Expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A and C in human pancreatic cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A and C in human pancreatic cancer
Rui-Feng Tang et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2006.
Abstract
Aim: To study the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) and VEGF-C and to determine whether the presence of VEGF-A and VEGF-C was associated with the clinicopathologic characteristics of pancreatic cancer.
Methods: VEGF-A and VEGF-C mRNA transcripts were examined by Northern blot in 6 human pancreatic cancer cell lines and 8 normal pancreatic tissues and 8 pancreatic carcinoma specimens. The expression of VEGF-A and VEGF-C proteins was examined by Western blot in the tested cell lines and by immunohistochemical stain in 50 pancreatic carcinoma samples.
Results: VEGF-A and VEGF-C mRNA transcripts were present in all the 6 human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Immunoblotting revealed the presence of VEGF-A and VEGF-C proteins in all the cell lines. Northern blot analysis of total RNA revealed 3.0-fold and 3.6-fold increase in VEGF-A and VEGF-C mRNA transcript in the cancer samples, respectively. Immunohistochemical analysis confirmed the expression of VEGF-A and VEGF-C in cancer cells within the tumor mass. Immunohistochemical analysis of 50 pancreatic cancer tissue samples revealed the presence of VEGF-A and VEGF-C immunoreactivity in 50% and 80% of the cancer tissue samples, respectively. The presence of VEGF-A in these cells was associated with larger tumor size and enhanced local spread (c2 = 6.690, P = 0.035<0.05) but was not associated with decreased patient survival. However, the presence of VEGF-C in the cancer cells was associated with increased lymph node metastasis (c2 = 5.710, P = 0.017 < 0.05), but was not associated with decreased patient survival. There was no correlation between the expression of VEGF-A and VEGF-C in the same cancer cells.
Conclusion: VEGF-A and VEGF-C are commonly overexpressed in human pancreatic cancer and may contribute to tumor growth and lymph node metastasis. There is no relationship between the expression of VEGF-A and VEGF-C in pancreatic cancer.
Figures
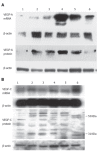
Figure 1
Expression of VEGF-A (A) and VEGF-C (B) in six human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Lane 1: COLO-357; lane 2: MIA-PaCa-2; leane 3: PANC-1; lane 4: T3M4; lane 5: ASPC-1; lane 6: CAPAN-1.
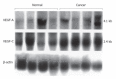
Figure 2
Northern blot analysis of VEGF-A and VEGF-C expression in human pancreatic tissues.
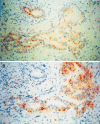
Figure 3
Immunohistochemical analysis of VEGF-A (A) and VEGF-C (B) expression in human pancreatic cancer tissues. In the pancreatic cancers, moderate to strong VEGF-A and VEGF-C immunoreactivity was present in the cytoplasm of cancer cells, ×400.
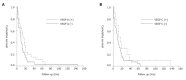
Figure 4
Survival curve. A: Cumulative survival (Kaplan-Meier) plot of the postoperative survival period of patients whose pancreatic tumors exhibited cytoplasmic VEGF-A immunostaining (solid line) versus those whose tumors were negative for VEGF-A (broken line), (P = 0.184); B: Cumulative survival (Kaplan-Meier) plot of the postoperative survival period of patients whose pancreatic tumors exhibited cytoplasmic VEGF-C immunostaining (solid line) versus those whose tumors were negative for VEGF-C (broken line), (P = 0.159).
Similar articles
- Overexpression of lymphangiogenic growth factor VEGF-C in human pancreatic cancer.
Tang RF, Itakura J, Aikawa T, Matsuda K, Fujii H, Korc M, Matsumoto Y. Tang RF, et al. Pancreas. 2001 Apr;22(3):285-92. doi: 10.1097/00006676-200104000-00010. Pancreas. 2001. PMID: 11291931 - Enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human pancreatic cancer correlates with local disease progression.
Itakura J, Ishiwata T, Friess H, Fujii H, Matsumoto Y, Büchler MW, Korc M. Itakura J, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 1997 Aug;3(8):1309-16. Clin Cancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9815813 - Interleukin-1alpha, 6 regulate the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor A, C in pancreatic cancer.
Tang RF, Wang SX, Zhang FR, Peng L, Wang SX, Xiao Y, Zhang M. Tang RF, et al. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005 Aug;4(3):460-3. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005. PMID: 16109537 - Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factors A and C in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Yanase M, Kato K, Yoshizawa K, Noguchi N, Kitahara H, Nakamura H. Yanase M, et al. J Oral Pathol Med. 2014 Aug;43(7):514-20. doi: 10.1111/jop.12167. Epub 2014 Apr 25. J Oral Pathol Med. 2014. PMID: 24762199 - Expression of VEGF-C and VEGF-D as significant markers for assessment of lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Feng Y, Wang W, Hu J, Ma J, Zhang Y, Zhang J. Feng Y, et al. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010 May;293(5):802-12. doi: 10.1002/ar.21096. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010. PMID: 20225197
Cited by
- Effect of CCR7, CXCR4 and VEGF-C on the lymph node metastasis of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Guo J, Lou W, Ji Y, Zhang S. Guo J, et al. Oncol Lett. 2013 May;5(5):1572-1578. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1261. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23761820 Free PMC article. - Pancreatic head carcinoma and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A) concentration in portal blood: its association with cancer grade, tumor size and probably poor prognosis.
Hogendorf P, Durczyński A, Kumor A, Strzelczyk J. Hogendorf P, et al. Arch Med Sci. 2014 May 12;10(2):288-93. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2014.42581. Epub 2014 May 13. Arch Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24904662 Free PMC article. - Targeting angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer: rationale and pitfalls.
Whipple C, Korc M. Whipple C, et al. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2008 Nov;393(6):901-10. doi: 10.1007/s00423-008-0280-z. Epub 2008 Jan 22. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2008. PMID: 18210149 Review. - Molecular mechanism underlying lymphatic metastasis in pancreatic cancer.
Xiao Z, Luo G, Liu C, Wu C, Liu L, Liu Z, Ni Q, Long J, Yu X. Xiao Z, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:925845. doi: 10.1155/2014/925845. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24587996 Free PMC article. Review. - Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors in the Vascularization of Pancreatic Tumors: Implications for Prognosis and Therapy.
Grobbelaar C, Steenkamp V, Mabeta P. Grobbelaar C, et al. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Mar 10;47(3):179. doi: 10.3390/cimb47030179. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40136433 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Zhang ZD. Cancer of the pancreas. In: Wu ZH, Wu ZD, Zheng S, An H, ed , et al., editors. Wai Ke Xue. 6th ed. Beijing: Renmin Weisheng Press; 2003. pp. 608–613.
- Parker SL, Tong T, Bolden S, Wingo PA. Cancer statistics, 1997. CA Cancer J Clin. 1997;47:5–27. - PubMed
- Nagakawa T, Konishi I, Higashino Y, Ueno K, Ohta T, Kayahara M, Ueda N, Maeda K, Miyazaki I. The spread and prognosis of carcinoma in the region of the pancreatic head. Jpn J Surg. 1989;19:510–518. - PubMed
- Nagakawa T, Kayahara M, Ueno K, Ohta T, Konishi I, Ueda N, Miyazaki I. A clinicopathologic study on neural invasion in cancer of the pancreatic head. Cancer. 1992;69:930–935. - PubMed
- Mollenhauer J, Roether I, Kern HF. Distribution of extracellular matrix proteins in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its influence on tumor cell proliferation in vitro. Pancreas. 1987;2:14–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous