Nod1-dependent control of tumor growth - PubMed (original) (raw)
Nod1-dependent control of tumor growth
Jean da Silva Correia et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006.
Abstract
Nod1, a cytosolic protein that senses meso-diaminopimelic acid-containing ligands derived from peptidoglycan, plays a role in host responses to invasive bacteria. Here we describe a function for Nod1, whereby it controls tumor formation. Cell lines derived from the human breast cancer epithelial cell line MCF-7 were used in a severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) mouse xenograft model to characterize a pathway linking Nod1 to the growth of estrogen-sensitive tumors. In MCF-7 cells, the absence of Nod1 correlates with tumor growth, an increased sensitivity to estrogen-induced cell proliferation, and a failure to undergo Nod1-dependent apoptosis. Conversely, overexpression of Nod1 in MCF-7 cells results in inhibition of estrogen-dependent tumor growth and reduction of estrogen-induced proliferative responses in vitro.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
Fig. 1.
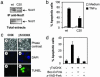
Nod1 is involved in TNFα-induced apoptosis and triggers an apoptotic cascade. (a) Nod1 protein is absent in MCF-7 C20 cells. Cell extracts from MCF-7 parental and MCF-7 C20 cells were either immunoprecipitated with a monoclonal anti-Nod1 antibody or directly loaded on SDS/PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting by using anti-Nod1 antibody. (b) MCF-7 C20 cells are more resistant to TNFα-induced apoptosis than parental cells. MCF-7 parental and MCF-7 C20 cells were treated with TNFα (10 ng/ml), and cell viability was determined by PI-exclusion assay and flow cytometry analysis. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of four independent experiments. (c) Morphological changes in γTriDAP-treated MCF-7 Nod1 cells. Cells were treated with γTriDAP/CHX (2, 4, 6) or CHX alone (1, 3, 5) and stained with DAPI (3, 4) or TUNEL (5, 6), fixed, and observed under a fluorescence microscope. (d) γTriDAP-induced apoptosis is abolished by broad-spectrum caspase inhibitors. MCF-7 Nod1 cells were pretreated with Z-VAD-Fmk or Boc-D-Fmk inhibitors (50 μM each) before addition of γTriDAP/CHX, and cell viability was measured.
Fig. 2.
Nod1 mediates γTriDAP-induced cell death. MCF-7 Blasto, MCF-7 Nod1, MCF-7 C20, and MCF-7 C20/Nod1 cells were treated with γTriDAP or αTriDAP (20 μg/ml each) in the presence or absence of CHX (3 μg/ml). Cell viability was measured by flow cytometry analysis. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of four independent experiments.
Fig. 3.
Synergic activation of apoptosis by γTriDAP and TNFα in SK-BR3 cells. SKBR3 Nod1 cells were treated with various combinations of TNFα (T), γTriDAP (γ), αTriDAP (α), and CHX (C). Cells were harvested 18 h posttreatment and analyzed for cell viability by PI staining and flow cytometry (Upper). Data are expressed as mean ± SD of six independent experiments. Cell extracts were also prepared and subjected to immunoblotting with specific antibodies recognizing proforms and cleaved fragments of PARP and caspases 3, 7, and 8. Results show a representative experiment from three independent experiments.
Fig. 4.
Nod2 does not induce apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. MCF-7 Blasto, MCF-7 Nod1, and MCF-7 Nod2 were treated with γTriDAP or MDP (20 μg/ml each) in the presence or absence of CHX. (a) Cell death was measured by flow cytometry. (b) Cell supernatants were harvested and assayed for IL-8 secretion. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (c) Expression of Nod1 and Nod2 was confirmed by Western blot analysis by using anti-Myc antibody.
Fig. 5.
The presence of Nod1 prevents tumor growth in SCID mice. (a) MCF-7 Blasto, MCF-7 C20, and MCF-7 C20/Nod1 cells (3 × 106 cells per mouse) were injected in the flanks of female SCID mice. Tumor size was measured once a week, and volume was determined according to the formula (_W_2 × L)/2. Each line represents tumor growth of 1 mouse (n = 4). (b) Mice were implanted with estrogen pellets before injection with MCF-7 cells, and tumor size was determined. Mean ± SD are shown for 8 mice. (c) MCF-7 C20 and MCF-7 RIP2ΔCARD cells show a higher sensitivity to estrogens. Indicated MCF-7 cells were exposed to increasing concentration of 17β-estradiol and pulsed with [3H]thymidine, and cell growth was determined by liquid scintillation. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (d) Down-regulation of endogenous ERα by Nod1. Total protein extracts from MCF-7 Blasto, MCF-7 C20, and MCF-7 C20/Nod1 cells and from cells isolated from tumors were analyzed by immunoblotting by using antibody against ERα and ERK2 as loading control.
References
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Medzhitov R. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
- Beutler B. Mol. Immunol. 2004;40:845–859. - PubMed
- Ting J. P., Davis B. K. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005;23:387–414. - PubMed
- Inohara N., Ogura Y., Chen F. F., Muto A., Nunez G. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:2551–2554. - PubMed
- Inohara N., Ogura Y., Fontalba A., Gutierrez O., Pons F., Crespo J., Fukase K., Inamura S., Kusumoto S., Hashimoto M., et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:5509–5512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources