et al. Virus Res. 2010 Apr;149(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.01.002. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Virus Res. 2010. PMID: 20093154 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources