Bone morphogenetic protein-4 enhances vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by human retinal pigment epithelial cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Bone morphogenetic protein-4 enhances vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by human retinal pigment epithelial cells
Rhonda R Vogt et al. J Cell Biochem. 2006.
Abstract
Retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells secrete vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a cytokine known to promote angiogenesis. Results from RNase protection assays (RPAs) show that RPE from non-diabetic human donors and from adult retinal pigment epithelium-19 (ARPE-19) cells expressed significant bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4) message. In addition, ARPE-19 cells cultured in high glucose (25 mM), compared to those in physiological glucose (5.5 mM) released significantly more BMP-4 into the conditioned media (CM). However, the effect of BMP-4 on the release of VEGF by ARPE-19 cells has not been studied. Accordingly, ARPE-19 cells were treated with BMP-4 to determine VEGF secretion. BMP-4 and VEGF levels in the CM and cell lysates were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Cells treated with exogenous BMP-4 had higher VEGF in the CM and this treatment effect was dose- and time-dependent, while cell lysates had low levels of VEGF. Addition of cycloheximide (CHX) or actinomycin-D (ACT) significantly reduced VEGF secretion from cells treated with BMP-4, suggesting that the BMP-4-induced secretion of VEGF requires new RNA and protein synthesis. Our results suggest that BMP-4 may play a role in the regulation of ocular angiogenesis associated with diabetic retinopathy (DR) by stimulating VEGF release from RPE cells.
(c) 2006 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
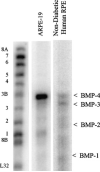
Fig. 1
BMP mRNA expression in ARPE-19 cells and in RPE cells from a non-diabetic human donor. Total RNA was isolated using the TRI reagent. Twenty micrograms of total RNA was used for the measurement of BMP mRNA expression by the RPA. The protected RNA fragments were fractionated on 5% polyacrylamide gels containing 8 M urea and detected by PhosphorImaging. Positions of labeled probes for the different BMPs and a housekeeping gene control (ribosomal protein L32) are marked on the left of the image. The protected fragments are indicated on the right with arrows.
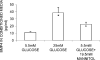
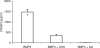
Fig. 2
Effect of glucose treatment on BMP-4 secretion by ARPE-19 cells. Cells were grown to confluence in media containing physiological glucose (5.5 mM) before being harvested and re-seeded into different media for 24 h. After cells were treated for 5 days, CM was collected for ELISA measurement of BMP-4. No change in total cell protein (ranged from 0.48 to 0.66 mg/well) was observed in glucose treatment. Mean and standard error from results of three experiments are indicated in the diagram. In each experiment, five observations were made in each treatment group. *Indicates statistically significant difference between BMP-4 concentration in CM from cells grown in 25 mM glucose and those from cells in 5.5 mM glucose+ 19.5 mM mannitol as compared to those from cells grown in 5 mM glucose, P ≤ 0.05.
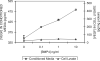
Fig. 3
Effect of exogenous BMP-4 concentration on VEGF secretion by ARPE-19 cells. ARPE-19 cells were grown to confluence in SF media containing 5.5 mM glucose before the addition of exogenous BMP-4 at 0.1, 1.0, or 10 ng/ml. For detailed treatment paradigm, see Materials and Methods. CM and cells were collected after a 24-h period of BMP-4 treatments. VEGF levels in the CM and cell lysate were measured using ELISA. Results of VEGF in the CM are mean and standard error from two representative experiments (with triplicate observations per concentration per experiment). Results of VEGF in the cell lysates were derived from one experiment (with triplicate measurements for each concentration).
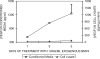
Fig. 4
Effect of exogenous BMP-4 treatment duration on VEGF secretion by ARPE-19 cells. ARPE-19 cells were grown to confluence in SF media containing 5.5 mM glucose before the addition of exogenous BMP-4 (10 ng/ml). For detailed treatment paradigm, see Materials and Methods. CM was collected from cells after the specified period of BMP-4 treatments. VEGF levels in the CM and cell lysate were measured using ELISA. Results of VEGF in the CM are mean and standard error from two representative experiments (with triplicate observations per time point per experiment). Results of VEGF in the cell lysates were derived from one experiment (with triplicate measurements for each time point).
Fig. 5
Effect of CHX and ACT on VEGF secretion by ARPE-19 cells. ARPE-19 cells were grown to confluence in SF media containing 5 mM glucose before the addition of exogenous BMP-4 (10 ng/ml) and CHX (3.6 μM) or ACT (0.5 μM). CM was collected from cells at the 5th day of treatment with BMP-4. VEGF in the CM was assayed using ELISA. One experiment was performed and four observations were made per treatment group. The mean ± SE are indicated. *Indicates significant difference between VEGF concentration in CM without inhibitors compared to those with CHX and with ACT.
Similar articles
- Bone morphogenetic proteins-2 and -4: negative growth regulators in adult retinal pigmented epithelium.
Mathura JR Jr, Jafari N, Chang JT, Hackett SF, Wahlin KJ, Della NG, Okamoto N, Zack DJ, Campochiaro PA. Mathura JR Jr, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000 Feb;41(2):592-600. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000. PMID: 10670493 - Insulin-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in retina.
Lu M, Amano S, Miyamoto K, Garland R, Keough K, Qin W, Adamis AP. Lu M, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999 Dec;40(13):3281-6. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999. PMID: 10586954 - Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and secretion by retinal pigment epithelial cells in high glucose and hypoxia is protein kinase C-dependent.
Young TA, Wang H, Munk S, Hammoudi DS, Young DS, Mandelcorn MS, Whiteside CI. Young TA, et al. Exp Eye Res. 2005 May;80(5):651-62. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2004.11.015. Epub 2005 Jan 4. Exp Eye Res. 2005. PMID: 15862172 - Autocrine and Paracrine Secretion of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in the Pre-Hypoxic Diabetic Retina.
Grigsby JG, Allen DM, Ferrigno AS, Vellanki S, Pouw CE, Hejny WA, Tsin ATC. Grigsby JG, et al. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017;13(2):161-174. doi: 10.2174/1573399812666161007165944. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017. PMID: 27748176 Review. - Effects of bone morphogenetic proteins on epithelial repair.
Hou Y, He YX, Zhang JH, Wang SR, Zhang Y. Hou Y, et al. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Nov;246(21):2269-2277. doi: 10.1177/15353702211028193. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 34233522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A new strategy to identify and annotate human RPE-specific gene expression.
Booij JC, ten Brink JB, Swagemakers SM, Verkerk AJ, Essing AH, van der Spek PJ, Bergen AA. Booij JC, et al. PLoS One. 2010 Mar 9;5(5):e9341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009341. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20479888 Free PMC article. - Fibronectin regulates growth factor signaling and cell differentiation in primary lens cells.
VanSlyke JK, Boswell BA, Musil LS. VanSlyke JK, et al. J Cell Sci. 2018 Nov 20;131(22):jcs217240. doi: 10.1242/jcs.217240. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 30404825 Free PMC article. - Engineered Extracellular Vesicles From Human Periodontal-Ligament Stem Cells Increase VEGF/VEGFR2 Expression During Bone Regeneration.
Pizzicannella J, Gugliandolo A, Orsini T, Fontana A, Ventrella A, Mazzon E, Bramanti P, Diomede F, Trubiani O. Pizzicannella J, et al. Front Physiol. 2019 Apr 30;10:512. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00512. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31114512 Free PMC article. - The Role of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins in Diabetic Complications.
Perera N, Ritchie RH, Tate M. Perera N, et al. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2019 Oct 29;3(1):11-20. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.9b00064. eCollection 2020 Feb 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2019. PMID: 32259084 Free PMC article. Review. - Activation of vascular bone morphogenetic protein signaling in diabetes mellitus.
Boström KI, Jumabay M, Matveyenko A, Nicholas SB, Yao Y. Boström KI, et al. Circ Res. 2011 Feb 18;108(4):446-57. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.236596. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21193740 Free PMC article.
References
- Abcouwer SF, Marjon PL, Loper RK, Vander Jagt DL. Response of VEGF expression to amino acid deprivation and inducers of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43:2791–2798. - PubMed
- Aiello LP, Wong JS. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in diabetic vascular complications. Kidney Int Suppl. 2000;77:S113–119. - PubMed
- Ayalasomayajula SP, Kompella UB. Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by 4-hydroxynonenal and its prevention by glutathione precursors in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;449:213–220. - PubMed
- Burgos R, Simo R, Audi L, Mateo C, Mesa J, Garcia-Ramirez M, Carrascosa A. Vitreous levels of vascular endothelial growth factor are not influenced by its serum concentrations in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia. 1997;40:1107–1109. - PubMed
- Castellon R, Caballero S, Hamdi HK, Atilano SR, Aoki AM, Tarnuzzer RW, Kenney MC, Grant MB, Ljubimov AV. Effects of tenascin-C on normal and diabetic retinal endothelial cells in culture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43:2758–2766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources