qnrB, another plasmid-mediated gene for quinolone resistance - PubMed (original) (raw)
qnrB, another plasmid-mediated gene for quinolone resistance
George A Jacoby et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Apr.
Abstract
A novel plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance gene, qnrB, has been discovered in a plasmid encoding the CTX-M-15 beta-lactamase from a Klebsiella pneumoniae strain isolated in South India. It has less than 40% amino acid identity with the original qnr (now qnrA) gene or with the recently described qnrS but, like them, codes for a protein belonging to the pentapeptide repeat family. Strains with qnrB demonstrated low-level resistance to all quinolones tested. The gene has been cloned in an expression vector attaching a polyhistidine tag, which facilitated purification to >or=95% homogeneity. As little as 5 pM of QnrB-His6 protected purified DNA gyrase against inhibition by 2 microg/ml (6 microM) ciprofloxacin. With a PCR assay qnrB has been detected in Citrobacter koseri, Enterobacter cloacae, and Escherichia coli isolates from the United States, linked to SHV-12 beta-lactamase and coding for a product differing in five amino acids from the Indian (now QnrB1) variety. The qnrB gene has been found near Orf1005 in some, but not all, plasmids and in association with open reading frames matching known chromosomal genes, suggesting that it too was acquired by plasmids from an as-yet-unknown bacterial source.
Figures
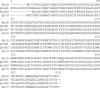
FIG. 1.
CLUSTAL W alignment of QnrA, QnrB1, QnrB2, and QnrS.
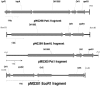
FIG. 2.
Maps of cloned qnrB genes. The sizes of the cloned fragments vary, as indicated by the 1-kb reference bars. Orf1 resembles pspF, Orf2 is related to genes of unknown function in various gram-negative bacteria, and Orf3 resembles sapA.
FIG. 3.
QnrB1 protection of DNA gyrase from ciprofloxacin inhibition of supercoiling. Reaction mixtures of 30 μl were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Reaction mixtures contained 0.2 μg relaxed pBR322 DNA (lanes 1 to 14), 6.7 nM gyrase (lanes 2 to 14), 2 μg/ml ciprofloxacin (lanes 3 to 14), and QnrB-His6 fusion protein at 25 μM (lane 4), 5 μM (lane 5), 2.5 μM (lane 6), 0.5 μM (lane 7), 50 nM (lane 8), 5 nM (lane 9), 0.5 nM (lane 10), 50 pM (lane 11), 5 pM (lane 12), or 0.5 pM (lane 13).
Similar articles
- [Investigation of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants in Enterobacteriaceae: a multicenter study].
Coban AY, Nohut OK, Tanrıverdi Çaycı Y, Bayramoğlu G, Pirinççiler M, Cetinkaya E, Cekiç Cihan C, Bozdoğan B, Durupınar B. Coban AY, et al. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2012 Jul;46(3):366-74. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2012. PMID: 22951649 Turkish. - Prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants QnrA, QnrB, and QnrS among clinical isolates of Enterobacter cloacae in a Taiwanese hospital.
Wu JJ, Ko WC, Tsai SH, Yan JJ. Wu JJ, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Apr;51(4):1223-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01195-06. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17242140 Free PMC article. - High rates of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance QnrB variants among ciprofloxacin-resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from urinary tract infections in Korea.
Shin JH, Jung HJ, Lee JY, Kim HR, Lee JN, Chang CL. Shin JH, et al. Microb Drug Resist. 2008 Sep;14(3):221-6. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2008.0834. Microb Drug Resist. 2008. PMID: 18707554 - Emergence of plasmid-mediated resistance to quinolones in Enterobacteriaceae.
Nordmann P, Poirel L. Nordmann P, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005 Sep;56(3):463-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki245. Epub 2005 Jul 14. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16020539 Review. - Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance.
Jacoby GA, Strahilevitz J, Hooper DC. Jacoby GA, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Oct;2(5):10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0006-2013. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0006-2013. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 25584197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Two-Dose Ceftiofur Treatment Increases Cephamycinase Gene Quantities and Fecal Microbiome Diversity in Dairy Cows Diagnosed with Metritis.
Ossa-Trujillo C, Taylor EA, Sarwar F, Vinasco J, Jordan ER, Buitrago JAG, Hagevoort GR, Lawhon SD, Piñeiro JM, Galloway-Peña J, Norman KN, Scott HM. Ossa-Trujillo C, et al. Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 8;11(11):2728. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112728. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004740 Free PMC article. - Phylogenetic analysis of chromosomally determined qnr and related proteins.
Jacoby GA, Hooper DC. Jacoby GA, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Apr;57(4):1930-4. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02080-12. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23318805 Free PMC article. - Spread of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase CTX-M-producing escherichia coli clinical isolates in community and nosocomial environments in Portugal.
Mendonça N, Leitão J, Manageiro V, Ferreira E, Caniça M. Mendonça N, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jun;51(6):1946-55. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01412-06. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17371815 Free PMC article. - Molecular characterization of antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli isolates recovered from food samples and outpatient Clinics, KSA.
Hemeg HA. Hemeg HA. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018 Jul;25(5):928-931. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.01.016. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30108443 Free PMC article. - Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinant QnrB4 identified in France in an Enterobacter cloacae clinical isolate coexpressing a QnrS1 determinant.
Cattoir V, Poirel L, Nordmann P. Cattoir V, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jul;51(7):2652-3. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01616-06. Epub 2007 May 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17502413 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
- Cheung, T. K., Y. W. Chu, M. Y. Chu, C. H. Ma, R. W. Yung, and K. M. Kam. 2005. Plasmid-mediated resistance to ciprofloxacin and cefotaxime in clinical isolates of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis in Hong Kong. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 56:586-589. - PubMed
- Hegde, S. S., M. W. Vetting, S. L. Roderick, L. A. Mitchenall, A. Maxwell, H. E. Takiff, and J. S. Blanchard. 2005. A fluoroquinolone resistance protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis that mimics DNA. Science 308:1480-1483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials