Altering the length of the lipopolysaccharide O antigen has an impact on the interaction of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium with macrophages and complement - PubMed (original) (raw)
Altering the length of the lipopolysaccharide O antigen has an impact on the interaction of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium with macrophages and complement
Gerald L Murray et al. J Bacteriol. 2006 Apr.
Abstract
A panel of isogenic Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strains that vary only in the length of the O antigen was constructed through complementation of a wzz double mutant (displaying unregulated O-antigen length) with one of two homologous (wzzST and wzzfepE) or three heterologous (wzzO139 of Vibrio cholerae and wzzSF and wzzpHS-2 of Shigella flexneri) wzz genes. Each gene was functional in the S. enterica serovar Typhimurium host and specified production of O-antigen polymers with lengths typical of those synthesized by the donor bacteria (ranging from 2 to >100 O-antigen repeat units). By use of this panel of strains, it was found that O-antigen length influences invasion/uptake by macrophage cells; this is the first time this has been shown with Salmonella. O-antigen length was confirmed to be related to complement resistance, with a minimum protective length of >4 and <15 repeat units. O antigen of 16 to 35 repeat units was found to activate complement more efficiently than other lengths, but this was unrelated to complement resistance. No evidence was found to suggest that modifying the length of the O-antigen polymer affected expression of the O1, O4, or O5 antigenic factors.
Figures
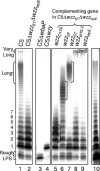
FIG. 1.
Analysis of LPS from S. enterica serovar Typhimurium C5 Oag modal-length variants and the wbaP (rough) mutant. Each lane corresponds to LPS from 2 × 108 bacteria, except lanes 3 and 4 (2 × 107 bacteria). The number of Oag RUs in each band is indicated on the left of the figure. A bracket denotes the zone of modal regulation for each strain. Lane 10 corresponds to C5Δ_wbaP_ (pGEM-T Easy-wbaP).
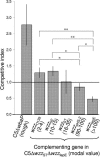
FIG. 2.
Competition invasion/uptake assays using RAW264.7 macrophages. Mixtures of bacteria with different Oag modal lengths and C5 (input ratio of 1:1) were used in invasion/uptake assays, and the competitive index was subsequently calculated (input ratio/output ratio). The horizontal line (competitive index of 1) indicates the strains that have a level of uptake equivalent to that of C5 under the conditions tested. Values below this line indicate strains with reduced uptake. Histograms show means ± standard errors from three assays (statistical analysis between histograms is indicated by horizontal lines; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; Student's t test).
Similar articles
- Regulation of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharide O antigen chain length is required for virulence; identification of FepE as a second Wzz.
Murray GL, Attridge SR, Morona R. Murray GL, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2003 Mar;47(5):1395-406. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03383.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12603743 - Novel Role of VisP and the Wzz System during O-Antigen Assembly in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Pathogenesis.
da Silva P, Manieri FZ, Herrera CM, Trent MS, Moreira CG. da Silva P, et al. Infect Immun. 2018 Jul 23;86(8):e00319-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00319-18. Print 2018 Aug. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29866904 Free PMC article. - Inducible serum resistance in Salmonella typhimurium is dependent on wzz(fepE)-regulated very long O antigen chains.
Murray GL, Attridge SR, Morona R. Murray GL, et al. Microbes Infect. 2005 Oct;7(13):1296-304. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2005.04.015. Epub 2005 Jun 9. Microbes Infect. 2005. PMID: 16027021 - Role of O-antigen variation in the immune response.
Reeves P. Reeves P. Trends Microbiol. 1995 Oct;3(10):381-6. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(00)88983-0. Trends Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8564356 Review. - Lipopolysaccharides and outer membrane proteins as main structures involved in complement evasion strategies of non-typhoidal Salmonella strains.
Krzyżewska-Dudek E, Kotimaa J, Kapczyńska K, Rybka J, Meri S. Krzyżewska-Dudek E, et al. Mol Immunol. 2022 Oct;150:67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2022.08.009. Epub 2022 Aug 20. Mol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35998438 Review.
Cited by
- Reduction of endotoxicity in Bordetella bronchiseptica by lipid A engineering: Characterization of lpxL1 and pagP mutants.
Pérez-Ortega J, Van Harten RM, Van Boxtel R, Plisnier M, Louckx M, Ingels D, Haagsman HP, Tommassen J. Pérez-Ortega J, et al. Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):1452-1468. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1929037. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34053396 Free PMC article. - Lipopolysaccharide O-antigen prevents phagocytosis of Vibrio anguillarum by rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) skin epithelial cells.
Lindell K, Fahlgren A, Hjerde E, Willassen NP, Fällman M, Milton DL. Lindell K, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37678. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037678. Epub 2012 May 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22662189 Free PMC article. - Structural characterization of closely related O-antigen lipopolysaccharide (LPS) chain length regulators.
Kalynych S, Yao D, Magee J, Cygler M. Kalynych S, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 May 4;287(19):15696-705. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.354837. Epub 2012 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22437828 Free PMC article. - Shigella flexneri remodeling and consumption of host lipids during infection.
Ascari A, Frölich S, Zang M, Tran ENH, Wilson DW, Morona R, Eijkelkamp BA. Ascari A, et al. J Bacteriol. 2023 Dec 19;205(12):e0032023. doi: 10.1128/jb.00320-23. Epub 2023 Nov 22. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 37991380 Free PMC article. - Chicken cecum immune response to Salmonella enterica serovars of different levels of invasiveness.
Berndt A, Wilhelm A, Jugert C, Pieper J, Sachse K, Methner U. Berndt A, et al. Infect Immun. 2007 Dec;75(12):5993-6007. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00695-07. Epub 2007 Aug 20. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17709416 Free PMC article.
References
- Altier, C. 2005. Genetic and environmental control of Salmonella invasion. J. Microbiol. 43:85-92. - PubMed
- Baker, S. J., J. S. Gunn, and R. Morona. 1999. The Salmonella typhi melittin resistance gene pqaB affects intracellular growth in PMA-differentiated U937 cells, polymyxin B resistance and lipopolysaccharide. Microbiology 145:367-378. - PubMed
- Batchelor, R. A., P. Alifano, E. Biffali, S. I. Hull, and R. A. Hull. 1992. Nucleotide sequences of the genes regulating O-polysaccharide antigen chain length (rol) from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: protein homology and functional complementation. J. Bacteriol. 174:5228-5236. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials