N6-methyl-adenine: an epigenetic signal for DNA-protein interactions - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
N6-methyl-adenine: an epigenetic signal for DNA-protein interactions
Didier Wion et al. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2006 Mar.
Abstract
N(6)-methyl-adenine is found in the genomes of bacteria, archaea, protists and fungi. Most bacterial DNA adenine methyltransferases are part of restriction-modification systems. Certain groups of Proteobacteria also harbour solitary DNA adenine methyltransferases that provide signals for DNA-protein interactions. In gamma-proteobacteria, Dam methylation regulates chromosome replication, nucleoid segregation, DNA repair, transposition of insertion elements and transcription of specific genes. In Salmonella, Haemophilus, Yersinia and Vibrio species and in pathogenic Escherichia coli, Dam methylation is required for virulence. In alpha-proteobacteria, CcrM methylation regulates the cell cycle in Caulobacter, Rhizobium and Agrobacterium, and has a role in Brucella abortus infection.
Figures
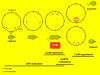
Figure 1
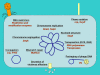
Overview of the roles of m6A in enteric bacteria: (i) defense against phages and transposons; (ii) regulation of chromosome replication, chromosome segregation, and reorganization of the nucleoid after DNA replication; (iii) DNA strand discrimination for mismatch repair: (iv) regulation of conjugal transfer of plasmids; (v) packaging of phage DNA into capsids; and (vi) transcriptional regulation of fimbrial operons and other virulence genes. When known, the methylation-sensitive DNA-binding proteins involved in each process are also indicated.
Figure 2
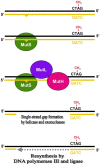
Dam-directed mismatch repair. Assembly of the MutHLS complex at a mismatch is followed by MutH-mediated cleavage of the newly synthesized strand (shown in yellow) at the nearest GATC. Transient GATC hemimethylation in the newly synthesized strand provides the signal for strand discrimination. Depending on the distance, cleavage may require DNA looping (not drawn for simplicity).
Figure 3
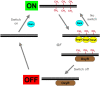
Regulation of the pap operon of uropathogenic E. coli (reproduced from ref. 52). Top panel: DNA adenine methylation states of the pap regulatory region. In the ON state, binding of Lrp to sites 4, 5, and 6 prevents methylation of GATCdist, while the unbound GATCprox is methylated. In the OFF state, Lrp binding to sites 1, 2, and 3 prevents methylation of GATCprox, while the unbound GATCdist is methylated. Bottom panel: Model for switching from phase OFF to phase ON. (A) In the OFF state, Lrp binds to sites 1–3, and prevents methylation of GATCprox. Non-methylated GATCs are shown as open circles, and methylated GATCs are shown as closed circles. Binding of Lrp to sites 1–3 reduces the affinity of Lrp for sites 4–6. (B) Every replication round offers an opportunity for switching. (C) In the presence of PapI, Lrp will translocate from sites 1–3 to sites 4–6. Lrp binding to GATCdist will prevent methylation of the nascent DNA strand, while the unbound GATCprox will undergo methylation. (D, E). If the intracellular concentration of cAMP is high, CRP will activate papI transcription. (F) PapB will stimulate papI transcription, creating a positive feedback loop that will perpetuate the ON state.
Figure 4
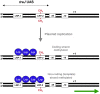
(Adapted from ref. 60). Model for switching in the agn43 gene. Methylation of GATC sites in the agn43 operator prevents binding of the OxyR repressor, and defines the ON state. After DNA replication, SeqA and OxyR compete for binding to the hemimethylated operator. SeqA binding is only transient and permits GATC methylation, thus propagating the ON state. In contrast, OxyR binding hinders GATC methylation, and agn43 is switched OFF in the following replication round. Switching to the ON state occurs when OxyR leaves the operator, permitting GATC methylation.
Figure 5
Model for regulation of traJ transcription in the Salmonella virulence plasmid. The transcriptional activator Lrp binds to two cognate sites in the traJ UAS. Lrp binding to the downstream site is inhibited by GATC methylation; as a consequence, t_raJ_ is not transcribed in a non-replicating plasmid. Passage of the replication fork leaves the traJ UAS hemimethylated. However, activation of transcription occurs only in one daughter plasmid DNA molecule, because methylation of the coding strain does not permit formation of the Lrp-DNA activating complex.
Figure 6
(Adapted from ref. 5). In Caulobacter crescentus, asymmetric cell division produces a non-replicating swarmer cell and a replicating stalked cell. In the swarmer cell, CtrA binding to the chromosomal origin of replication (Cori) inhibits DNA replication initiation, whereas CtrA proteolysis allows replication to occur in the stalked cell. Hence, DNA replication is only initiated on the methylated Cori of the stalked cell. Because CcrM methylase is degraded after cell division, passage of the replication fork is not followed by methylation of the daughter DNA strands. The extent of hemimethylation indicates the distance covered by the replication machinery, and can be viewed as a measure of time. The existence of DNA-binding proteins (e. g., transcription factors) that recognize hemimethylated sites could thus permit an ordered sequence of events occuring during DNA synthesis.
Similar articles
- DNA adenine methylation and bacterial pathogenesis.
Heusipp G, Fälker S, Schmidt MA. Heusipp G, et al. Int J Med Microbiol. 2007 Feb;297(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.10.002. Epub 2006 Nov 27. Int J Med Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17126598 Review. - DNA methyltransferases and epigenetic regulation in bacteria.
Adhikari S, Curtis PD. Adhikari S, et al. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016 Sep;40(5):575-91. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuw023. Epub 2016 Jul 29. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27476077 Review. - Epigenetic regulation of the bacterial cell cycle.
Collier J. Collier J. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2009 Dec;12(6):722-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.08.005. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19783470 Review. - Detection of N6-methyladenine in GATC sequences of Selenomonas ruminantium.
Pristas P, Molnarova V, Javorsky P. Pristas P, et al. J Basic Microbiol. 1998;38(4):283-7. J Basic Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9791949 - Inactivation of deoxyadenosine methyltransferase (dam) attenuates Haemophilus influenzae virulence.
Watson ME Jr, Jarisch J, Smith AL. Watson ME Jr, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2004 Jul;53(2):651-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04140.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15228541
Cited by
- Crosstalk between 6-methyladenine and 4-methylcytosine in Geobacter sulfurreducens exposed to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field.
Shi Z, Zhang Y, Chen W, Yu Z. Shi Z, et al. iScience. 2024 Jul 27;27(9):110607. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110607. eCollection 2024 Sep 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39262814 Free PMC article. - Unravelling the Epigenetic Code: DNA Methylation in Plants and Its Role in Stress Response.
Talarico E, Zambelli A, Araniti F, Greco E, Chiappetta A, Bruno L. Talarico E, et al. Epigenomes. 2024 Aug 8;8(3):30. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes8030030. Epigenomes. 2024. PMID: 39189256 Free PMC article. Review. - The Restriction Activity Investigation of Rv2528c, an Mrr-like Modification-Dependent Restriction Endonuclease from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Liu T, Wei W, Xu M, Ren Q, Liu M, Pan X, Feng F, Han T, Gou L. Liu T, et al. Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 18;12(7):1456. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071456. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065224 Free PMC article. - Bacmethy: A novel and convenient tool for investigating bacterial DNA methylation pattern and their transcriptional regulation effects.
Liu JH, Zhang Y, Zhou N, He J, Xu J, Cai Z, Yang L, Liu Y. Liu JH, et al. Imeta. 2024 Mar 19;3(3):e186. doi: 10.1002/imt2.186. eCollection 2024 Jun. Imeta. 2024. PMID: 38898993 Free PMC article. - Temporal dynamics and metagenomics of phosphorothioate epigenomes in the human gut microbiome.
Byrne SR, DeMott MS, Yuan Y, Ghanegolmohammadi F, Kaiser S, Fox JG, Alm EJ, Dedon PC. Byrne SR, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 29:2024.05.29.596306. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.29.596306. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38854053 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
- Cheng X. Structure and function of DNA methyltransferases. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1995;24:293–318. - PubMed
- Marinus MG. Methylation of DNA. In: Neidhardt FC, et al., editors. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology. ASM Press; Washington, D. C: 1996. pp. 782–791. A comprehensive summary of the first two decades of research on Dam methylation.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases