B cell-deficient NOD.H-2h4 mice have CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells that inhibit the development of spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis - PubMed (original) (raw)
B cell-deficient NOD.H-2h4 mice have CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells that inhibit the development of spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis
Shiguang Yu et al. J Exp Med. 2006.
Abstract
Wild-type (WT) NOD.H-2h4 mice develop spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis (SAT) when given 0.05% NaI in their drinking water, whereas B cell-deficient NOD.H-2h4 mice are SAT resistant. To test the hypothesis that resistance of B cell-deficient mice to SAT was due to the activity of regulatory CD4+CD25+ T (T reg) cells activated if autoantigen was initially presented on non-B cells, CD25+ T reg cells were transiently depleted in vivo using anti-CD25. B cell-deficient NOD.H-2h4 mice given three weekly injections of anti-CD25 developed SAT 8 wk after NaI water. Thyroid lesions were similar to those in WT mice except there were no B cells in thyroid infiltrates. WT and B cell-deficient mice had similar numbers of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ cells. Mice with transgenic nitrophenyl-specific B cells unable to secrete immunoglobulin were also resistant to SAT, and transient depletion of T reg cells resulted in severe SAT with both T and B cells in thyroid infiltrates. T reg cells that inhibit SAT were eliminated by day 3 thymectomy, indicating they belong to the subset of naturally occurring T reg cells. However, T reg cell depletion did not increase SAT severity in WT mice, suggesting that T reg cells may be nonfunctional when effector T cells are activated; i.e., by autoantigen-presenting B cells.
Figures
Figure 1.
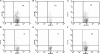
Flow cytometric analysis of CD4+CD25+ splenic T cells from 6-wk-old WT (A), B cell–deficient (B), and NP Tg (C) NOD.H-2h4 mice, CD8+CD25+ splenic T cells from NP Tg (D) mice, and CD4+CD25+ splenic T cells from NP Tg mice given anti-CD25 2 (E) or 7 (F) d previously as analyzed by flow cytometry. Results are representative of 5–10 mice analyzed in each group. The percentages of CD25+ cells in the gated CD4+ or CD8+ cells are indicated in the top right of each panel.
Figure 2.
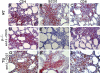
Hematoxylin and eosin–stained thyroids from WT, B cell–deficient, and NP Tg NOD.H-2h4 mice 2 mo after NaI water. (A) WT mouse with 2+ SAT, (B) WT mouse with 4+ SAT, and (C) B cell–deficient mouse given rat Ig; severity score, 0. (D and E) B cell–deficient mice given anti-CD25; D, 1+; E, 2+. (F) Rat Ig–treated NP Tg mouse; severity score, 0. (G–J) NP Tg mice given anti-CD25; G, 2+; H, 3+; I and J, 4–5+. Magnification: A–G and J, 100; H and I, 40.
Figure 3.
Immunohistochemical staining for CD4, CD8, and B220 in WT mice and in B cell–deficient and NP Tg mice given anti-CD25 beginning at 10 d of age as described in Materials and methods. All mice were given 0.05% NaI water at 8 wk of age. All infiltrating lymphocytes in B cell–deficient thyroids are CD4 and CD8+ T cells. WT and NP Tg thyroids also have many B220+ B cells. Magnification: 400.
Figure 4.
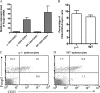
CD4+CD25+ T cells from WT and B cell–deficient mice express similar amounts of Foxp3. (A) Expression of Foxp3 mRNA by CD4+CD25-depleted and CD4+CD25-enriched cells from 6–8-wk-old naive WT and B cell–deficient NOD.H-2h4 mice. There was no significant difference in expression of Foxp3 by CD25+ cells from WT and B cell–deficient mice (P > 0.3). (B) Spleen cells from WT and B cell–deficient mice express similar numbers of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ cells when analyzed by flow cytometry using a Foxp3 staining kit as described in Materials and methods. Bars represent mean percentages of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ cells from five individual 8-wk-old B cell–deficient (μ−/−) or WT mice. (C and D) Representative Foxp3 staining results for a B cell–deficient (C) or WT (D) mouse.
Similar articles
- Transient depletion of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells results in multiple autoimmune diseases in wild-type and B-cell-deficient NOD mice.
Ellis JS, Wan X, Braley-Mullen H. Ellis JS, et al. Immunology. 2013 Jun;139(2):179-86. doi: 10.1111/imm.12065. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23293979 Free PMC article. - Early requirement for B cells for development of spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis in NOD.H-2h4 mice.
Braley-Mullen H, Yu S. Braley-Mullen H, et al. J Immunol. 2000 Dec 15;165(12):7262-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.12.7262. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11120860 - Reduced effectiveness of CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in CD28-deficient NOD.H-2h4 mice leads to increased severity of spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis.
Ellis JS, Hong SH, Zaghouani H, Braley-Mullen H. Ellis JS, et al. J Immunol. 2013 Nov 15;191(10):4940-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301253. Epub 2013 Oct 4. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24098053 Free PMC article. - Control of type 1 autoimmune diabetes by naturally occurring CD4+CD25+ regulatory T lymphocytes in neonatal NOD mice.
Piccirillo CA, Tritt M, Sgouroudis E, Albanese A, Pyzik M, Hay V. Piccirillo CA, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Jun;1051:72-87. doi: 10.1196/annals.1361.048. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16126946 Review. - CD4(+)CD25 (+) regulatory T cells in human lupus erythematosus.
Kuhn A, Beissert S, Krammer PH. Kuhn A, et al. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009 Jan;301(1):71-81. doi: 10.1007/s00403-008-0891-9. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009. PMID: 18985367 Review.
Cited by
- Peripheral immunophenotyping of AITD subjects reveals alterations in immune cells in pediatric vs adult-onset AITD.
Stensland ZC, Coleman BM, Rihanek M, Baxter RM, Gottlieb PA, Hsieh EWY, Sarapura VD, Simmons KM, Cambier JC, Smith MJ. Stensland ZC, et al. iScience. 2021 Dec 13;25(1):103626. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103626. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 35005561 Free PMC article. - Disappearance of Anti-Thyroid Autoantibodies following Thymectomy in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis.
Rotondo Dottore G, Leo M, Ricciardi R, Maestri M, Bucci I, Lucchi M, Melfi F, Guida M, De Rosa A, Petrucci L, Ionni I, Lanzolla G, Nicolì F, Mantuano M, Ricci D, Latrofa F, Mariotti S, Marcocci C, Marinò M. Rotondo Dottore G, et al. Eur Thyroid J. 2021 Jun;10(3):237-247. doi: 10.1159/000510701. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Eur Thyroid J. 2021. PMID: 34178710 Free PMC article. - Reversal of Abnormal CD4+ T Cell Metabolism Alleviates Thyroiditis by Deactivating the mTOR/HIF1a/Glycolysis Pathway.
Zhao L, Wu Q, Wang X, Wang S, Shi X, Shan Z, Teng W. Zhao L, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 4;12:659738. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.659738. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34149615 Free PMC article. - Activation of thyroid antigen-reactive B cells in recent onset autoimmune thyroid disease patients.
Smith MJ, Rihanek M, Coleman BM, Gottlieb PA, Sarapura VD, Cambier JC. Smith MJ, et al. J Autoimmun. 2018 May;89:82-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 9. J Autoimmun. 2018. PMID: 29233566 Free PMC article. - CD19+CD24hiCD38hi regulatory B cells are associated with insulin resistance in type I Hashimoto's thyroiditis in Chinese females.
Yang M, Du C, Wang Y, Liu J. Yang M, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2017 Oct;14(4):3887-3893. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4925. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29042997 Free PMC article.
References
- Braley-Mullen, H., G.C. Sharp, B. Medling, and H. Tang. 1999. Spontaneous thyroiditis in NOD.H-2h4 mice. J. Autoimmun. 12:157–165. - PubMed
- Rasooly, L., C.L. Burek, and N.R. Rose. 1996. Iodine-induced autoimmune thyroiditis in NOD.H-2h4 mice. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 81:287–292. - PubMed
- Hutchings, P., S. Verma, J.M. Phillips, S.Z. Harach, S. Howlett, and A. Cooke. 1999. Both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are required for iodine accelerated thyroiditis in NOD.H-2h4 mice. Cell. Immunol. 192:113–121. - PubMed
- Yu, S., B. Medling, H. Yagita, and H. Braley-Mullen. 2001. Characteristics of inflammatory cells in spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis of NOD.H-2h4 mice. J. Autoimmun. 16:37–46. - PubMed
- Braley-Mullen, H., and S. Yu. 2000. Early requirement for B cells for development of spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis in NOD.H-2h4 mice. J. Immunol. 165:7262–7269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials