Switching TNF antagonists in patients with chronic arthritis: an observational study of 488 patients over a four-year period - PubMed (original) (raw)
Switching TNF antagonists in patients with chronic arthritis: an observational study of 488 patients over a four-year period
Juan J Gomez-Reino et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006.
Abstract
The objective of this work is to analyze the survival of infliximab, etanercept and adalimumab in patients who have switched among tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonists for the treatment of chronic arthritis. BIOBADASER is a national registry of patients with different forms of chronic arthritis who are treated with biologics. Using this registry, we have analyzed patient switching of TNF antagonists. The cumulative discontinuation rate was calculated using the actuarial method. The log-rank test was used to compare survival curves, and Cox regression models were used to assess independent factors associated with discontinuing medication. Between February 2000 and September 2004, 4,706 patients were registered in BIOBADASER, of whom 68% had rheumatoid arthritis, 11% ankylosing spondylitis, 10% psoriatic arthritis, and 11% other forms of chronic arthritis. One- and two-year drug survival rates of the TNF antagonist were 0.83 and 0.75, respectively. There were 488 patients treated with more than one TNF antagonist. In this situation, survival of the second TNF antagonist decreased to 0.68 and 0.60 at 1 and 2 years, respectively. Survival was better in patients replacing the first TNF antagonist because of adverse events (hazard ratio (HR) for discontinuation 0.55 (95% confidence interval (CI), 0.34-0.84)), and worse in patients older than 60 years (HR 1.10 (95% CI 0.97-2.49)) or who were treated with infliximab (HR 3.22 (95% CI 2.13-4.87)). In summary, in patients who require continuous therapy and have failed to respond to a TNF antagonist, replacement with a different TNF antagonist may be of use under certain situations. This issue will deserve continuous reassessment with the arrival of new medications.
Figures
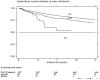
Figure 1
Survival curve of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonists in BIOBADASER during the first two years of use, ranked by order of treatment. The numbers under the curves represent the patients known to be still on treatment by the end of the interval. Differences in the number between intervals do not mean that patients failed (stopped TNF antagonist). They actually represent the patients known to be still on treatment as of the time marked.
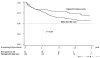
Figure 2
Survival of the second tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonist depending on the reason of replacement of first treatment. The numbers under the curves represent the patients known to be still on treatment by the end of the interval. Differences in the number between intervals do not mean that patients failed (stopped TNF antagonist). They actually represent the patients known to be still on treatment as of the time marked. AE, adverse effect.
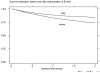
Figure 3
Survival estimates of infliximab before and after the marketing authorization of etanercept (p < 0.001).
Similar articles
- Outcomes after switching from one anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agent to a second anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agent in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from a large UK national cohort study.
Hyrich KL, Lunt M, Watson KD, Symmons DP, Silman AJ; British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Hyrich KL, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Jan;56(1):13-20. doi: 10.1002/art.22331. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17195186 - Persistence with anti-tumor necrosis factor therapies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: observations from the RADIUS registry.
Markenson JA, Gibofsky A, Palmer WR, Keystone EC, Schiff MH, Feng J, Baumgartner SW. Markenson JA, et al. J Rheumatol. 2011 Jul;38(7):1273-81. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.101142. Epub 2011 May 15. J Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21572150 - Treatment patterns in the first year after initiating tumor necrosis factor blockers in real-world settings.
Bonafede M, Fox KM, Watson C, Princic N, Gandra SR. Bonafede M, et al. Adv Ther. 2012 Aug;29(8):664-74. doi: 10.1007/s12325-012-0037-5. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Adv Ther. 2012. PMID: 22886712 - [Tumour necrosis factor antagonists: infliximab, adalimumab and etanercept].
Breedveld FC. Breedveld FC. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2005 Oct 8;149(41):2273-7. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2005. PMID: 16240851 Review. Dutch. - TNF alpha inhibition as treatment modality for certain rheumatologic and gastrointestinal diseases.
Wiedmann MW, Mössner J, Baerwald C, Pierer M. Wiedmann MW, et al. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2009 Sep;9(3):295-314. doi: 10.2174/187153009789044347. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19594416 Review.
Cited by
- Switching between anti-tumour necrosis factors: trying to get a handle on a complex issue.
van Vollenhoven RF. van Vollenhoven RF. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007 Jul;66(7):849-51. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.069872. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007. PMID: 17576784 Free PMC article. - DAS-28-based EULAR response and HAQ improvement in rheumatoid arthritis patients switching between TNF antagonists.
Navarro-Sarabia F, Ruiz-Montesinos D, Hernandez B, Navarro-Compán V, Marsal S, Barcelo M, Perez-Pampín E, Gómez-Reino JJ. Navarro-Sarabia F, et al. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009 Jul 23;10:91. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-10-91. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009. PMID: 19627609 Free PMC article. - Incidence of Infectious Adverse Events in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis on Biologic Drugs-Data From the Brazilian Registry for Biologics Monitoring.
Cecconi M, Ranza R, Titton DC, Moraes JCB, Bertolo M, Bianchi W, Brenol C, Carvalho HM, de Castro GRW, Costa IP, Cunha MFL, Duarte Â, Fernandes V, Freire M, Louzada-Junior P, Macieira JC, Miranda JRS, Pereira IA, Pinheiro GRC, Stadler B, Toledo RA, Valim V, Descalzo MA, Pinto RMC, Laurindo I. Cecconi M, et al. J Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Mar;26(2):73-78. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000000935. J Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32073519 Free PMC article. - Efficacy and safety of anti-TNF therapies in psoriatic arthritis: an observational study from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register.
Saad AA, Ashcroft DM, Watson KD, Symmons DP, Noyce PR, Hyrich KL; BSRBR. Saad AA, et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010 Apr;49(4):697-705. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep423. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010. PMID: 20056769 Free PMC article. - Golimumab for rheumatoid arthritis.
Singh JA, Noorbaloochi S, Singh G. Singh JA, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;2010(1):CD008341. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008341. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. PMID: 20091667 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Maini R, St Clair EW, Breedveld F, Furst D, Kalden J, Weisman M, Smolen J, Emery P, Harriman G, Feldmann M, Lipsky P. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet. 1999;354:1932–1939. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)05246-0. - DOI - PubMed
- Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD, Bulpitt KJ, Fleischmann RM, Fox RI, Jackson CG, Lange M, Burge DJ. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:253–259. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199901283400401. - DOI - PubMed
- den Broeder A, van de Putte L, Rau R, Schattenkirchner M, Van Riel P, Sander O, Binder C, Fenner H, Bankmann Y, Velagapudi R, et al. A single dose, placebo controlled study of the fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibody adalimumab (D2E7) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2002;29:2288–2298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials