Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants in the Caenorhabditis elegans infection model - PubMed (original) (raw)
Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants in the Caenorhabditis elegans infection model
Costi D Sifri et al. Infect Immun. 2006 Feb.
Abstract
Small colony variants (SCVs) of Staphylococcus aureus are slow-growing morphological variants that have been implicated in persistent, relapsing, and antibiotic-resistant infections. The altered phenotype of SCVs in most strains has been attributed to defects in electron transport due to mutations in hemin or menadione biosynthesis. The pathogenic capacity of SCVs compared to phenotypically normal strains is variable depending on the attribute examined, with some studies showing reduced virulence of SCVs and others demonstrating normal or heightened virulence. Recently, the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans has been successfully employed as an alternative host to investigate virulence mechanisms of a variety of bacterial pathogens, including S. aureus. In this study, we show that clinical SCVs as well as hemB- and menD-deficient mutants of S. aureus are greatly reduced in virulence in the C. elegans infection model.
Figures
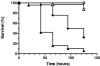
FIG. 1.
Survival of C. elegans on clinically isolated S. aureus SCVs. Survival of nematodes fed S. aureus A22223I (clinical wild-type isolate; closed triangles; n = 69) versus A22223II (hemin-auxotrophic SCV; open triangles; n = 65) and A22616/5 (clinical wild-type isolate; closed diamonds; n = 55) versus A22616/3 (menadione-auxotrophic SCV; open diamonds; n = 56) is shown. Survival was plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method, and pairwise comparisons using the log rank test between the SCV and matched wild-type isolates were significant at a P value of <0.0001.
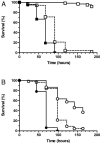
FIG. 2.
Survival of C. elegans on SCV hemB mutants. (A) Survival of nematodes fed S. aureus Newman (wild type; closed squares; n = 57), III33 (hemB SCV; open squares with a solid line; n = 61), and KM2 (_hemB_-complemented III33; open squares with a dashed line; n = 52). (B) Survival of nematodes fed S. aureus COL (wild type; closed circles; n = 55), Ia48 (hemB SCV; open circles with a solid line; n = 56), and KM1 (_hemB_-complemented Ia48; open circles with a dashed line; n = 61). Survival was plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method. Pairwise comparisons using the log rank test by strain were as follows: Newman versus III33, III33 versus KM2, COL versus Ia48, and Ia48 versus KM1 (all P < 0.0001).
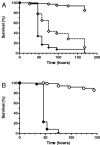
FIG. 3.
Survival of C. elegans on SCV menD mutants. (A) Survival of nematodes fed S. aureus 8325-4 (wild type; closed diamonds; n = 91), DB24 (menD SCV; open diamonds with a solid line; n = 83), and DB25 (_menD_-repaired DB24; open diamonds with a dashed line; n = 92). (B) Survival of nematodes fed S. aureus COL (wild type; closed circles; n = 92) and COL menD (menD SCV; open circles; n = 93). Survival was plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method. Pairwise comparisons using the log rank test by strain were as follows: 8325-4 versus DB24, DB24 versus DB24, and COL versus COL menD (all P < 0.0001).
FIG. 4.
Colonization of the C. elegans digestive tract. Differential interference contrast photomicrographs of the terminal bulb and anterior intestinal tract of nematodes after feeding for 20 h on lawns of (A) COL, (B) Ia48, or (C) KM1 are shown.
Similar articles
- Increased expression of clumping factor and fibronectin-binding proteins by hemB mutants of Staphylococcus aureus expressing small colony variant phenotypes.
Vaudaux P, Francois P, Bisognano C, Kelley WL, Lew DP, Schrenzel J, Proctor RA, McNamara PJ, Peters G, Von Eiff C. Vaudaux P, et al. Infect Immun. 2002 Oct;70(10):5428-37. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.10.5428-5437.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12228267 Free PMC article. - Transcription of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants isolated from cystic fibrosis patients is influenced by SigB.
Moisan H, Brouillette E, Jacob CL, Langlois-Bégin P, Michaud S, Malouin F. Moisan H, et al. J Bacteriol. 2006 Jan;188(1):64-76. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.1.64-76.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16352822 Free PMC article. - Staphylococcus aureus menD and hemB mutants are as infective as the parent strains, but the menadione biosynthetic mutant persists within the kidney.
Bates DM, von Eiff C, McNamara PJ, Peters G, Yeaman MR, Bayer AS, Proctor RA. Bates DM, et al. J Infect Dis. 2003 May 15;187(10):1654-61. doi: 10.1086/374642. Epub 2003 Apr 30. J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12721946 - Small colony variants (SCVs) of Staphylococcus aureus--a bacterial survival strategy.
Kahl BC. Kahl BC. Infect Genet Evol. 2014 Jan;21:515-22. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.05.016. Epub 2013 May 27. Infect Genet Evol. 2014. PMID: 23722021 Review. - Staphylococcus aureus Small Colony Variants (SCVs): a road map for the metabolic pathways involved in persistent infections.
Proctor RA, Kriegeskorte A, Kahl BC, Becker K, Löffler B, Peters G. Proctor RA, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Jul 28;4:99. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00099. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25120957 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A defect in menadione biosynthesis induces global changes in gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus.
Kohler C, von Eiff C, Liebeke M, McNamara PJ, Lalk M, Proctor RA, Hecker M, Engelmann S. Kohler C, et al. J Bacteriol. 2008 Oct;190(19):6351-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.00505-08. Epub 2008 Aug 1. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18676673 Free PMC article. - Effect of low temperature on growth and ultra-structure of Staphylococcus spp.
Onyango LA, Dunstan RH, Gottfries J, von Eiff C, Roberts TK. Onyango LA, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029031. Epub 2012 Jan 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22291884 Free PMC article. - Proteome changes of Caenorhabditis elegans upon a Staphylococcus aureus infection.
Bogaerts A, Beets I, Temmerman L, Schoofs L, Verleyen P. Bogaerts A, et al. Biol Direct. 2010 Feb 17;5:11. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-5-11. Biol Direct. 2010. PMID: 20163716 Free PMC article. - An aroD Ochre Mutation Results in a Staphylococcus aureus Small Colony Variant That Can Undergo Phenotypic Switching via Two Alternative Mechanisms.
Zhang P, Wright JA, Osman AA, Nair SP. Zhang P, et al. Front Microbiol. 2017 May 31;8:1001. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01001. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28620368 Free PMC article. - Cloning, Expression and Characterization of NAD Kinase from Staphylococcus aureus Involved in the Formation of NADP (H): A Key Molecule in the Maintaining of Redox Status and Biofilm Formation.
Prasad UV, Vasu D, Gowtham RR, Pradeep CK, Swarupa V, Yeswanth S, Choudhary A, Sarma PVGK. Prasad UV, et al. Adv Biomed Res. 2017 Jul 31;6:97. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.211833. eCollection 2017. Adv Biomed Res. 2017. PMID: 28828348 Free PMC article.
References
- Bates, D. M., C. von Eiff, P. J. McNamara, G. Peters, M. R. Yeaman, A. S. Bayer, and R. A. Proctor. 2003. Staphylococcus aureus menD and hemB mutants are as infective as the parent strains, but the menadione biosynthetic mutant persists within the kidney. J. Infect. Dis. 187:1654-1661. - PubMed
- Baumert, N., C. von Eiff, F. Schaaff, G. Peters, R. A. Proctor, and H. G. Sahl. 2002. Physiology and antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants. Microb. Drug Resist. 8:253-260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources