MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis
H-W Hwang et al. Br J Cancer. 2006.
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a recently discovered class of approximately 18-24 nucleotide RNA molecules that negatively regulate target mRNAs. All studied multicellular eukaryotes utilise miRNAs to regulate basic cellular functions including proliferation, differentiation, and death. It is now apparent that abnormal miRNA expression is a common feature of human malignancies. In this review, we will discuss how miRNAs influence tumorigenesis by acting as oncogenes and tumour suppressors.
Figures
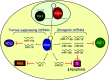
Figure 1
The biogenesis and functions of cancer-associated human miRNAs. A simplified schematic of miRNA biogenesis is shown. MicroRNAs are initially transcribed by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and sequentially processed by drosha and dicer (see text for details). MicroRNAs with tumour suppressing or oncogenic properties are shown with their experimentally validated targets.
Republished in
- MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis.
Hwang HW, Mendell JT. Hwang HW, et al. Br J Cancer. 2007;96 Suppl:R40-4. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17393584
Similar articles
- MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis.
Hwang HW, Mendell JT. Hwang HW, et al. Br J Cancer. 2007;96 Suppl:R40-4. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17393584 - Beyond HPV: oncomirs as new players in cervical cancer.
Reshmi G, Pillai MR. Reshmi G, et al. FEBS Lett. 2008 Dec 24;582(30):4113-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.11.011. Epub 2008 Nov 24. FEBS Lett. 2008. PMID: 19032954 Review. - [Advances in the studies of miRNAs and cell apoptosis].
Guo L, Ding ZH. Guo L, et al. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2007 Oct;38(4):331-5. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2007. PMID: 18232304 Review. Chinese. - A small piece in the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes.
Kent OA, Mendell JT. Kent OA, et al. Oncogene. 2006 Oct 9;25(46):6188-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209913. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 17028598 Review. - MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor?
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK. Shenouda SK, et al. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009 Dec;28(3-4):369-78. doi: 10.1007/s10555-009-9188-5. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009. PMID: 20012925 Review.
Cited by
- Epigenetic regulation of miRNA-211 by MMP-9 governs glioma cell apoptosis, chemosensitivity and radiosensitivity.
Asuthkar S, Velpula KK, Chetty C, Gorantla B, Rao JS. Asuthkar S, et al. Oncotarget. 2012 Nov;3(11):1439-54. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.683. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 23183822 Free PMC article. - Identification and bioinformatics analysis of miRNAs involved in bovine skeletal muscle satellite cell myogenic differentiation.
Wang YM, Ding XB, Dai Y, Liu XF, Guo H, Zhang Y. Wang YM, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 Jun;404(1-2):113-22. doi: 10.1007/s11010-015-2371-9. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25732542 - MicroRNA in Cancer and Cachexia--A Mini-Review.
Acunzo M, Croce CM. Acunzo M, et al. J Infect Dis. 2015 Jul 15;212 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S74-7. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv197. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26116737 Free PMC article. Review. - emiRIT: a text-mining-based resource for microRNA information.
Roychowdhury D, Gupta S, Qin X, Arighi CN, Vijay-Shanker K. Roychowdhury D, et al. Database (Oxford). 2021 May 28;2021:baab031. doi: 10.1093/database/baab031. Database (Oxford). 2021. PMID: 34048547 Free PMC article. - Modeling of miRNA and drug action in the EGFR signaling pathway.
Li J, Pandey V, Kessler T, Lehrach H, Wierling C. Li J, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030140. Epub 2012 Jan 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22253908 Free PMC article.
References
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297 - PubMed
- Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, Sharon E, Spector Y, Bentwich Z (2005) Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet 37: 766–770 - PubMed
- Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH, Cuppen E (2005) Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell 120: 21–24 - PubMed
- Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2003) Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 113: 25–36 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources