The antitumor thioredoxin-1 inhibitor PX-12 (1-methylpropyl 2-imidazolyl disulfide) decreases thioredoxin-1 and VEGF levels in cancer patient plasma - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
The antitumor thioredoxin-1 inhibitor PX-12 (1-methylpropyl 2-imidazolyl disulfide) decreases thioredoxin-1 and VEGF levels in cancer patient plasma
Amanda F Baker et al. J Lab Clin Med. 2006 Feb.
Abstract
Thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1) is a small redox protein that is overexpressed in many human tumors, where it is associated with aggressive tumor growth and decreased patient survival. Trx-1 is secreted by tumor cells and is present at increased levels in the plasma of cancer patients. PX-12 is an irreversible inhibitor of Trx-1 currently in clinical development as an antitumor agent. We have used SELDI-TOF mass spectroscopy to measure plasma Trx-1 from patients treated with PX-12 during a phase I study. Mean plasma Trx-1 levels at pretreatment were significantly elevated in the cancer patients at 182.0 ng/mL compared with 27.1 ng/mL in plasma from healthy volunteers. PX-12 treatment significantly lowered plasma Trx-1 in cancer patients having the highest plasma Trx-1 pretreatment levels. High-plasma vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels have been correlated to decreased patient survival. PX-12 treatment also significantly lowered plasma VEGF levels in cancer patients with high pretreatment VEGF levels. SELDI-TOF mass spectrometry identified seven additional plasma proteins whose levels decreased after PX-12 administration, one of which was identified as a truncated form of transthyretin. The results of this study suggest that the lowering of elevated levels of plasma Trx-1 in cancer patients may provide a surrogate for the inhibition of tumor Trx-1 by PX-12. Furthermore, PX-12 decreases plasma VEGF levels that may contribute to the antitumor activity of PX-12.
Figures
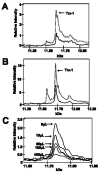
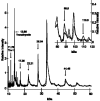
Figure 1
Trx-1 in mouse and human plasma. A. Recombinant mouse Trx-1 added to mouse plasma (gray line) increased the endogenous peak (black line) at 11.68 kDa corresponding to the predicted molecular weight of mouse Trx-1. B. Recombinant purified human Trx-1 added to normal human plasma (gray line) increased the endogenous human Trx-1 peak (black line) at 11.73 kDa. C. Overlay of the spectra showing depletion of the 11.73 kDa peak after immunodepletion. Arrows reflect the volume of anti-Trx-1 bound beads used to remove Trx-1 protein from plasma.
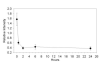
Figure 2
PX-12 decreases Trx-1 in mouse plasma. Each point represents the mean ± S.E. of four non-tumor bearing mice injected with 25mg/kg PX-12.
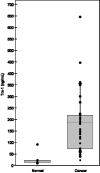
Figure 3
Plasma Trx-1 levels in healthy volunteers and cancer patients. Samples from 7 normal subjects and 31 cancer patients from a Phase I study of PX-12. Plasma was collected before treatment with PX-12. Pretreatment compared to normal controls (p<0.001). The graph shows: mean, 25 and 75 percentiles (gray box), 10 and 90 percentiles (whiskers).
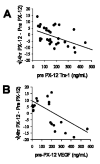
Figure 4
Decrease in patient plasma Trx-1 and VEGF after PX-12 administration. The change in plasma Trx-1 or VEGF 4 hr after PX-12 administration compared to the pretreatment level in the same patient, plotted against the pretreatment level. The relationship between preand post-PX-12 treatment Trx-1 levels was assessed using a linear regression model with a square root transformation of the dependent variable. A. Plasma Trx-1. The line is the correlation (R2 = 0.225), n = 31, p = 0.007. B. Plasma VEGF. The line is the correlation (R2 = 0.465), n = 19, p = 0.001.
Figure 5
Representative SELDI-TOF spectra from plasma of one patient pre-PX-12 administration (solid line) compared to plasma 4 hrs post-PX-12 treatment (dashed line).
Similar articles
- A phase IB trial of 24-hour intravenous PX-12, a thioredoxin-1 inhibitor, in patients with advanced gastrointestinal cancers.
Baker AF, Adab KN, Raghunand N, Chow H, Stratton SP, Squire SW, Boice M, Pestano LA, Kirkpatrick DL, Dragovich T. Baker AF, et al. Invest New Drugs. 2013 Jun;31(3):631-641. doi: 10.1007/s10637-012-9846-2. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Invest New Drugs. 2013. PMID: 22711542 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - A phase I trial of PX-12, a small-molecule inhibitor of thioredoxin-1, administered as a 72-hour infusion every 21 days in patients with advanced cancers refractory to standard therapy.
Ramanathan RK, Stephenson JJ, Weiss GJ, Pestano LA, Lowe A, Hiscox A, Leos RA, Martin JC, Kirkpatrick L, Richards DA. Ramanathan RK, et al. Invest New Drugs. 2012 Aug;30(4):1591-6. doi: 10.1007/s10637-011-9739-9. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Invest New Drugs. 2012. PMID: 21863237 Clinical Trial. - Thioredoxin system modulation by plant and fungal secondary metabolites.
Dal Piaz F, Braca A, Belisario MA, De Tommasi N. Dal Piaz F, et al. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(5):479-94. doi: 10.2174/092986710790226165. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 19941471 Review. - The thioredoxin reductase/thioredoxin system: novel redox targets for cancer therapy.
Biaglow JE, Miller RA. Biaglow JE, et al. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005 Jan;4(1):6-13. doi: 10.4161/cbt.4.1.1434. Epub 2004 Jan 8. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15684606 Review.
Cited by
- Inhibition of Transglutaminase 2 as a Therapeutic Strategy in Celiac Disease-In Vitro Studies in Intestinal Cells and Duodenal Biopsies.
Stricker S, de Laffolie J, Zimmer KP, Rudloff S. Stricker S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 1;24(5):4795. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054795. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902226 Free PMC article. - A redox state-dictated signalling pathway deciphers the malignant cell specificity of CD40-mediated apoptosis.
Dunnill CJ, Ibraheem K, Mohamed A, Southgate J, Georgopoulos NT. Dunnill CJ, et al. Oncogene. 2017 May 4;36(18):2515-2528. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.401. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27869172 Free PMC article. - Redox Homeostasis and Cellular Antioxidant Systems: Crucial Players in Cancer Growth and Therapy.
Marengo B, Nitti M, Furfaro AL, Colla R, Ciucis CD, Marinari UM, Pronzato MA, Traverso N, Domenicotti C. Marengo B, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:6235641. doi: 10.1155/2016/6235641. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27418953 Free PMC article. Review. - DCPIP (2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol) as a genotype-directed redox chemotherapeutic targeting NQO1*2 breast carcinoma.
Cabello CM, Lamore SD, Bair WB 3rd, Davis AL, Azimian SM, Wondrak GT. Cabello CM, et al. Free Radic Res. 2011 Mar;45(3):276-92. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2010.526766. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Free Radic Res. 2011. PMID: 21034357 Free PMC article. - Identification of novel nuclear targets of human thioredoxin 1.
Wu C, Jain MR, Li Q, Oka S, Li W, Kong AN, Nagarajan N, Sadoshima J, Simmons WJ, Li H. Wu C, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Dec;13(12):3507-18. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.040931. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 25231459 Free PMC article.
References
- Gromer S, Urig S, Becker K. The thioredoxin system--from science to clinic. Med Res Rev. 2004;24(1):40–89. - PubMed
- Arner ES, Holmgren A. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267(20):6102–6109. - PubMed
- Powis G, Montfort WR. Properties and biological activities of thioredoxins. Annu Rev Pharmacol Tox. 2001;41:261–295. - PubMed
- Fujii J, Ikeda Y. Advances in our understanding of peroxiredoxin, a multifunctional, mammalian redox protein. Redox Rep. 2002;7(3):123–130. - PubMed
- Mitomo K, Nakayama K, Fujimoto K, Sun X, Seki S, Yamamoto K. Two different cellular redox systems regulate the DNA-binding activity of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B in vitro. Gene. 1994;145(2):197–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 CA023074/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA098920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA17094/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA090821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA017094/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA090824/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA023074/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA077204/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous