Targeting Toll-like receptor signaling in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and autoreactive B cells as a therapy for lupus - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Targeting Toll-like receptor signaling in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and autoreactive B cells as a therapy for lupus
Petar S Lenert. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006.
Abstract
This review focuses on the role of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in lupus and on possibilities to treat lupus using TLR modulating inhibitory oligodeoxynucleotides (INH-ODNs). TLRs bridge innate and adaptive immune responses and may play an important role in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Of particular interest are TLR3, -7, -8, and -9, which are localized intracellularly. These TLRs recognize single-stranded or double-stranded RNA or hypomethylated CpG-DNA. Exposure to higher order CpG-DNA ligands or to immune complexed self-RNA triggers activation of autoreactive B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. INH-ODNs were recently developed that block all downstream signaling events in TLR9-responsive cells. Some of these INH-ODNs can also target TLR7 signaling pathways. Based on their preferential cell reactivity, we classify INH-ODNs into class B and class R. Class B ('broadly reactive') INH-ODNs target a broad range of TLR-expressing cells. Class R ('restricted') INH-ODNs easily form DNA duplexes or higher order structures, and are preferentially recognized by autoreactive B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells, rather than by non-DNA specific follicular B cells. Both classes of INH-ODNs can block animal lupus. Hence, therapeutic application of these novel INH-ODNs in human lupus, particularly class R INH-ODNs, may result in more selective and disease-specific immunosuppression.
Figures
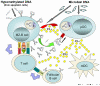
Figure 1
The innate model of lupus pathogenesis: central role of TLR-activated MZ-B cells and pDCs. Presented is a schematic overview of innate activation of MZ-B cells and pDCs with hypomethylated CpG-DNA or microbial DNA. Exposure to self CpG-DNA derived from apoptotic cells initially engages anti-dsDNA reactive low-affinity MZ-B cells. Endosomal delivery of CpG-DNA leads to TLR9-dependent and TLR9-independent activation of MZ-B cells, resulting in enhanced MHC class II, CD40, and CD86 upregulation and more efficient antigen processing/peptide presentation to histone-specific autoreactive T cells. Maturation of MZ-B cells drives secretion of anti-dsDNA antibodies, which then combine with freely circulating dsDNA to promote FcγR-dependent endogenous IFN-α secretion by pDCs (as well as activation of RF-specific B cells). IFN-α produced by pDCs, through a positive feedback loop, further enhances MZ-B cell activation and autoantibody secretion. IFN-α additionally diverts some autoreactive B cell precursors toward the follicular B cell pathway, activates T cells, and promotes development of myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs). Activated T cells direct isotype switching and affinity maturation in autoreactive B cells dependent on CD40/CD40L interaction and IFN-γ secretion. Independently of T cells, pDC-derived IFN-α can additionally help CpG-DNA activated B cells to express T-bet, a key transcription factor that induces isotype switch to complement fixing IgG2a in mice. Myeloid dendritic cell derived BAFF may further promote survival and differentiation of autoreactive B cells. Higher affinity microbial CpG-DNA released during infections directly triggers MZ-B cells and pDC activation, causing flares of lupus. ds, double stranded; IFN, interferon; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MZ, marginal zone; pDC, plasmacytoid dendritic cell; TCR, T-cell receptor; TLR, Toll-like receptor.
Similar articles
- DNA-like class R inhibitory oligonucleotides (INH-ODNs) preferentially block autoantigen-induced B-cell and dendritic cell activation in vitro and autoantibody production in lupus-prone MRL-Fas(lpr/lpr) mice in vivo.
Lenert P, Yasuda K, Busconi L, Nelson P, Fleenor C, Ratnabalasuriar RS, Nagy PL, Ashman RF, Rifkin IR, Marshak-Rothstein A. Lenert P, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):R79. doi: 10.1186/ar2710. Epub 2009 May 28. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19476613 Free PMC article. - Guanine-modified inhibitory oligonucleotides efficiently impair TLR7- and TLR9-mediated immune responses of human immune cells.
Römmler F, Hammel M, Waldhuber A, Müller T, Jurk M, Uhlmann E, Wagner H, Vollmer J, Miethke T. Römmler F, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Feb 19;10(2):e0116703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116703. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25695778 Free PMC article. - B-cell receptor for antigen modulates B-cell responses to complex TLR9 agonists and antagonists: implications for systemic lupus erythematosus.
Goeken JA, Layer T, Fleenor S, Laccheo M, Lenert P. Goeken JA, et al. Lupus. 2010 Oct;19(11):1290-301. doi: 10.1177/0961203310371157. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Lupus. 2010. PMID: 20605877 - Roles of B Cell-Intrinsic TLR Signals in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Ma K, Li J, Fang Y, Lu L. Ma K, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jun 9;16(6):13084-105. doi: 10.3390/ijms160613084. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26068236 Free PMC article. Review. - CpG-DNA as immune response modifier.
Dalpke AH, Heeg K. Dalpke AH, et al. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004 Oct;294(5):345-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2004.07.005. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15532993 Review.
Cited by
- Dendritic cells and the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus.
Monrad S, Kaplan MJ. Monrad S, et al. Immunol Res. 2007;37(2):135-45. doi: 10.1007/BF02685895. Immunol Res. 2007. PMID: 17695248 Review. - Modulating toll-like receptor 7 and 9 responses as therapy for allergy and autoimmunity.
Matesic D, Lenert A, Lenert P. Matesic D, et al. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012 Feb;12(1):8-17. doi: 10.1007/s11882-011-0233-4. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012. PMID: 22086297 Review. - Toll-like receptors and innate immune responses in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Lafyatis R, Marshak-Rothstein A. Lafyatis R, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(6):222. doi: 10.1186/ar2321. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 18086320 Free PMC article. - Classification, mechanisms of action, and therapeutic applications of inhibitory oligonucleotides for Toll-like receptors (TLR) 7 and 9.
Lenert PS. Lenert PS. Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:986596. doi: 10.1155/2010/986596. Epub 2010 May 18. Mediators Inflamm. 2010. PMID: 20490286 Free PMC article. Review. - Enhancing the Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapies with an Anti-Fibrotic Agent for the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease.
Li Y, Ricardo SD, Samuel CS. Li Y, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 27;23(11):6035. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116035. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Abreu MT, Fukata M, Arditi M. TLR signaling in the gut in health and disease. J Immunol. 2005;174:4453–4460. - PubMed
- Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335–376. - PubMed
- Barton GM, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and their ligands. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002;270:81–92. - PubMed
- Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kaisho T, Sato S, Sanjo H, Matsumoto M, Hoshino K, Wagner H, Takeda K, et al. A toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature. 2000;408:740–745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources